An 18 month old baby presented with hip deformity – MRI bilateral hips was advised
An 18 month old baby presented with hip deformity – MRI bilateral hips was advised.
Findings
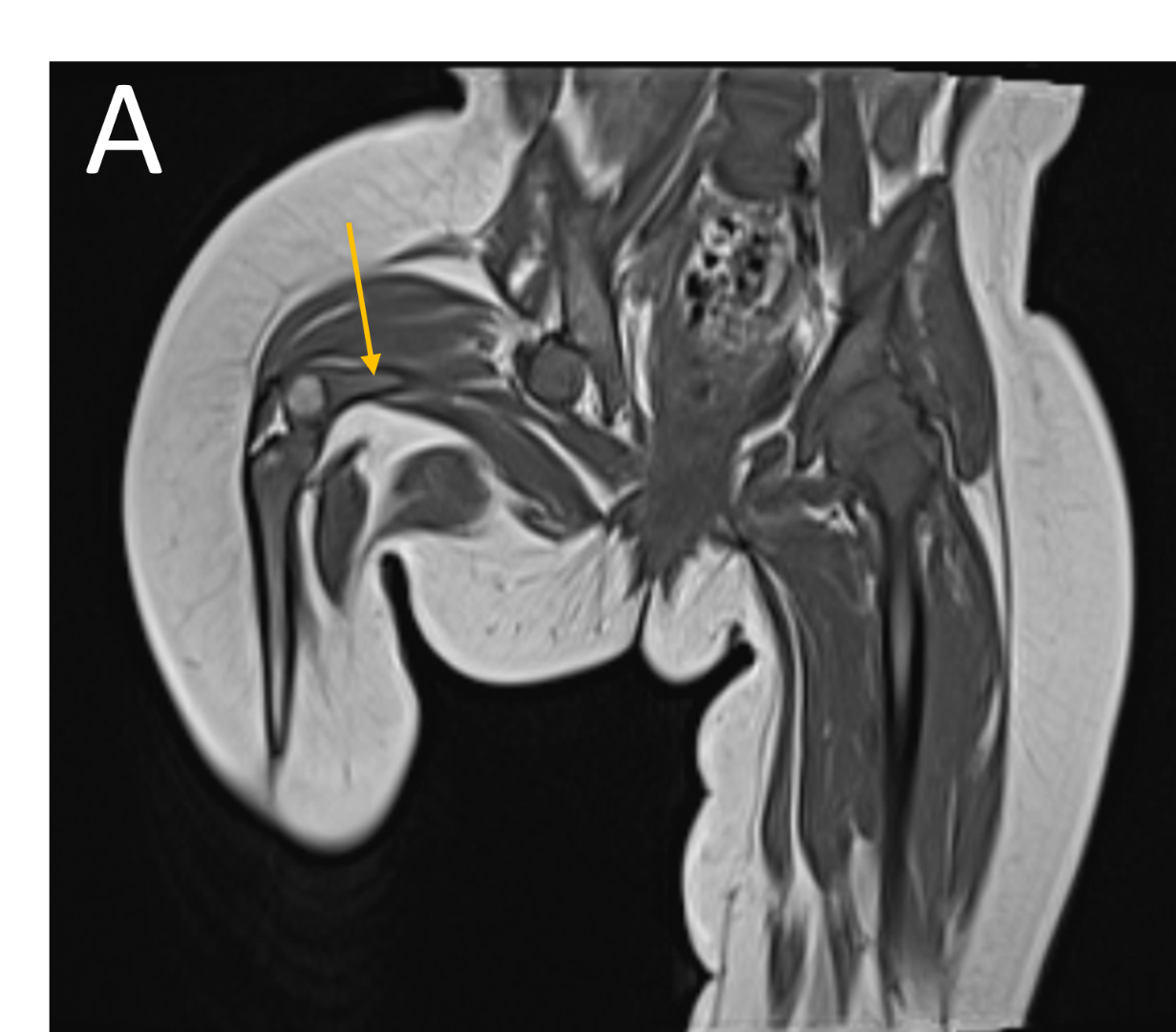
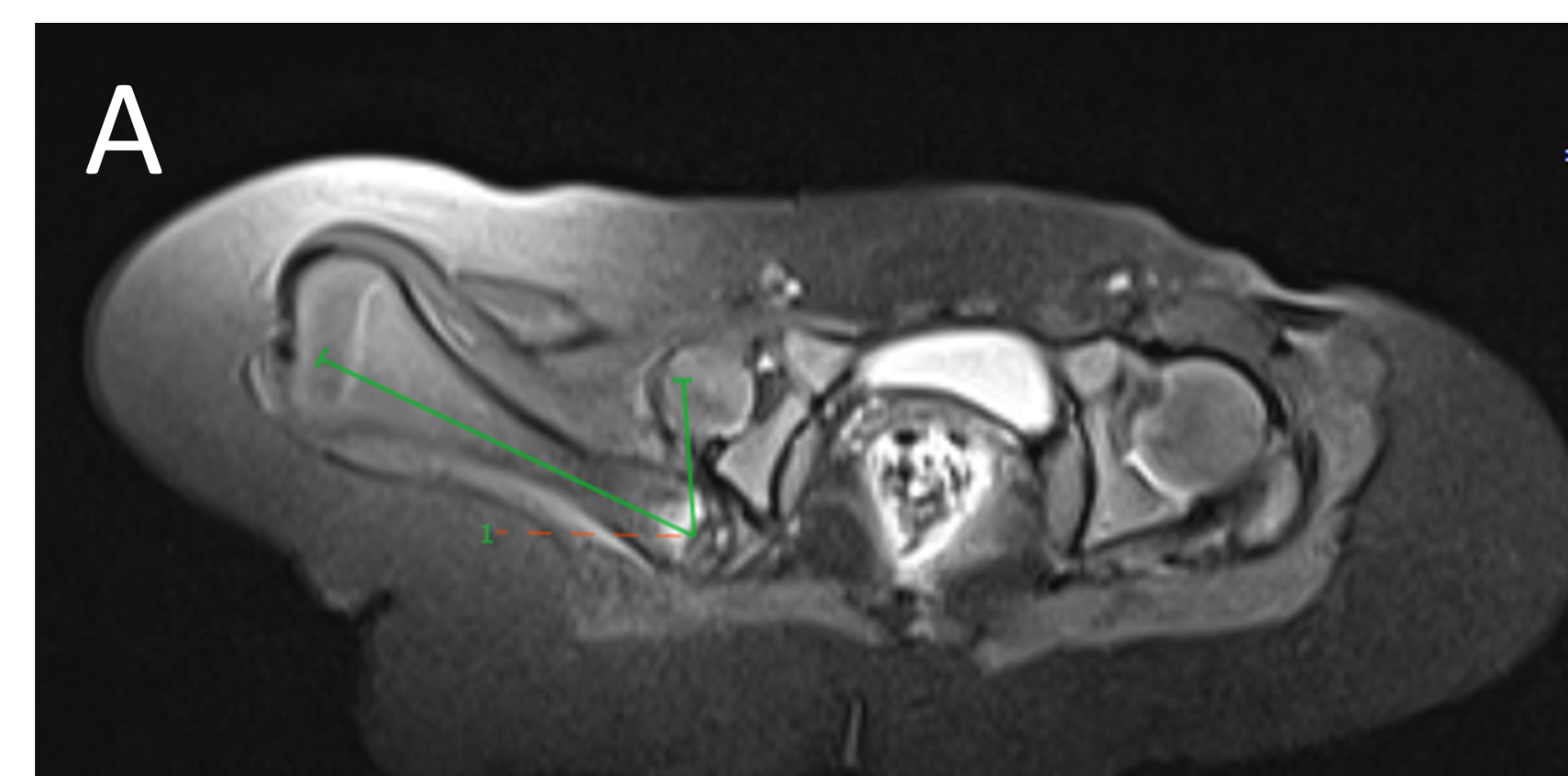
- A.FINDINGS – MR BILATERAL HIPS
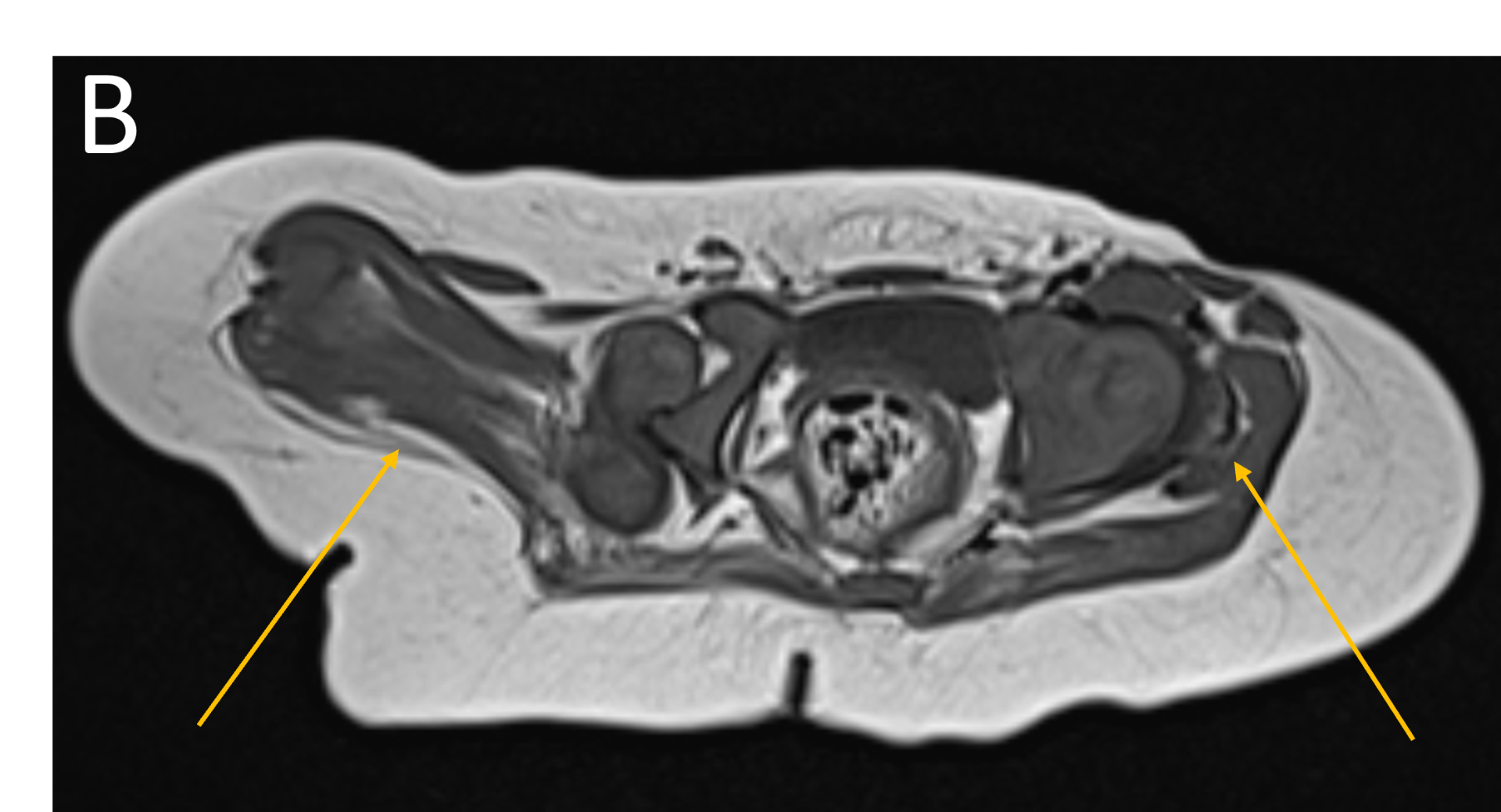
- B.FINDINGS – MR BILATERAL HIPS
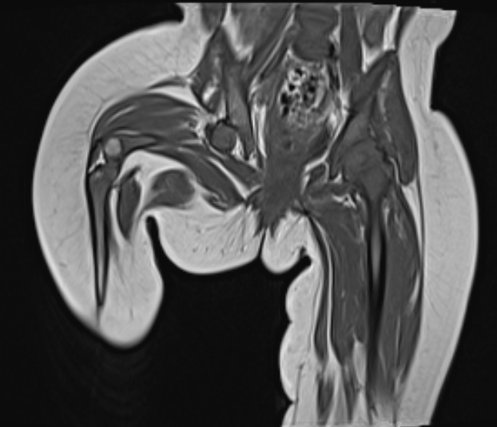
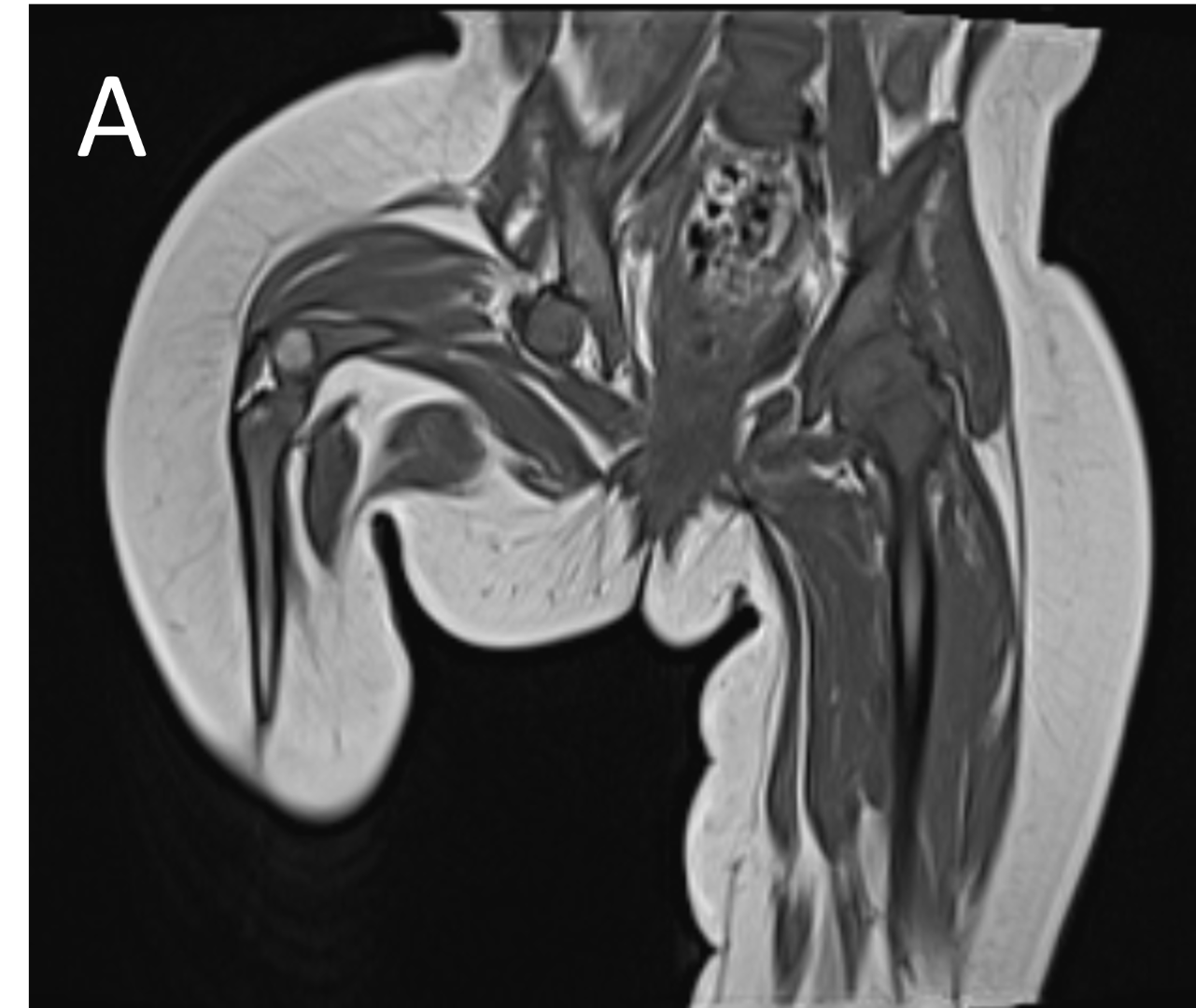
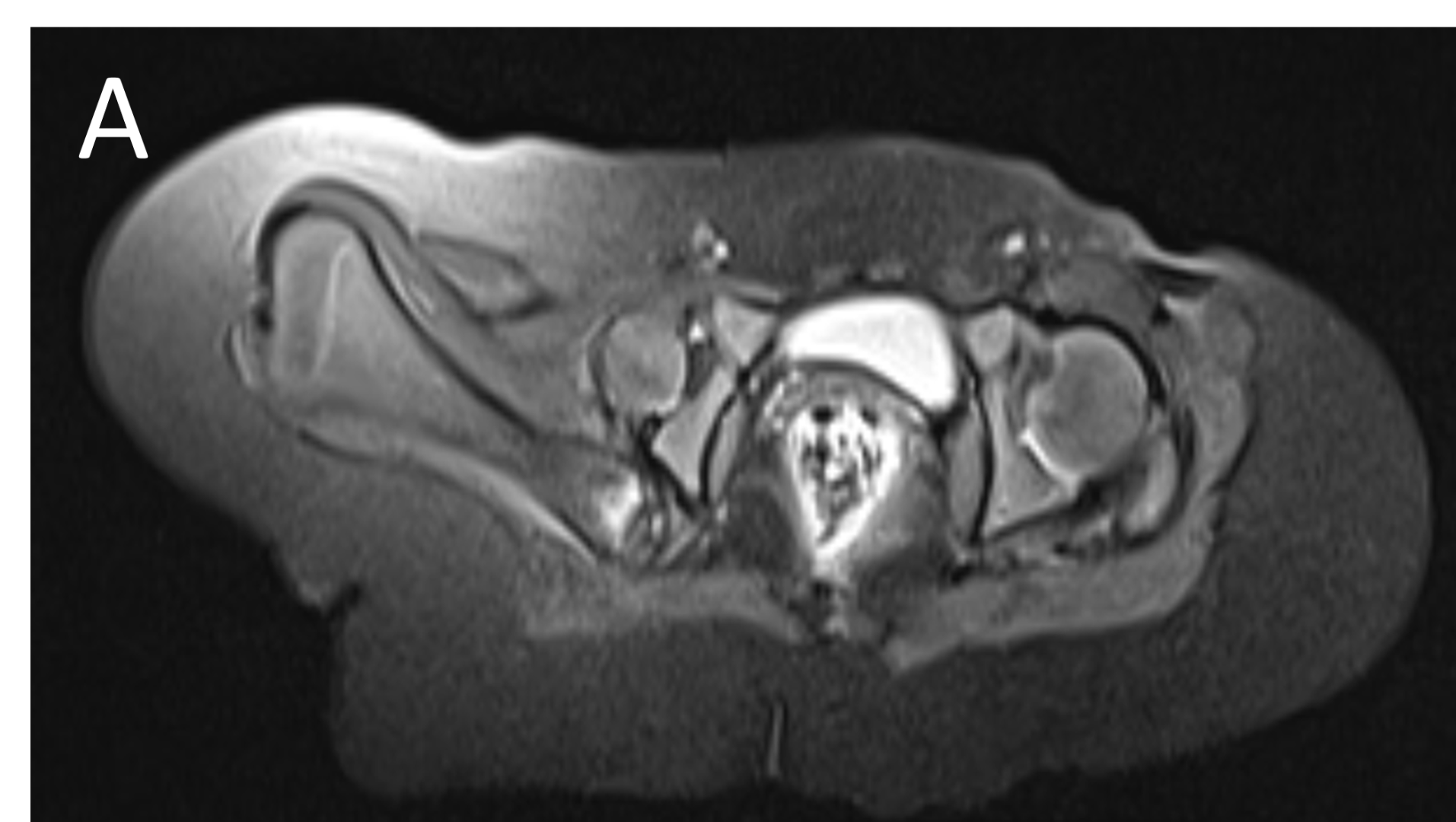
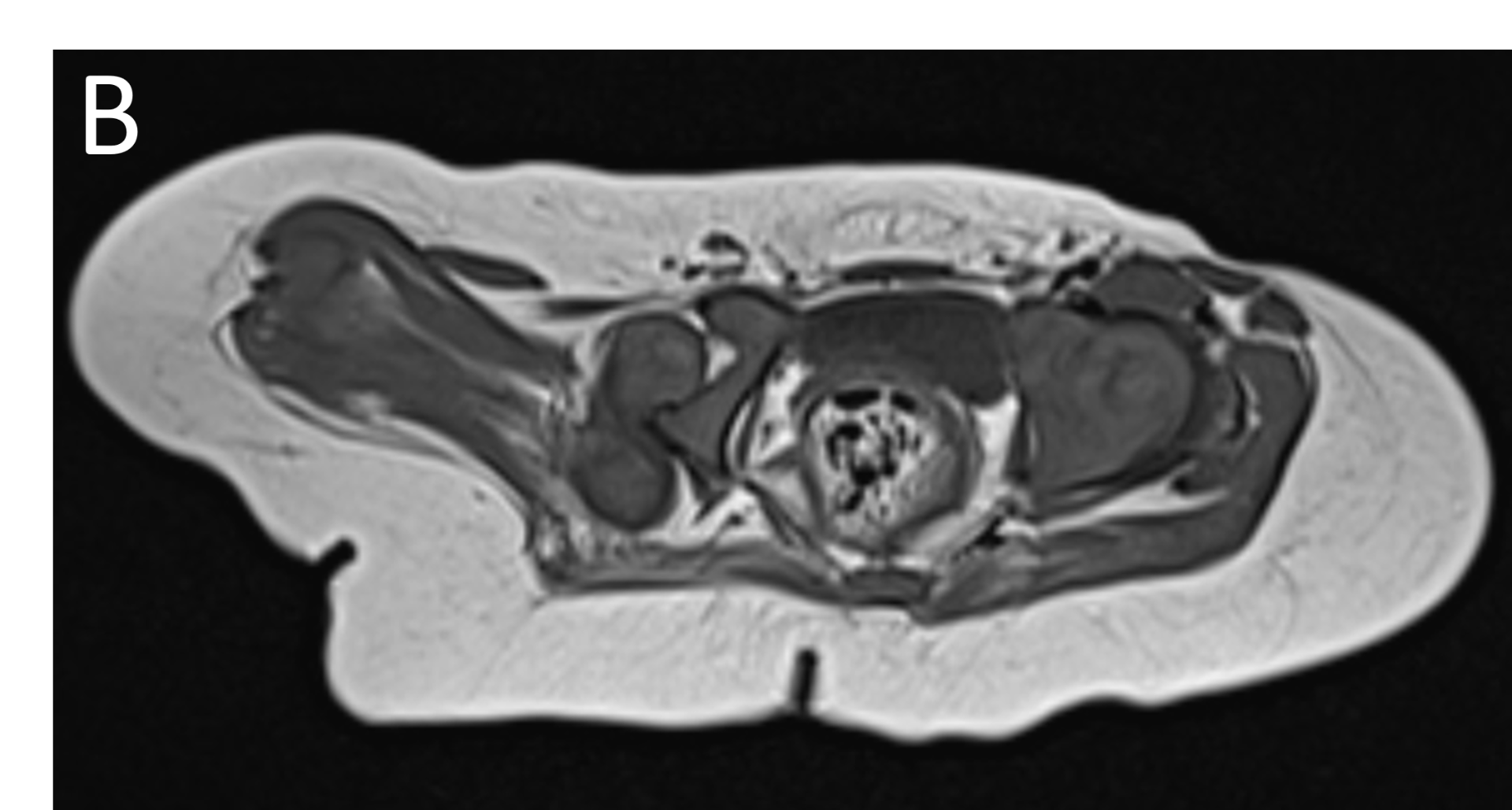
- A.LEGENDS – MR BILATERAL HIPS :Right femur is shortened, with a coxa vara deformity. Femoral shaft measures 7.2 cm in length. The acetabulum is moderately dysplastic and anteriorly rotated, But contains the femoral head. The femoral head and neck appear hypoplastic and posteriorly and externally rotated.
- B.LEGENDS – MR BILATERAL HIPS : Generalised atrophy of muscles of thigh and gluteal region on the right compared to the left.
DIAGNOSIS
PROXIMAL FOCAL FEMORAL DEFICIENCY
DISCUSSION
- PFFD is characterized by abnormal development of the proximal femur, ranging from mild shortening and deformity to complete absence of the femoral head and/or acetabulum
- Incidence: Extremely rare, with estimates from 1.1–2.0 per 100,000 live births.
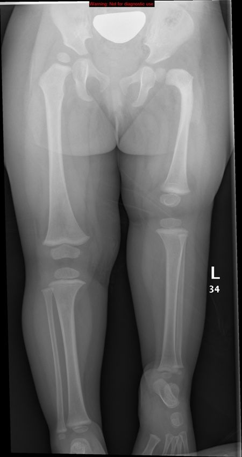
- Conventional Radiography
- Primary diagnostic tool: AP pelvis and lower limb X-rays -bone shortening, abnormal femoral neck orientation, and acetabular changes.?
- Classic features:
- Shortened, sometimes transverse or horizontally placed proximal femoral shaft
- Coxa vara with neck-shaft angle <120°
- Dysplastic or absent acetabulum in higher-grade cases (Aitken classification)
- Comparison with contralateral side for symmetry and severity
Common limb anomalies associated with proximal focal femoral deficiency (PFFD) include:
- Fibular hemimelia
- Clubfoot(CTEV)
- Flat feet (valgus foot)
- Knee instability (cruciate ligament deficiency)
- Tibial anomalies
- Patellar hypoplasia or agenesis
- Limb malrotation
- Spinal deformities
Proximal focal femoral deficiency (PFFD) is radiologically classified into types using the Aitken classification.
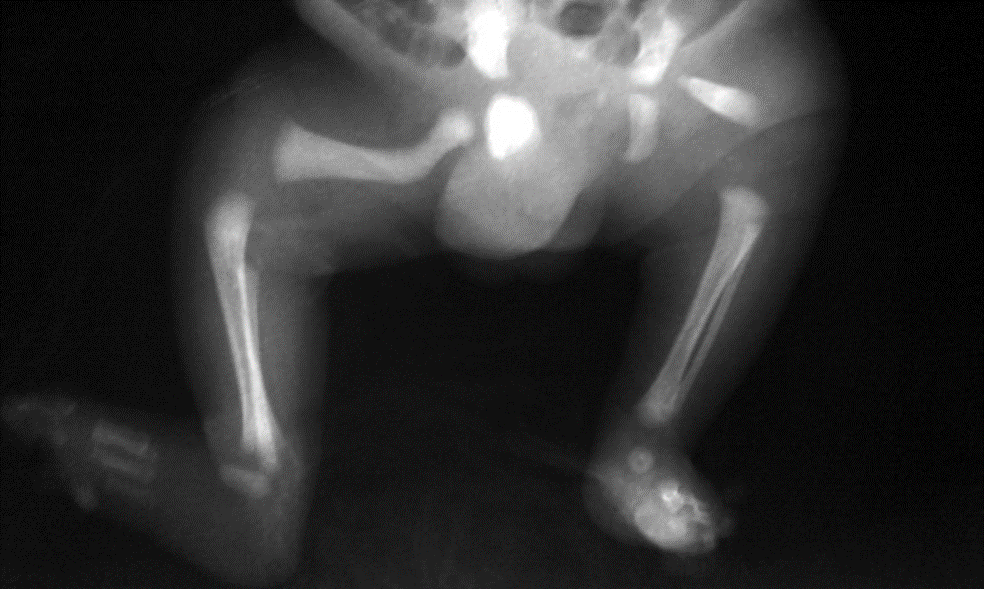
Bilateral Proximal focal femoral deficiency (class B on right side and class C on left side).
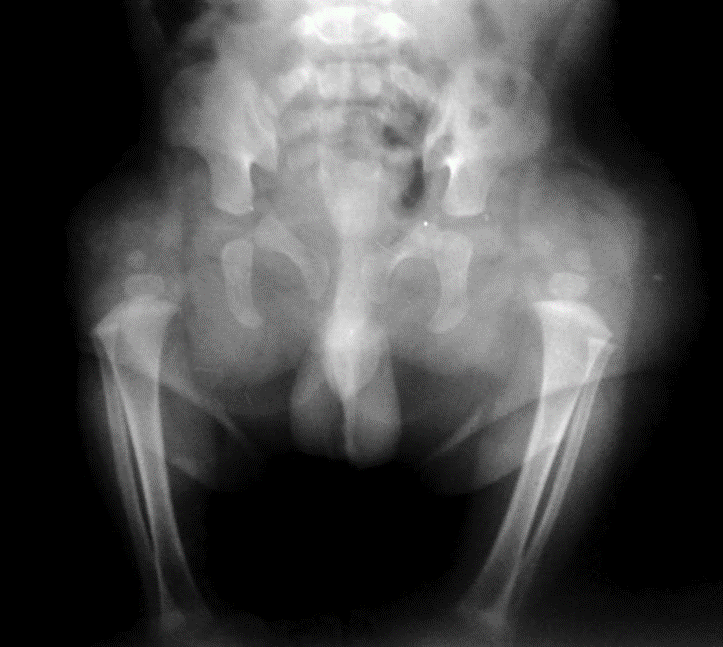
Congenital marked hypoplasia of both femurs consistent with bilateral proximal focal femoral deficiency. femoral head and almost all the femur are absent bilaterally, associated with absent acetabula. This is consistent with class D deformity.
Treatment and Prognosis
Treatment ranges from non-operative prosthetic management to complex surgical reconstruction and limb lengthening, tailored to severity. Prognosis depends on deformity severity; mild cases often achieve good function, while severe cases may require lifelong prosthetics.
REFERENCES
- Pediatric Radiology. MRI evaluation of proximal focal femoral deficiency.Pediatr Radiol. 2011.
- Skeletal Radiology. Role of MRI in classification of proximal focal femoral deficiency.Skeletal Radiol.
- Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology. Proximal femoral focal deficiency.Semin Musculoskelet Radiol.
DR. KAMESH G
CONSULTANT RADIOLOGIST
MANIPAL HOSPITAL, YESHWANTHPUR
DR.FATHIMATH ASHILI KM
RADIOLOGY RESIDENT
MANIPAL HOSPITAL, YESHWANTHPUR