An 11 year old with breathing difficulty and left sided proptosis
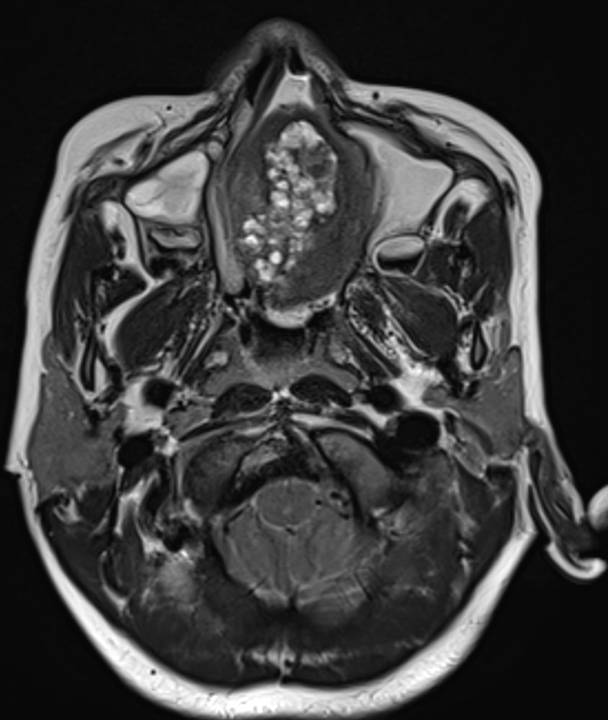
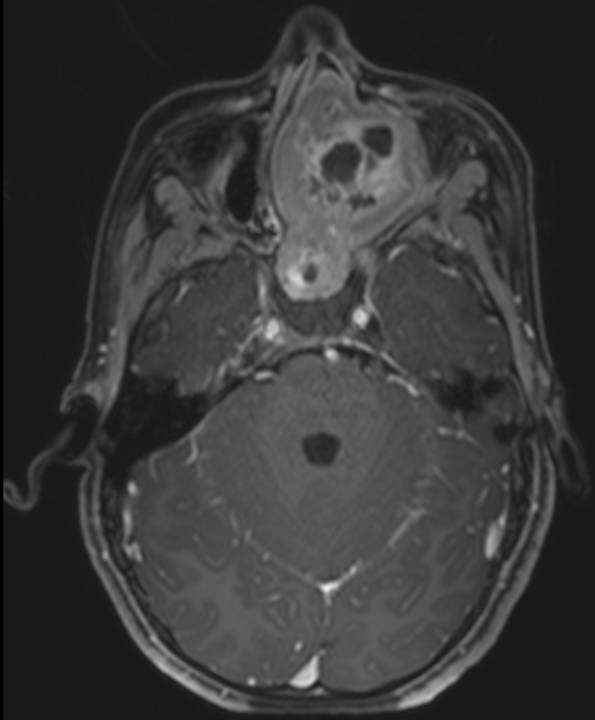
- Axial T2 weighted images demonstrate an expansile multi cystic heterogeneously T2 hyperintense mass lesion filling the left ethmoid air cells and nasal cavity. Cystic spaces demonstrate T2 hypointense fluid-fluid levels, suggestive of haemorrhagic or proteinaceous content.
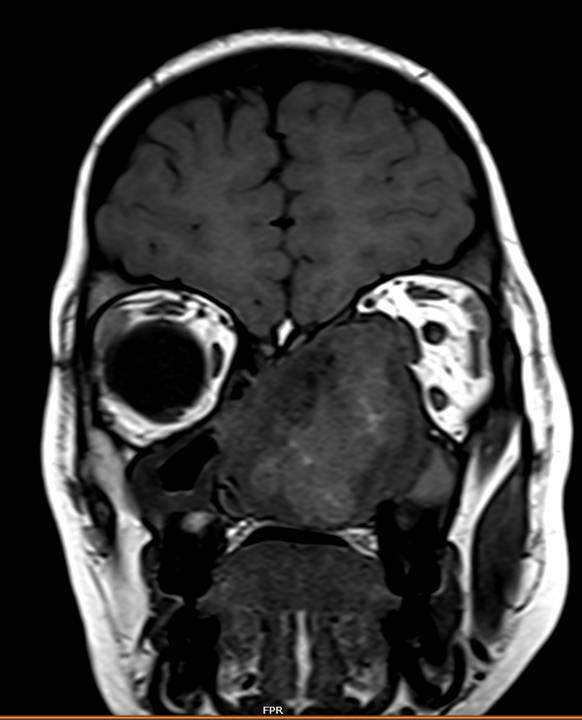
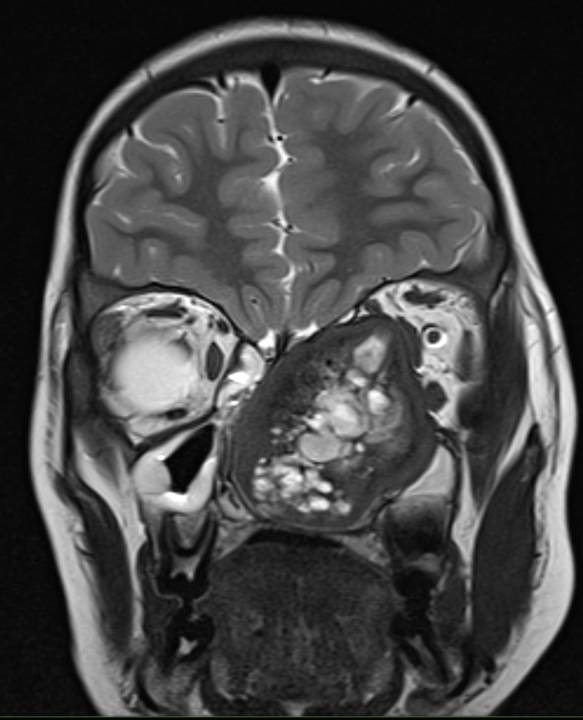
- Coronal T1 and T2 weighted images demonstrate thick T2 hypointense peripheral rim and T1 hyperintensity within the cystic spaces.
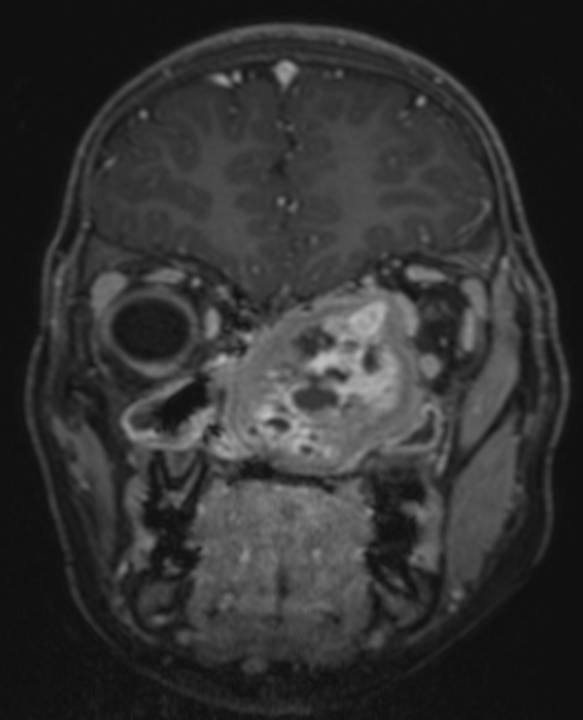
- Axial and coronal contrast enhanced T1 fat-suppressed sequences demonstrate heterogenous post-contrast enhancement with enhancement of the cyst walls.
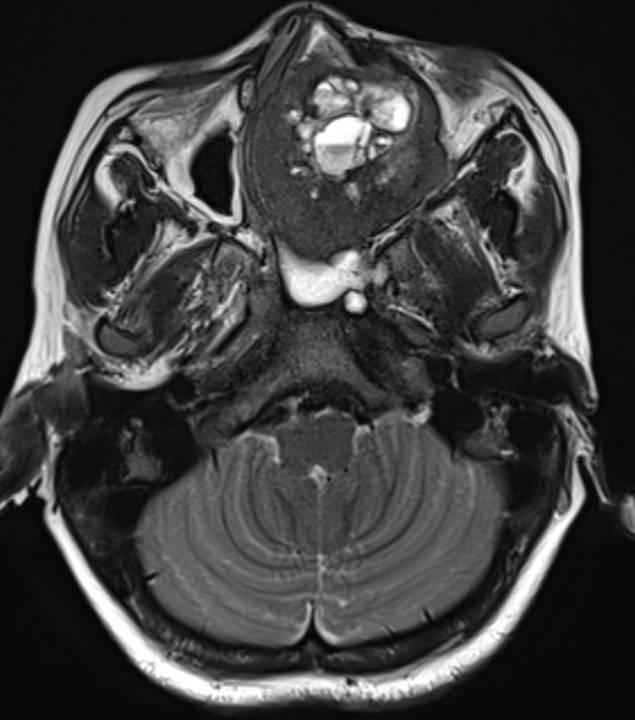
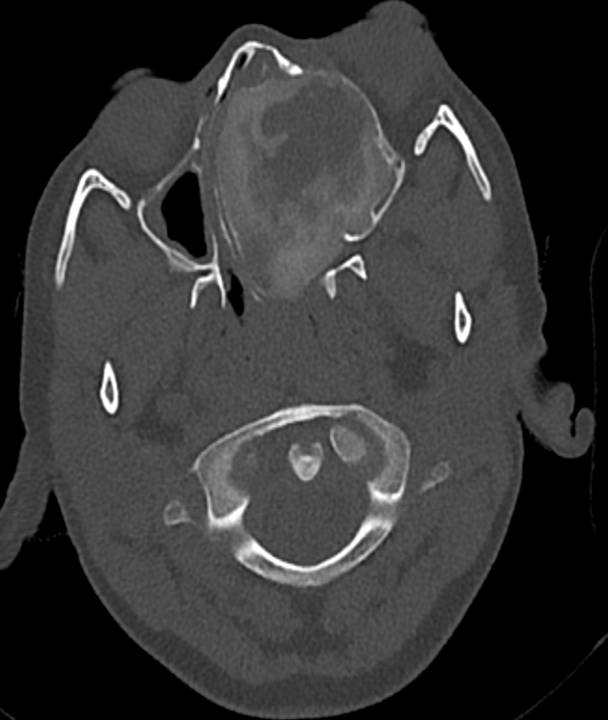
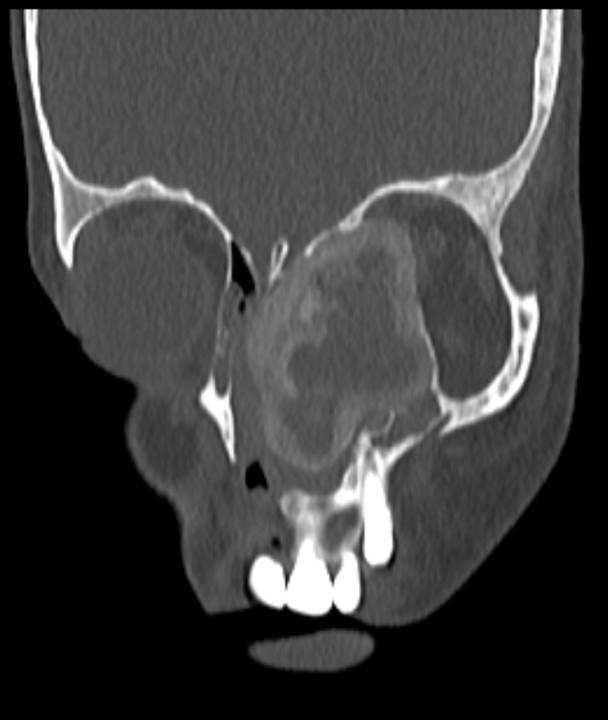
- Axial CT with coronal reformatted images demonstrate peripheral ground glass matrix, corresponding to T2 hypointense rim, with central hypodense areas. Proptosis of left globe seen on CT axial image.
Diagnosis:
Fibrous dysplasia of the left ethmoid (craniofacial FD)
Discussion:
- Fibrous dysplasia is a developmental abnormality in which a defect in osteoblastic differentiation and maturation results in replacement of normal bone marrow with fibro-osseous tissue.
- Types:
Monostotic type – Ribs, proximal femur and craniofacial bones.
Polyostotic type – two or more bones, most common in femur, tibia and pelvis. - Imaging:
Well circumscribed lesions in characteristic locations with no periosteal reaction.
CT demonstrates the ground-glass matrix.
A thick sclerotic margin (‘rind’ sign) is characteristic.
MRI demonstrates marked variability and can often resemble a tumor or aggressive lesion.
Differential diagnosis:
This depends on the location of the lesion.
Skull and facial bones: Paget’s disease, Simple bone cyst, Aneurysmal bone cyst.
Limbs: Admantinoma, Osteofibrous dysplasia, Non ossifying fibroma.
Dr. Akshay K,
Radiology Resident,
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group.
Dr. Anita Nagadi,
MD, MRCPCH, FRCR, CCT (UK)
Lead Head & Neck, Oncology
Senior Consultant Radiologist
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group.