A 25-year-old man with the right sided upper abdominal pain
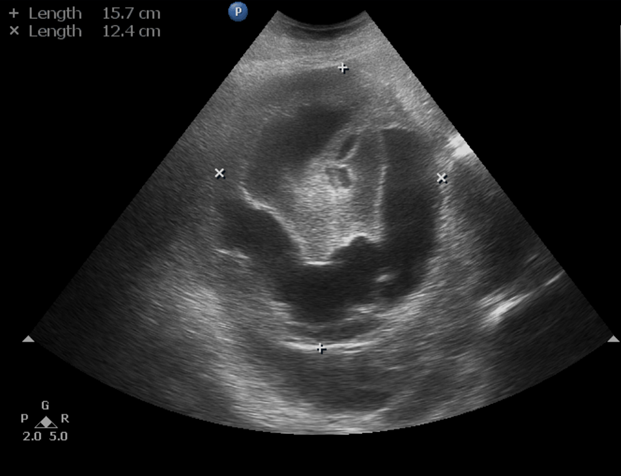
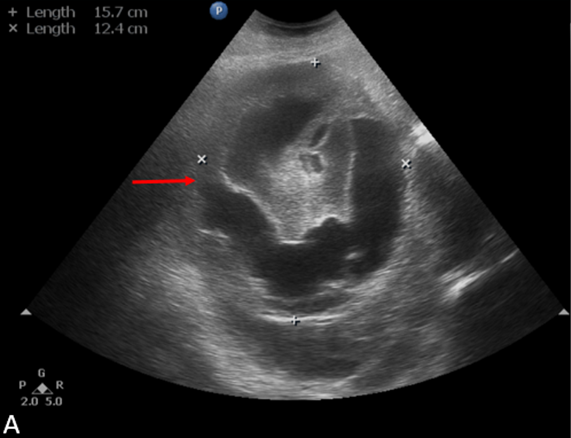
- Ultrasound abdomen and pelvis demonstrates a large solid-cystic heterogeneous suprarenal mass lesion.
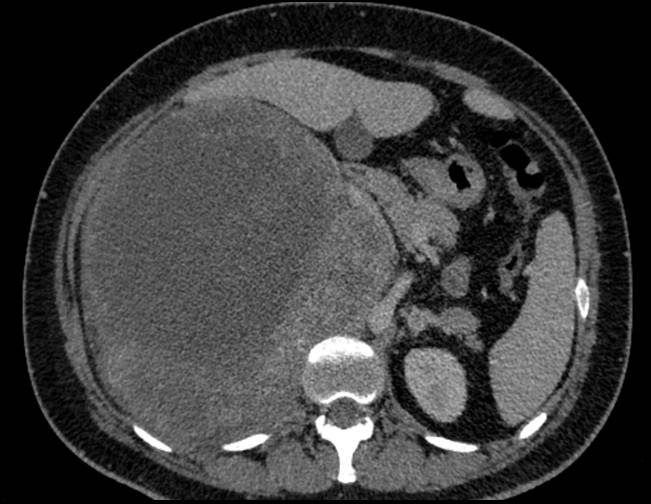
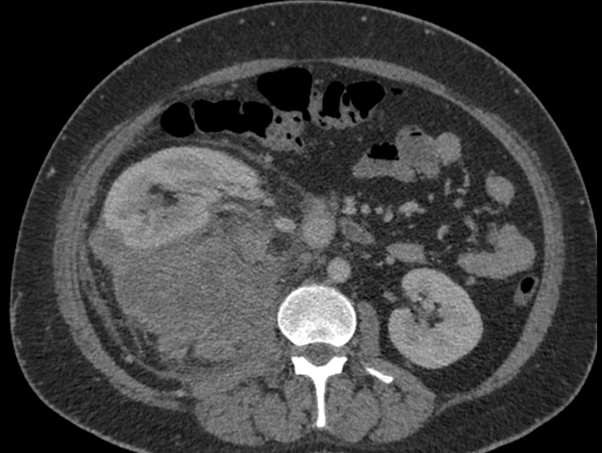
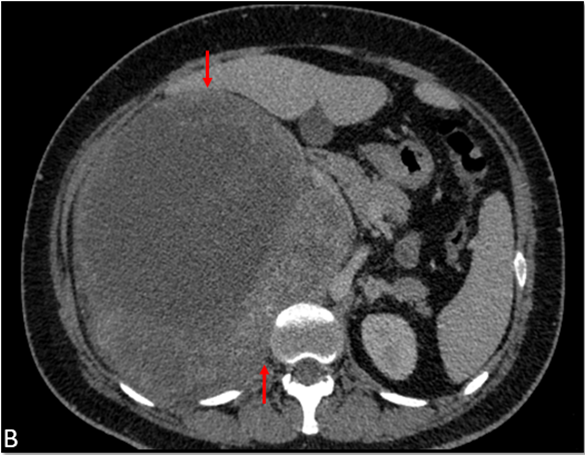
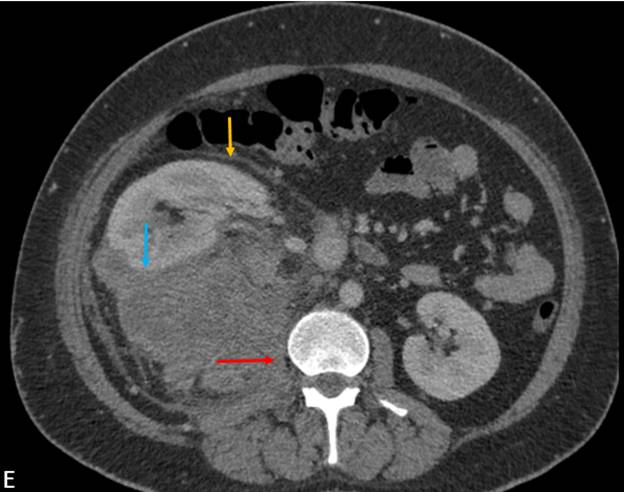
- Axial CECT demonstrates a large heterogeneously enhancing mass lesion (measuring ~20 cm) in the right suprarenal region with multiple large hypo dense non-enhancing areas. No calcification/ fatty elements. The mass abuts the inferior aspect of liver, the posterior aspect of right hemi diaphragm and medially displaces the IVC. The right adrenal gland is not separately visualized from the lesion.
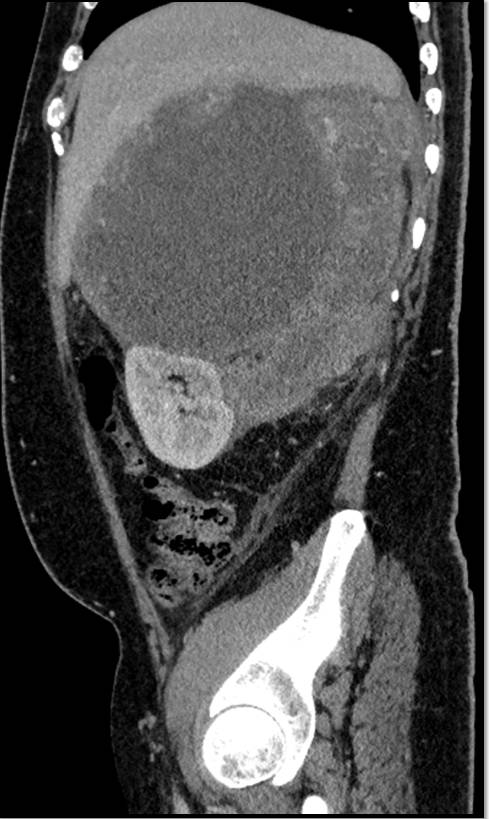
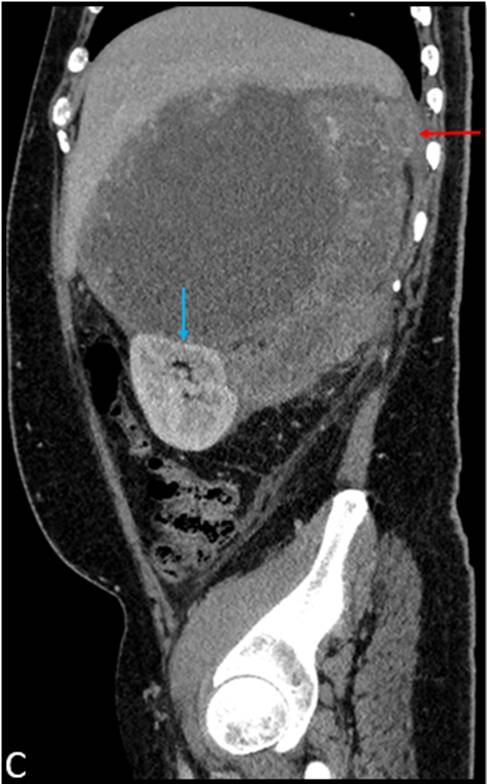
- Sagittal reformat demonstrates compression and inferior displacement of the right kidney.
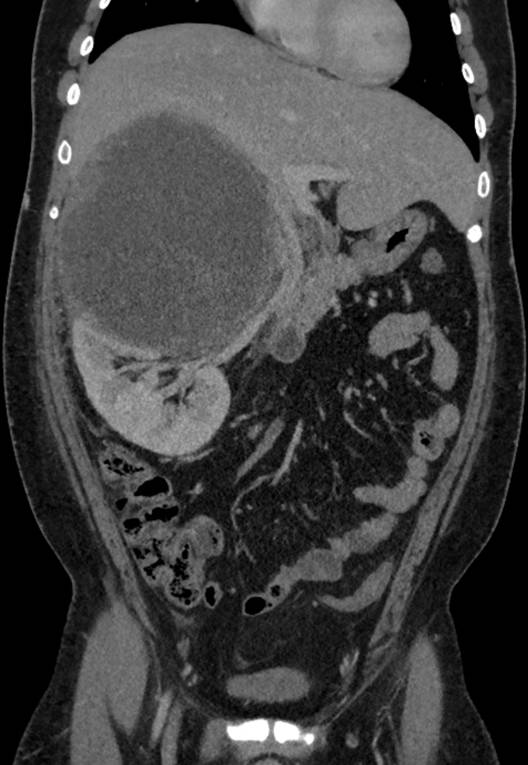
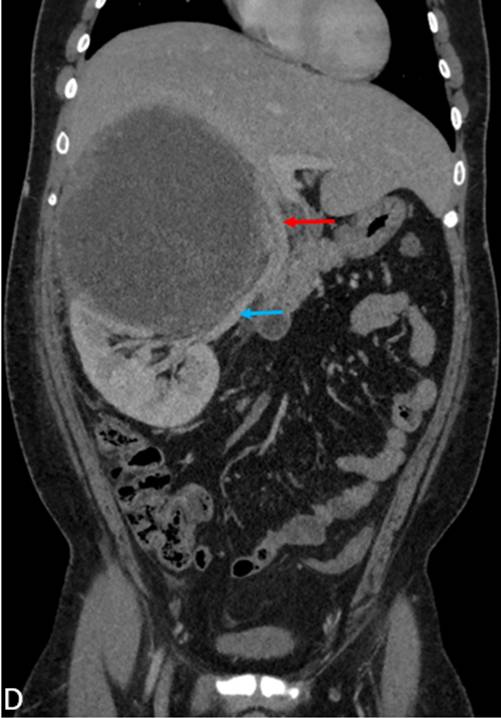
- Coronal reformat demonstrates displacement of IVC and right renal vein with luminal narrowing and no evidence of invasion
- Axial CECT demonstrates the caudal extension of the mass into the posterior perinephric space and thickening of the anterior renal fascia.
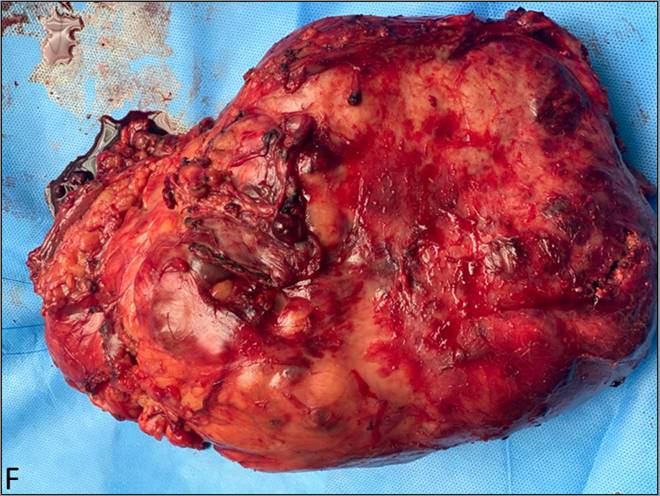
- Gross pathology post-operative specimen demonstrates a large non-encapsulated mass with necrotic areas.
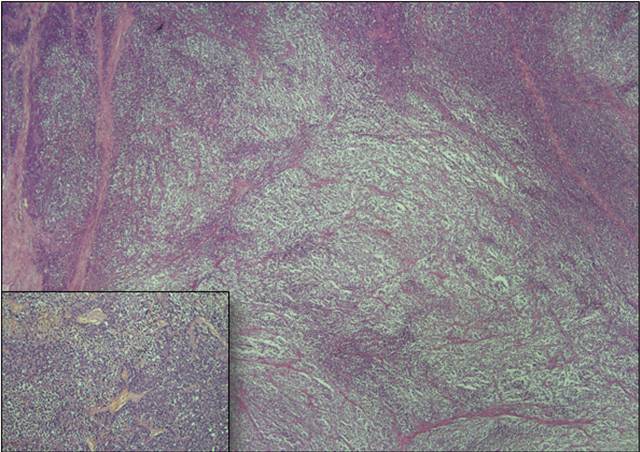
- HPE – The tumor is composed of nests and sheets of round tumor cells separated by fibro-vascular septae and multiple foci of necrosis. The tumor cells exhibit fine nuclear chromatin, prominent nucleoli, brisk mitoses, apoptosis, and a moderate amount of pale cytoplasm. Immunohistochemistry was performed and tumor cells diffusely express CD 99 & NKX 2.2 and were immunonegative to synaptophysin, chromogranin A, cytokeratin, EMA, Pax 8, Melan A, Inhibin & TLE-1.
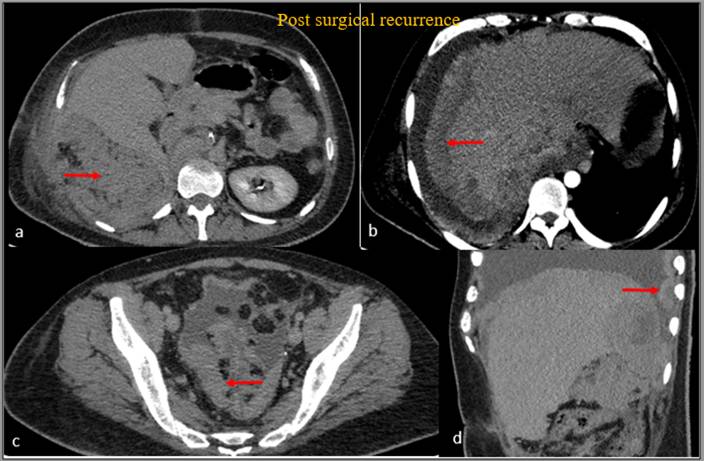
- Axial CECT demonstrates an ill-defined nodular enhancing soft tissue lesion in the right retroperitoneum in the surgical bed, multiple peritoneal deposits along the liver surface causing scalloping of underlying liver parenchyma, multiple peritoneal deposits in the pelvis and thick nodular right pleural deposits.
Diagnosis:
Primary retroperitoneal Ewing’s sarcoma.
Discussion:
- Ewing’s sarcoma / Embryonal tumours belong to a rare group of malignant neoplasms with small round-cell morphology.
- Although these tumours arise from a common precursor cell, each entity represents a different expression of the same neoplasm, characterized by distinct cellular differentiation or anatomic location.
- Most of the Ewing’s sarcoma / Embryonal tumours are diagnosed during the first two decades of life.
- The most common soft tissue sites are the chest wall, lower extremities, and pelvis/hip region. They are rarely found in the retroperitoneum, upper extremities, or internal organs.
- Patients often present with a painless mass or vague abdominal or chest pain, depending on tumour site.
Retroperitoneal Ewing’s sarcoma:
- Ewing’s sarcoma of the retroperitoneum is difficult to differentiate from other retroperitoneal tumours.
- Invasion of the renal vein, inferior vena cava, and liver can be seen in Ewing’s sarcoma, renal cell carcinoma, and adrenocortical carcinoma.
- Differentiation aspects that favour the diagnosis of Ewing’s sarcoma are earlier age of presentation, absence of metastatic lymphadenopathy, and absence of calcifications.
- Ewing’s sarcoma tends to be unilateral and does not cross midline. The definitive diagnosis can be made only by histopathological analysis.
Imaging differentials:
- Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma: more common in females and median age of presentation is around 50 years.
- Primary Retroperitoneal Malignancy:
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma.
- Leiomyosarcoma.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma.
- Fibrosarcoma.
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour.
- Hemangiopericytoma
- Large exo-phytic renal cell carcinoma.
References:
- Reis F, Macedo E, França Junior MC, Amstalden EI, Appenzeller S. Retroperitoneal Ewing’s sarcoma/embryonal tumor: a rare differential diagnosis of back pain. Radiol Bras. 2017;50(6):409-410. doi:10.1590/0100-3984.2015.0236.
- Al-Dasuqi K, Irshaid L, Mathur M. Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Primary Retroperitoneal Neoplasms. RadioGraphics. 2020 Oct;40(6):1631-57.
- Javery O, Krajewski K, O’Regan K, et al. A to Z of extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma family of tumors in adults imaging features of primary disease, metastatic patterns, and treatment responses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:W1015–W1022.
Dr. Bhupendar Singh,
DNB Radiology Resident,
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group.
Dr. Rajesh V Helavar MD, PDCC,
Consultant, Abdominal and Interventional Radiology
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group.