A 56yrs old lady presented with complaints of altered sensation, numbness and weakness in right inner hand, little and ring fingers for the past 1 month
A 56yrs old lady presented with complaints of altered sensation, numbness and weakness in right inner hand, little and ring fingers for the past 1 month
- Symptoms were gradually progressive. Pain was also present in the right elbow joint.
FINDINGS:
1. Ultrasound of the right and left elbow joints at cubital tunnel.
2. Non contrast MRI of the elbow joint.
- A. Axial PDFS images above the level of elbow.
- B. Axial PDFS images at the level of elbow.
- C. Axial PDFS images below the level of elbow.
3. Non contrast MRI of the elbow joint
- A. Axial T2 images above the level of elbow.
- B. Axial T2 images at the level of elbow.
- C. Axial T2 images below the level of elbow.
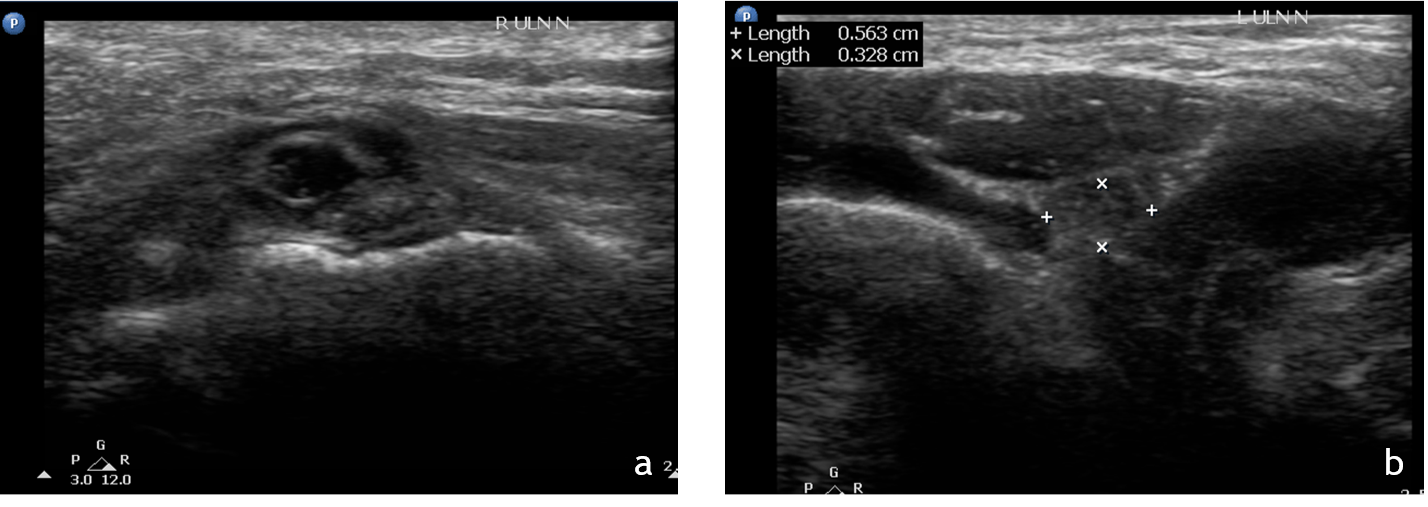
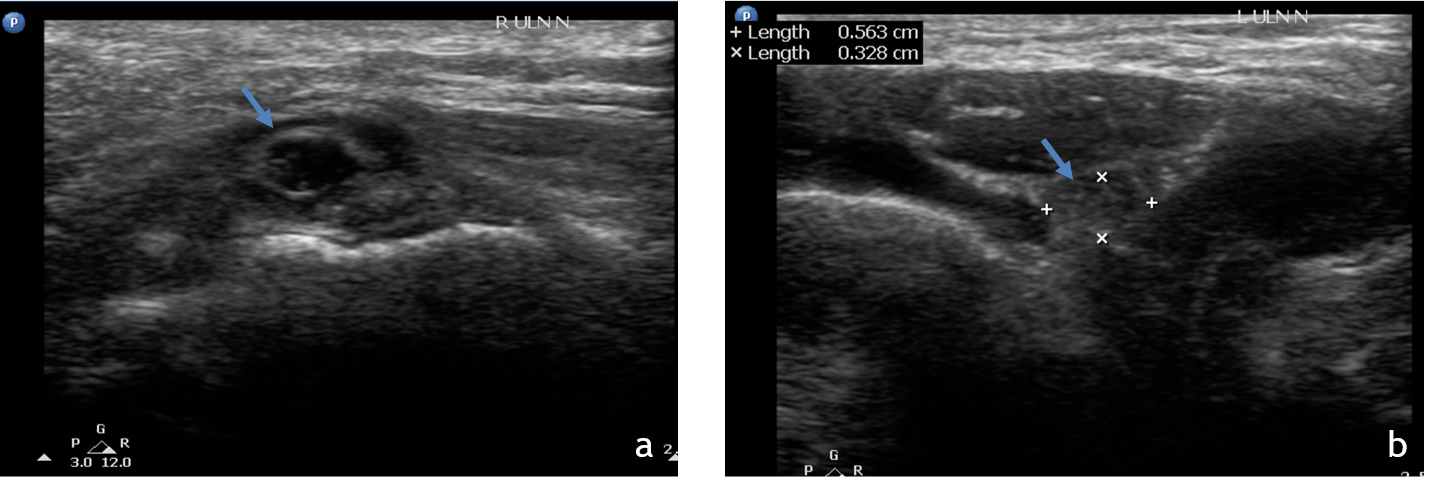
1. Ultrasound of the right(a) and left(b) elbow joints at cubital tunnel
- Right ulna nerve is loss the normal echotexture and is enlarged in size (arrow)as compared to the left side.
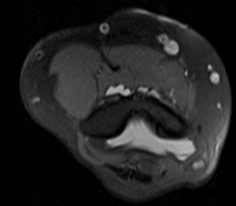
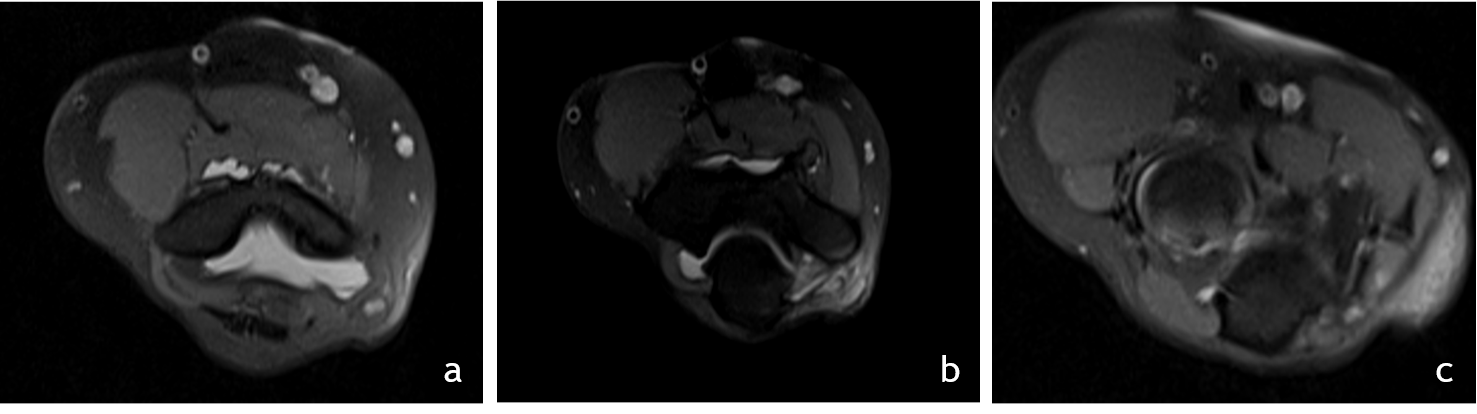
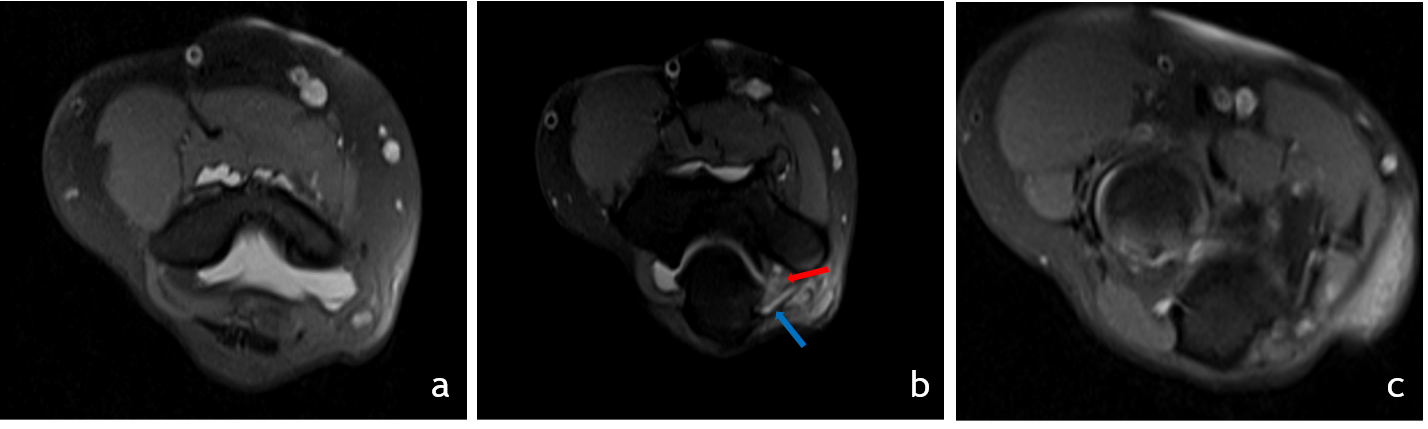
2. Serial Axial T2 images above(a), at (b) and below (c) the level of elbow joint
- The ulnar nerve (red arrow) is thickened, edematous and is significantly compressed and stretched at the cubital tunnel.
- Significant thickening of the roof of cubital tunnel(blue arrow), surface osteophytes in ulna and humerus. The ulna nerve appears tethered to the roof of cubital tunnel.
- The ulna nerve above and below the level of elbow joint is normal in caliber (images a and c).
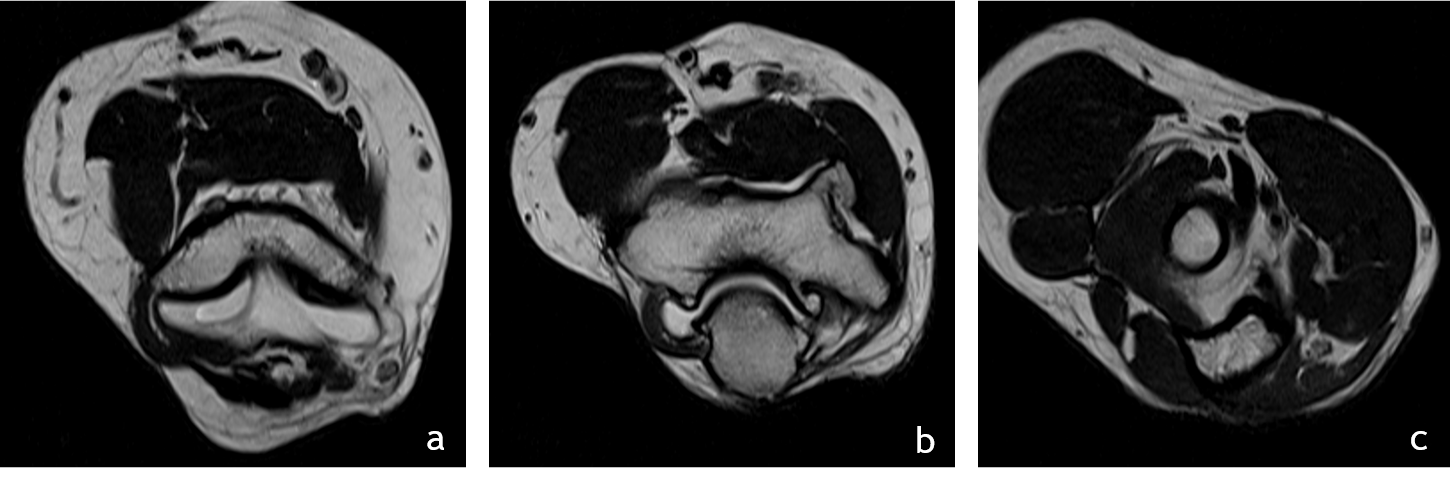
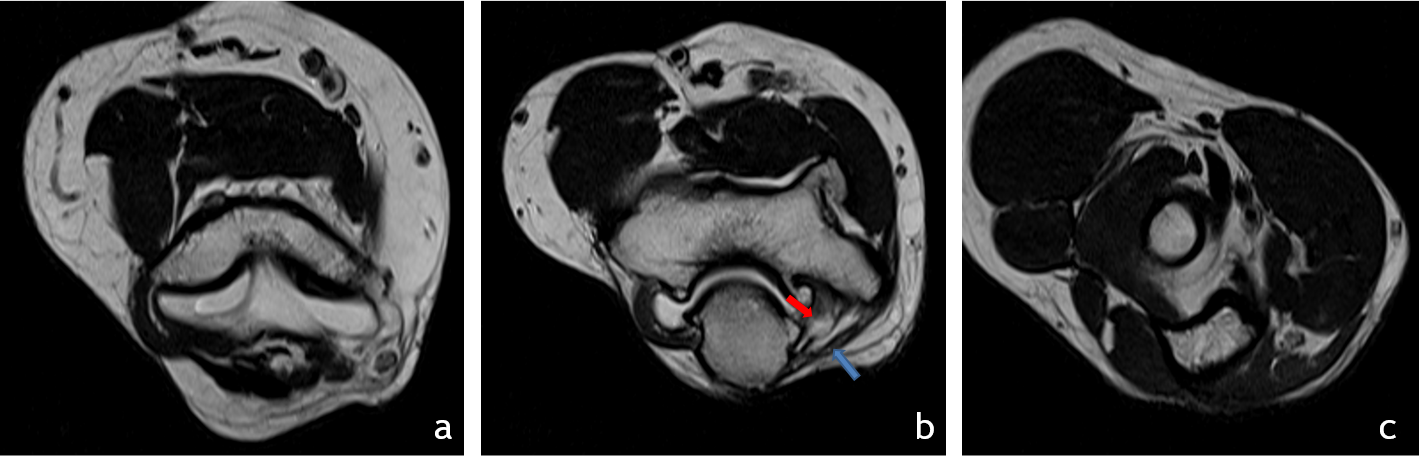
3. Serial Axial T2 images above(a), at (b) and below (c) the level of elbow joint
- The ulnar nerve (red arrow) is thickened, edematous and is significantly compressed and stretched at the cubital tunnel.
- Significant thickening of the roof of cubital tunnel(blue arrow), surface osteophytes in ulna and humerus. The ulna nerve appears tethered to the roof of cubital tunnel.
- The ulna nerve above and below the level of elbow joint is normal in caliber (images a and c).
DIAGNOSIS:
- Right cubital tunnel syndrome
MANAGEMENT:
- Patient underwent right cubital tunnel decompression and anterior transposition of ulnar nerve.
- Mild improvement in the symptoms was noticed post surgery.
DISCUSSION:
- Cubital tunnel syndrome is a type of ulnar nerve compression neuropathy (tunnel syndrome) due to pathological compression of the ulnar nerve along its course within the cubital tunnel.
- Second most common peripheral neuropathy of the upper extremity.
- Patients usually present with altered sensation in the little and ring fingers – commonest is the sensory loss followed by motor.
- The ulnar nerve is vulnerable to stretching and compression injury as it crosses the elbow joint, which undergoes a large arc of flexion during normal range of motion.
- The cubital tunnel represents one of several small passages through which the ulnar nerve passes near the elbow, and is considered the most common specific site of injury.
- During normal elbow flexion, the ulnar nerve experiences tension and axial compression due to increased pressure within the cubital tunnel, up to twenty-fold. Any local structural abnormality may exacerbate the mechanical forces on the nerve, which may result in neuropathy.
IMAGING FEATURES :
Ultrasound
- Ulnar nerve thickening and oedematous changes.
- Cross-sectional area of the ulnar nerve of more than 9 mm2.
- A ratio of 1.5:1, comparing the ulnar nerve area at the level of the cubital tunnel with that proximal to the cubital tunnel.
- The ulnar nerve in patients with cubital tunnel syndrome is usually hypoechoic on ultrasound due to neural oedema.
MRI
Ulnar nerve thickening
- keep in mind that cross-sectional area of ulnar nerve varies according to the degree of elbow flexion; thus, comparison must be done with the contralateral elbow.
Ulnar nerve T2 hyperintensity
- Eedema-like signal changes or atrophy of the flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum profundus - secondary to ulnar neuropathy.
Dr. Deepti H V
Senior Consultant
Department of Radiology
Manipal hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru.
Dr. Ram Sanjith V
Cross Section Fellow
Manipal hospital, Bengaluru.