A 42 year old lady presented with progressive paraparesis
- There was no history of trauma.
- MRI of cervical spine with screening of brachial plexus.
FINDINGS:`
- A. T2 TSE axial at C6-C7 level and parasagittal T2FS of cervical spine.
- B. T2 FS coronal of cervical spine and brachial plexus.
- C. T2FS axial and coronal of bilateral shoulder girdle.
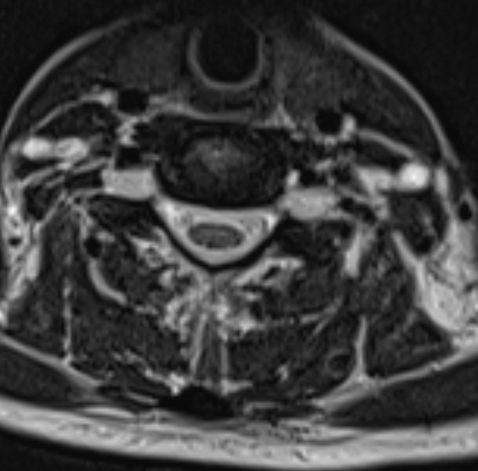
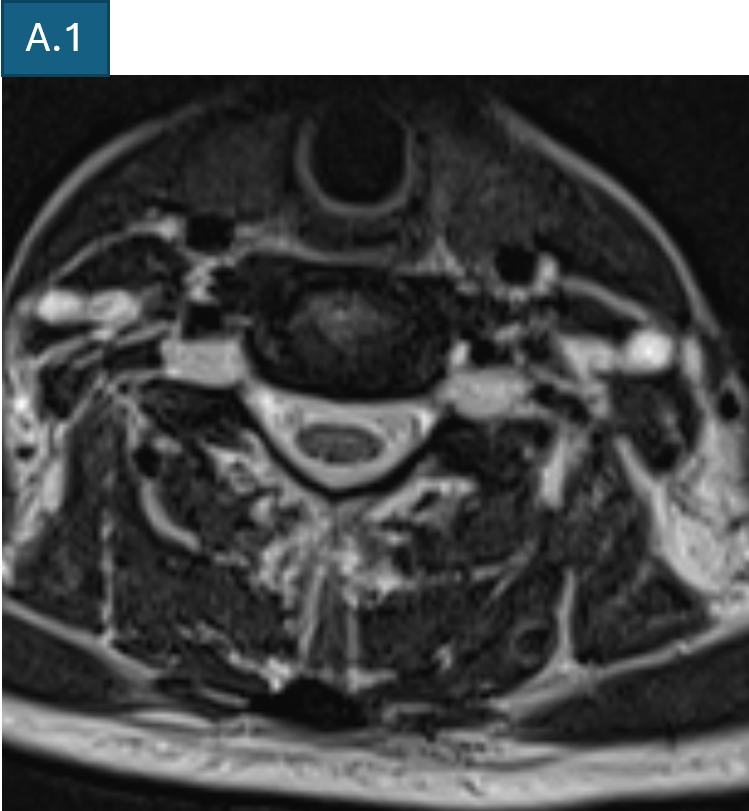
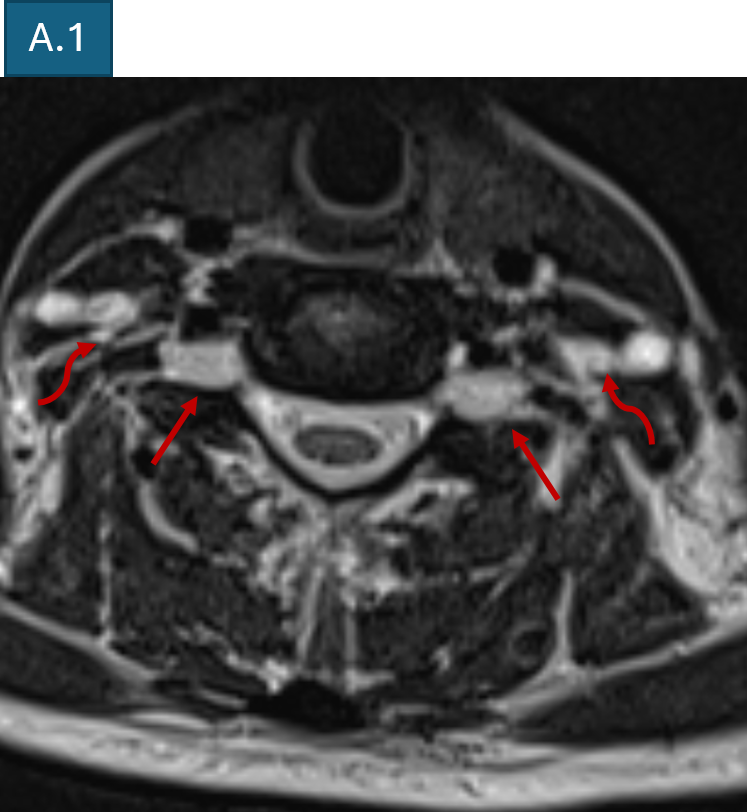
- A1. T2 TSE axial at C6-C7 level shows enlarged bilateral C7 nerve roots at dorsal root ganglion (straight arrow) and enlarged bilateral extraforaminal C6 nerve roots (curved arrows)
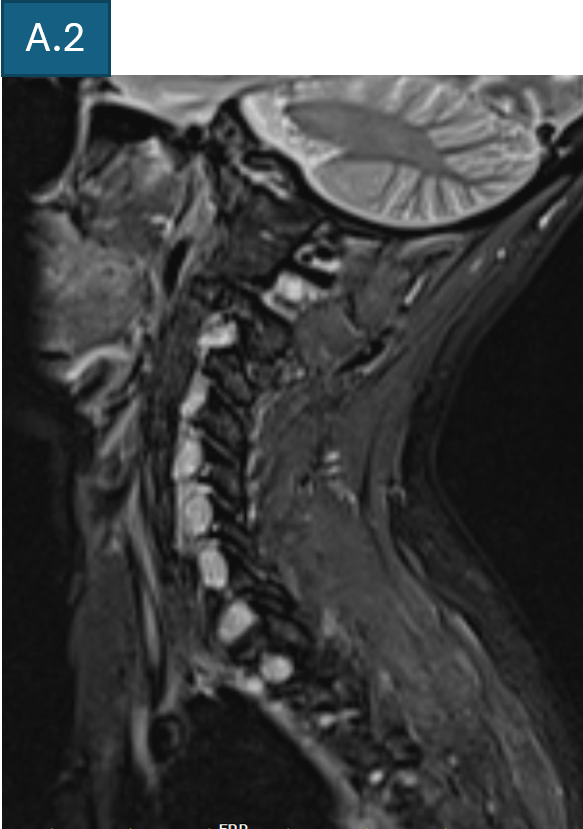
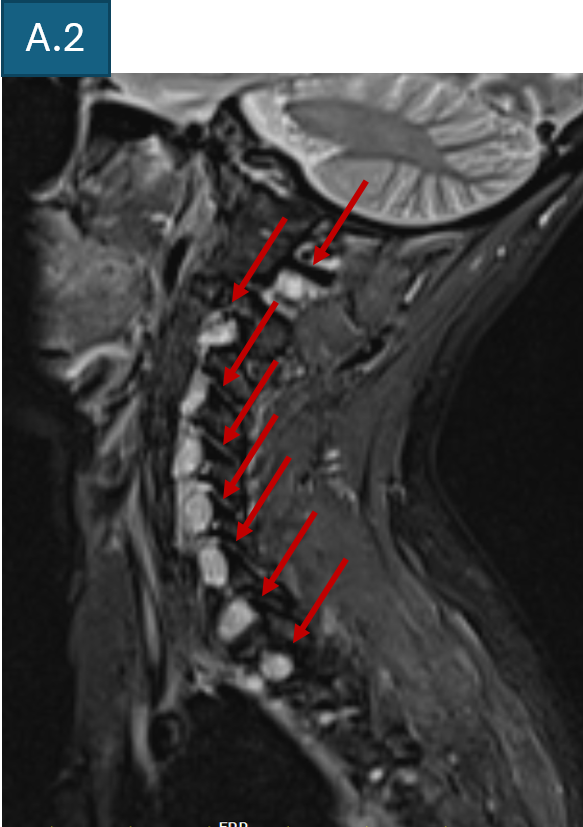
- A2. Parasagittal T2FS images of cervical spine show enlarged C2-T2 nerve roots
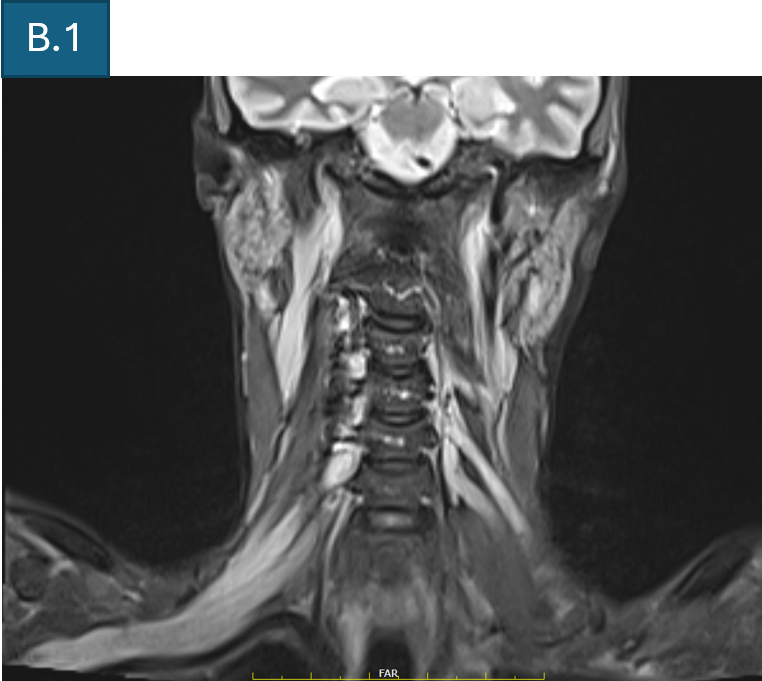
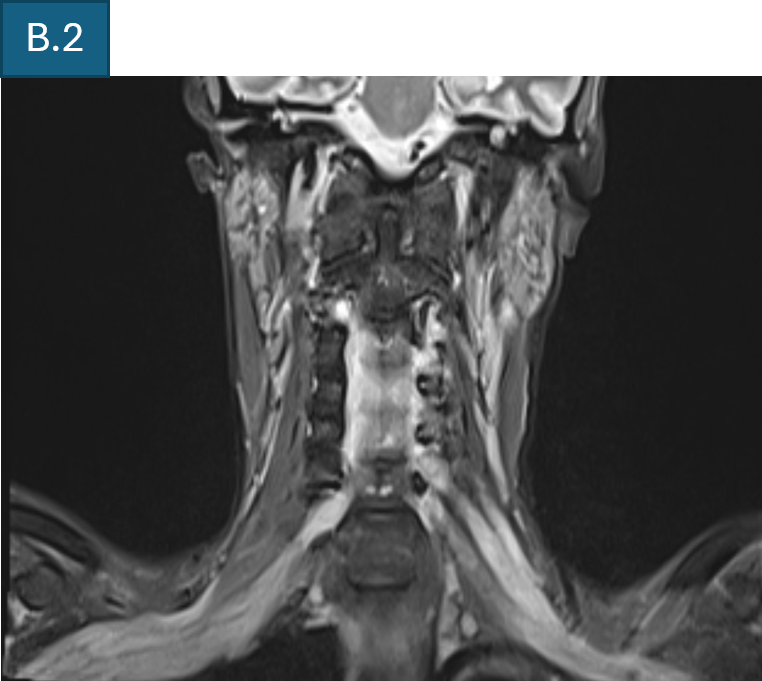
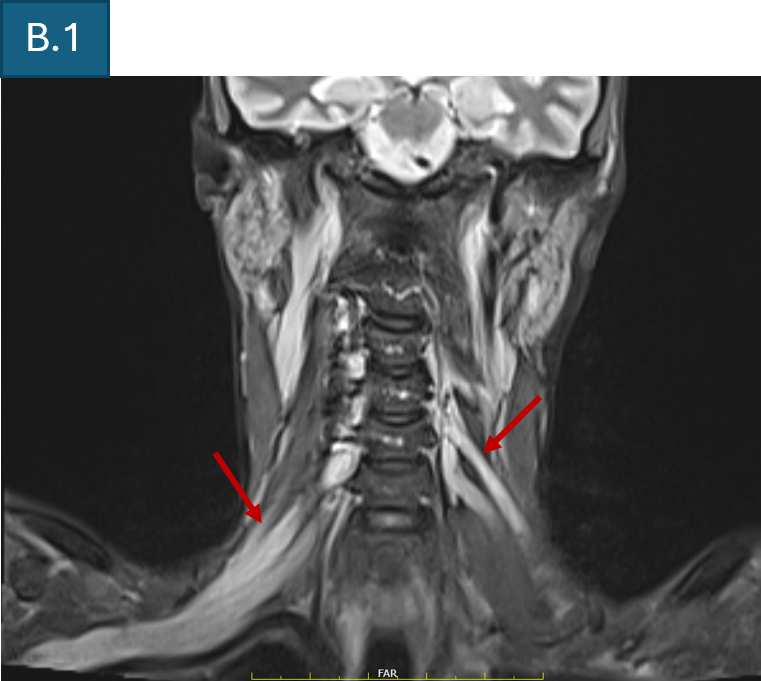
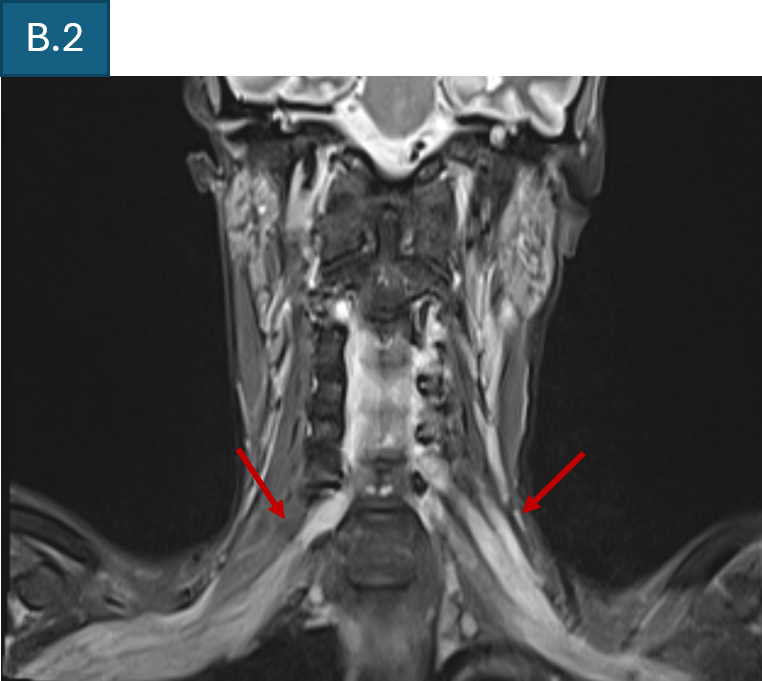
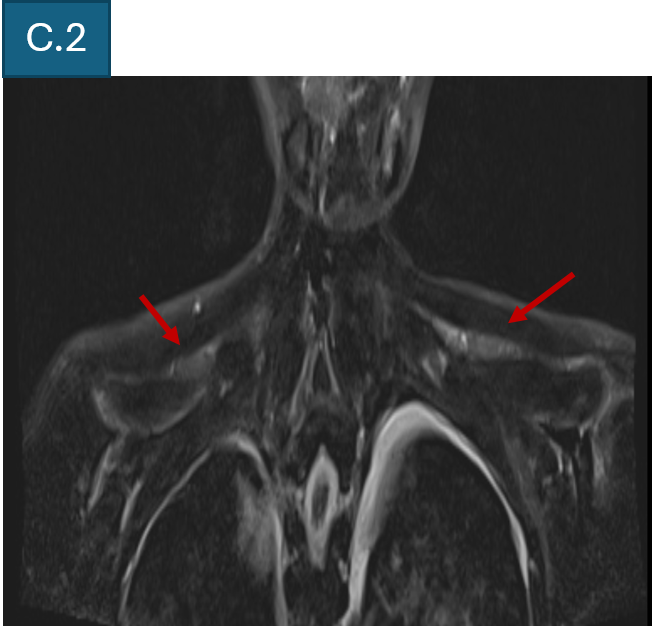
- B. T2 FS coronal of cervical spine and brachial plexus shows diffuse bilateral symmetrical thickening of all components of brachial plexus.
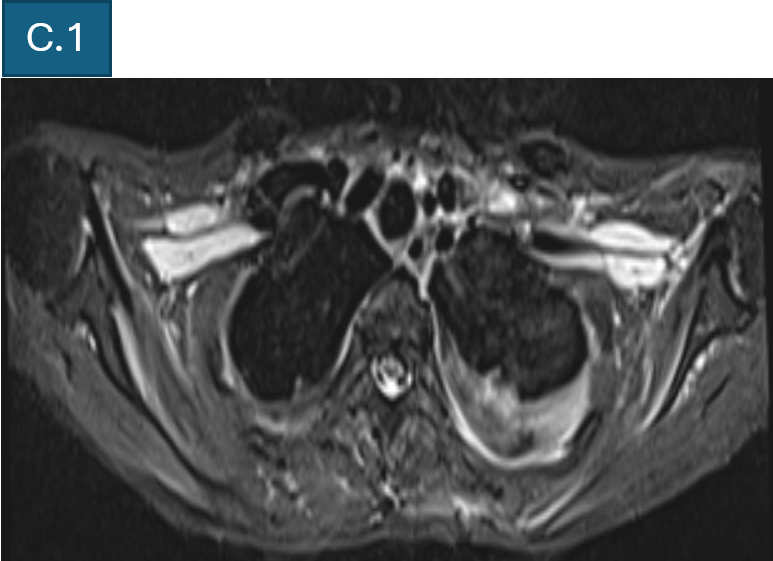
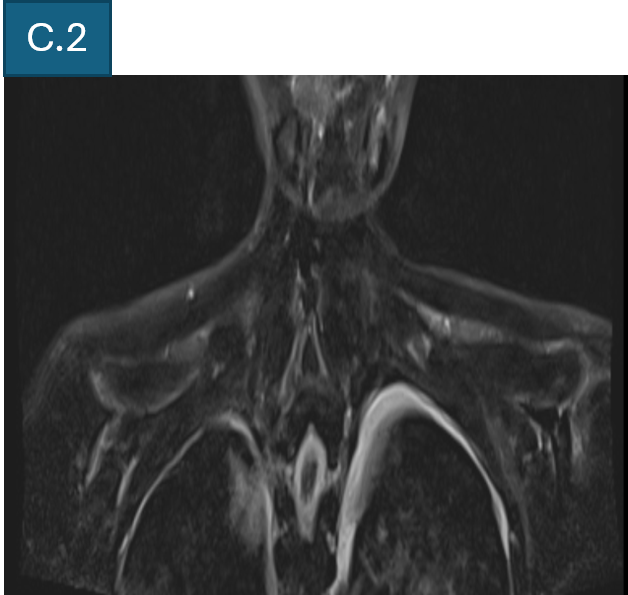
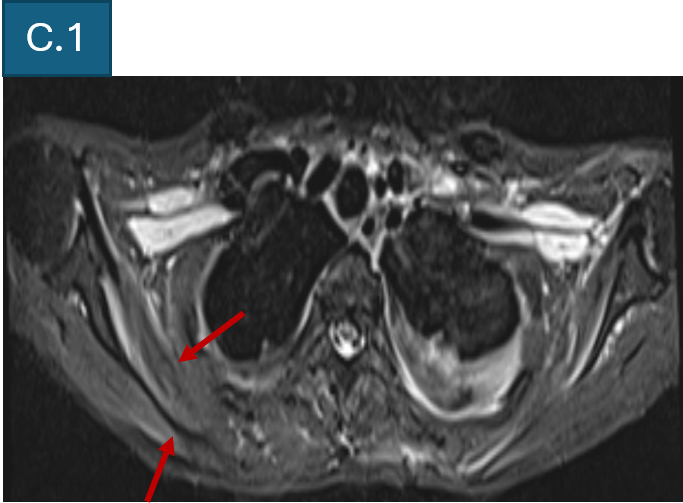
- C. T2FS axial and coronal images of bilateral shoulder girdle shows intramuscular edema and volume loss, representing subacute denervation changes.
DIAGNOSIS:
- Hypertrophic peripheral neuropathy.
DISCUSSION:
- Charcot - Marie – Tooth disease (CMT) and Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) are the leading causes of hypertrophic peripheral polyneuropathy. Other causes include leprosy, amyloid deposition and neurofibromatosis.
- Differential diagnosis of hypertrophic polyneuropathy remains challenging but is important because of different treatments and prognosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a useful adjunct to clinical and electrophysiological studies, and can identify the hypertrophic nerve segments and guide a fascicular biopsy. A fascicular biopsy will often be necessary for precise diagnosis.
- Charcot - Marie – Tooth disease (CMT) is the most common hereditary neuromuscular disease.
- It primarily affects the peripheral nervous system, manifesting with chronic progressive motor deficits and sensory symptoms. Due to its chronic nature patients demonstrate muscle atrophy and deformities, beginning with the feet followed by hand involvement. Sensory symptoms include loss of vibration, positional sense and subsequent loss of pain and temperature sensation.
- Electrophysiological studies aid in differentiating between two major subtypes: a demyelinating form (CMT1) and an axonal form (CMT2).
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is one of the most prevalent acquired immune-mediated peripheral neuropathies.
- CIDP manifests as progressive symmetric weakness in proximal and distal muscles and sensory ataxia. Diagnostic criteria for CIDP include motor or sensory dysfunction involving more than one limb and reduced or absent reflexes for greater than 8 weeks.
- Electrophysiological studies of CIDP patients reveal slowed nerve conduction velocities with unequal multifocal demyelination.
Imaging (MRI findings):
- Charcot - Marie – Tooth disease (CMT) : Partial or diffuse peripheral nerve thickening, iso- or hypointense nerves on T2-weighted images (occasionally with central T2 hyperintensity) and mild diffuse enhancement.
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) : May reveal normal calibre or enlarged nerve roots (particularly brachial plexus or cauda equina). Increased STIR signal intensity is usually identified. Enhancement is more common in patients with nerve root hypertrophy and suggests active disease. Although central nervous system involvement is rare, MRI may reveal demyelinating lesions in the brain.
Treatment:
- Charcot - Marie – Tooth disease (CMT) : Predominantly supportive and includes orthotics, pain management (NSAIDS/ anti epileptics) and rehabilitation.
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) : Primarily focused on reducing inflammation to prevent further demyelination and axonal degeneration. Mainstay therapies include corticosteroids, intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) and plasma exchange.
REFERENCES:
- https://radsource.us/congenital-and-acquired-hypertrophic-peripheral-neuropathies/
- De Smet, M. De Maeseneer, A. Talebian Yazdi, T. Stadnik, J. De Mey, MRI in hypertrophic mono- and polyneuropathies, Clinical Radiology, Volume 68, Issue 3, 2013, Pages 317-322, ISSN 0009-9260
Dr Dayananda Sagar G (MD )
Senior Consultant Radiologist
MHRG, Manipal Hospital, Mysore.
Dr Kanupriya Grover
Cross Sectional Imaging Fellow.
MHRG, Manipal Hospital.