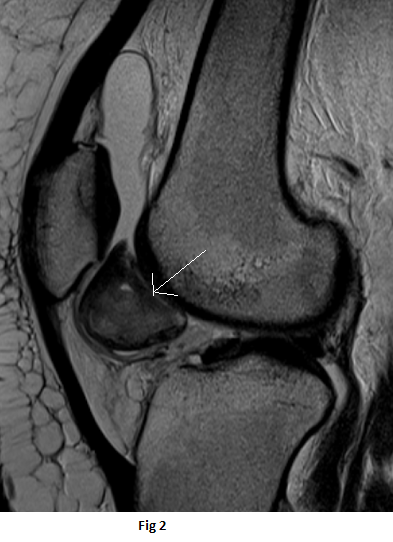
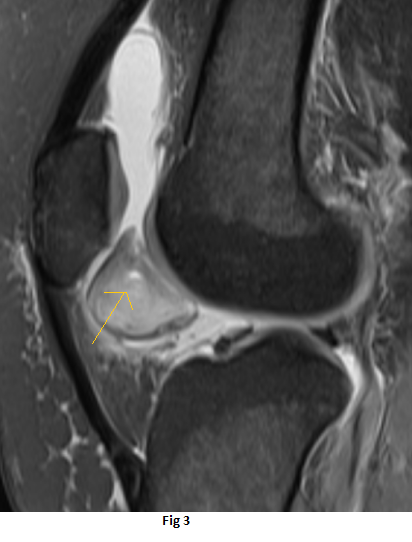
History of recurrent right knee pain and swelling of 22 year old
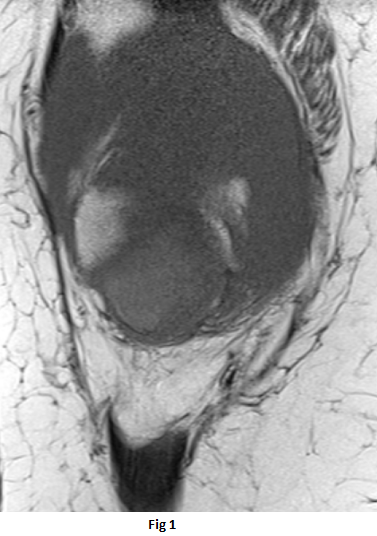
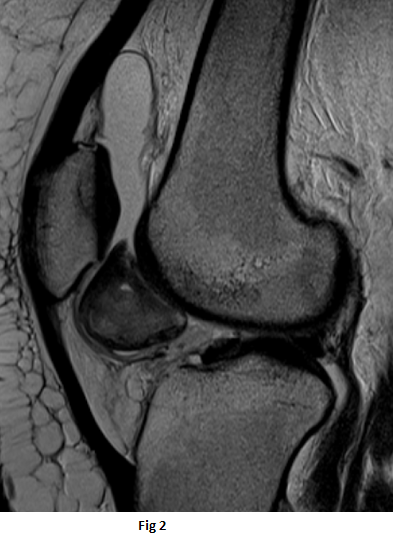
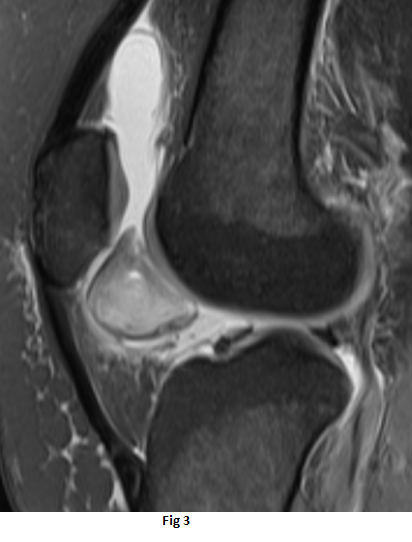
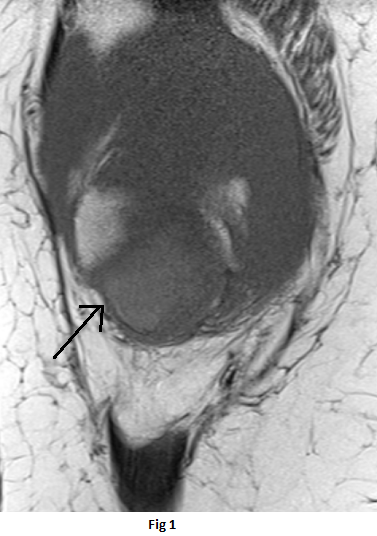
- Well-circumscribed lesion between the distal half of the retropatellar region and the distal femur trochlea superior to the infrapatellar (Hoffa’s) fat pad.
- The lesion is isointense to the muscles on T1 weighted sequence(black arrow), heterogeneous high signal on PDFS sequences (orange arrow) with peripheral T1 and T2 hypointense rim(white arrow)
DIAGNOSIS:
- Focal nodular synovitis
DISCUSSION:
- also known as “synovial giant cell tumor”
- It is found most frequently in the tendon sheaths of the small joints of the fingers and toes. A focal intraarticular mass is an uncommon presentation, but when it is seen, the most typical site of involvement is the knee joint.
- Proposed etiology is either inflammatory process or a benign neoplasm of the synovium. Other causes include traumatic, toxic, allergic and genetic factors.
- The symptoms may include pain, swelling or fullness, joint-line tenderness, restricted knee motion, and a palpable mass.
- observation of a pedicle is relevant because torsion of this pedicle can produce acute knee pain.
IMAGING FEATURES
- Well-defined, small ovoid lesion or as a large Poly lobulated soft-tissue mass with iso- or hyperintense signal intensity relative to skeletal muscle on T1-weighted images and variable signal intensity on T2-weighted images.
- Circular regions of intermixed low signal intensity corresponded to regions of high hemosiderin concentration, and the conspicuity of this pattern increased on gradient-echo images.
- Enhancement of localized nodular synovitis is presumably related to the presence of numerous proliferative capillaries in the collagenous stroma.
- Characteristic features of pigmented villo nodular synovitis, not found in localized nodular synovitis, are the presence of diffuse frondlike projections of synovium, an abundance of hemosiderin deposition and hemorrhagic joint effusion.
MANAGEMENT
- Surgical intervention is the best therapeutic choice for patients with localized nodular synovitis.
- Recurrence is rare compared to pigmented villo nodular synovitis.
DIFFERENTIALS
- Focal pigmented villo nodular synovitis.
- Chondroma or osteochondroma
-signal intensity pattern consistent with either cartilage or bone marrow and lacks the deposition of hemosiderin.
- Hoffa’s disease
– ill-defined margins.
Dr Naveen SS,MD
Cross sectional imaging fellow MHRG
Dr Dayanand Sagar G, MD
Consultant Radiologist MHRG