An 18 year old gentleman with swelling in the floor of mouth since few months
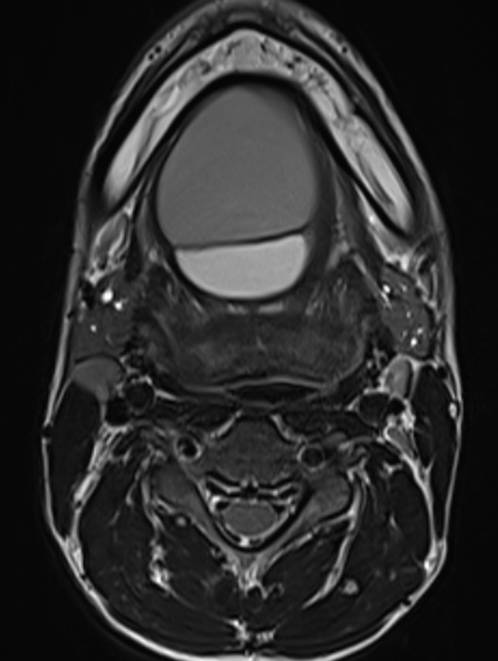
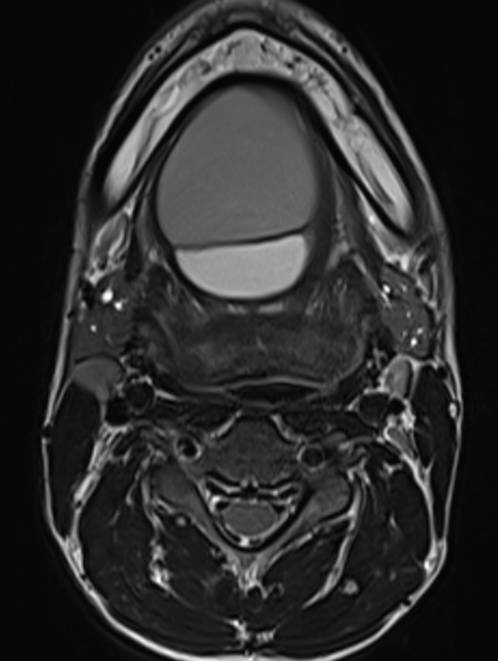
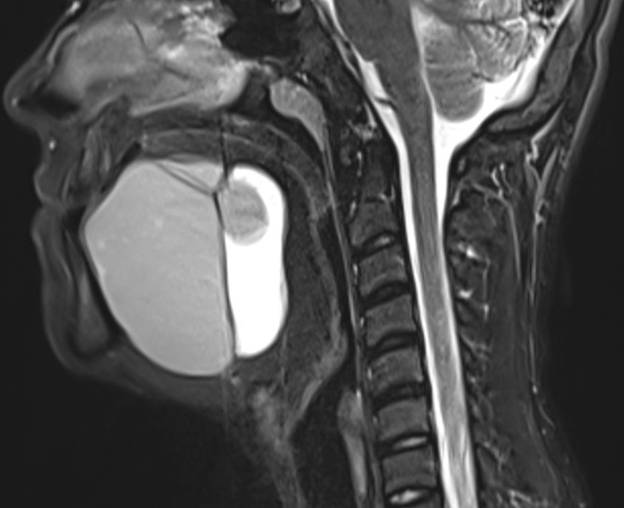
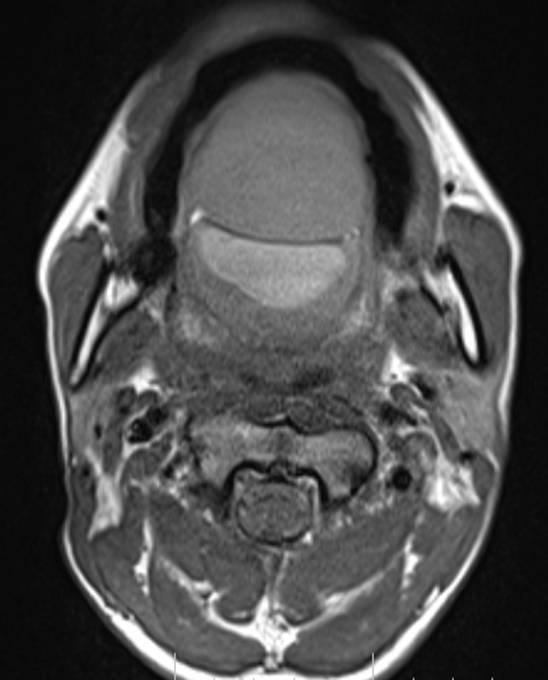
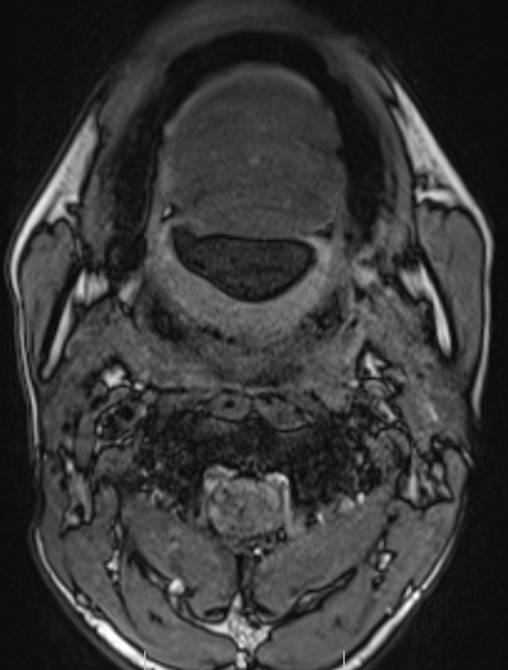
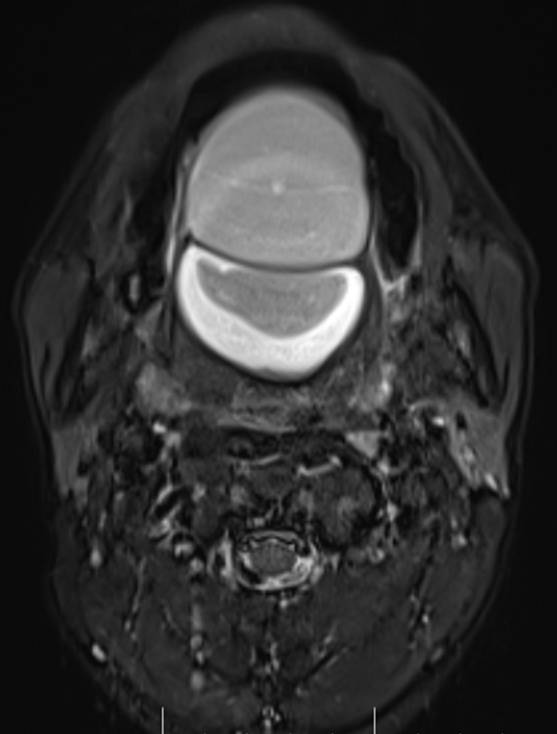
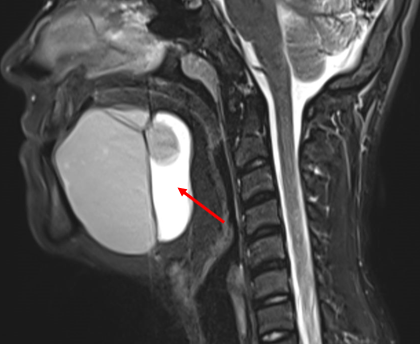
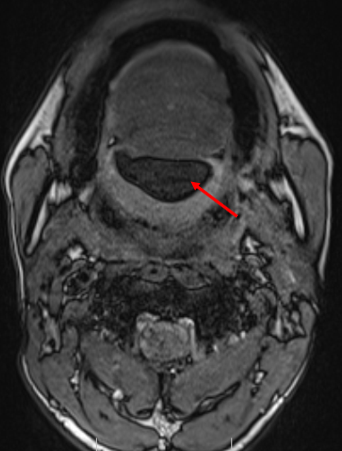
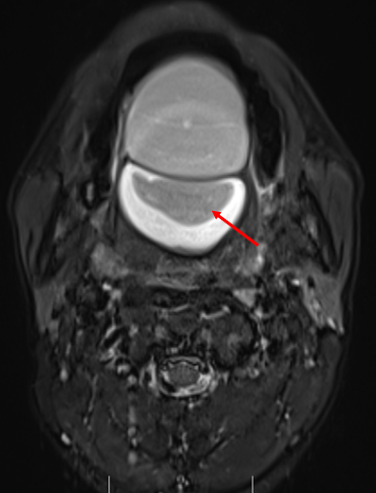
- Axial and coronal T2W, axial T1W, axial T1W opposed phase and axial STIR images demonstrate a large midline multiloculated cystic lesion in the floor of mouth (sublingual space), splaying the genioglossus and mylohyoid muscles laterally on either side.
- The lesion displaces the tongue superiorly and posteriorly and causes mild narrowing of the oropharyngeal airway.
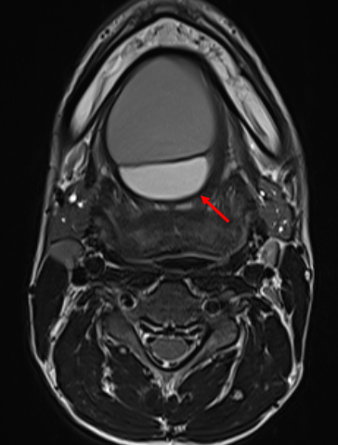
- The lesion contains large areas of fat signal which are demonstrated by red arrows. Thick septae and fluid signal are also seen.
Diagnosis:
Floor of mouth dermoid cyst with superimposed infection.
Discussion:
Common cystic lesions that occur in the floor of mouth are ranula, dermoid/ epidermoid, thyroglossal cysts and lymphangiomas
- Ranula: This is a mucous retention cyst that arises from a sublingual gland or minor salivary gland
- Simple Ranula: Confined to the sublingual space
- Plunging ranula: Extends into the submandibular space
Ranulas do not contain fat and do not demonstrate diffusion restriction
- Dermoid/ Epidermoid:
Epidermoid cysts are lined by simple squamous epithelium whilst dermoid cysts contain dermal appendages. The two are readily differentiated histopathologically. Dermoid cysts can contain multiple fat globules giving rise to a ‘sac of marbles’ appearance and may occasionally demonstrate calcification. - Thyroglossal cysts
Usually located around the hyoid bone and are rare in the floor of mouth. MRI appearance is that of cyst and superimposed infection may be present. - Lymphangioma
Can occur in the floor of mouth and may extend across compartments. These demonstrate fluid signal and fine internal septations if multilocular. Fluid-fluid levels may be present. - Dermoid:
They are lined by keratinizing squamous epithelium and appear as well-demarcated cysts.
They may contain fatty and calcific components as well as fluid.
CT images may show calcifications.
The complex content of dermoid cysts helps differentiate them from epidermoid cysts and ranulas
References:
- Imaging the Floor of the Mouth and the Sublingual Space. Sarah J. La’Porte, Jaspal K. Juttla, Ravi K. Lingam. RadioGraphics Vol. 31, No. 5
- Giarraputo L, Savastano S, D’Amore E, Baciliero U. Dermoid Cyst of the Floor of the Mouth: Diagnostic Imaging Findings. Cureus. 2018;10(4):e2403. Published 2018 Apr 2. doi:10.7759/cureus.2403
Dr. G. Chennakesava, MD
Cross-sectional imaging fellow
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group
Dr Harsha C Chadaga, DMRD, DNB, PDCC (Neuroradiology)
Senior Consultant and Head Radiology Services
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group