A 29-year-old male came with history of breathlessness
Known case of decompensated heart failure precipitated by pneumonia
FINDINGS:
- CT contrast chest Axial and Coronal
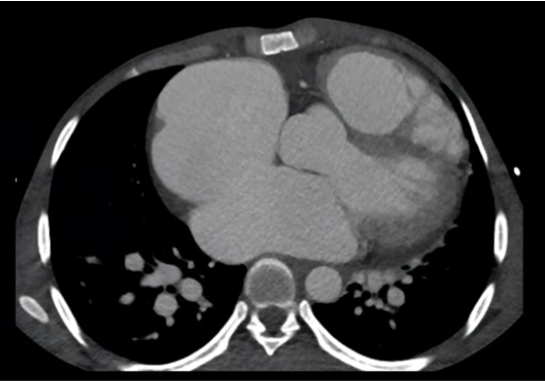
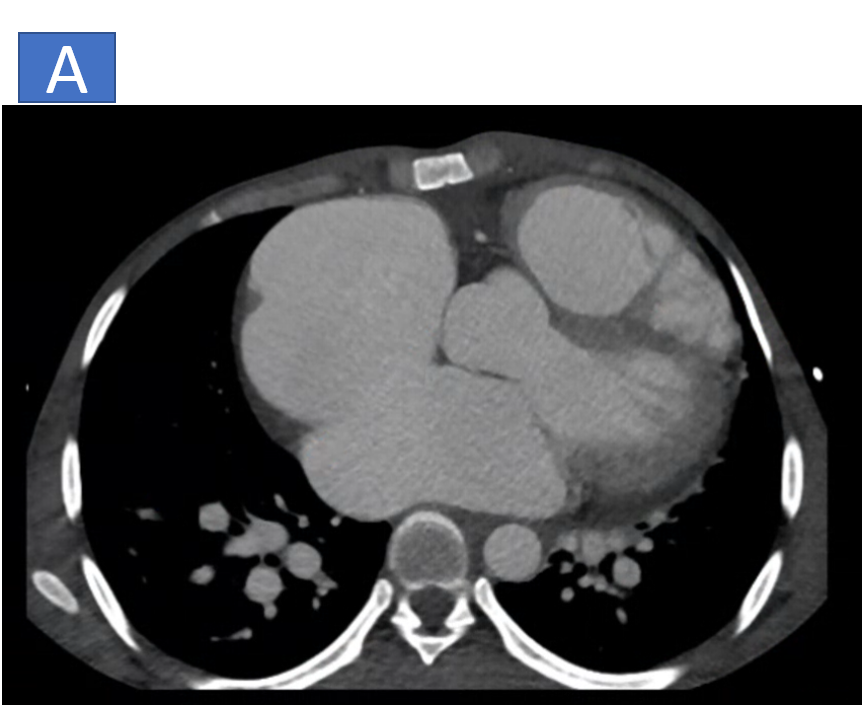
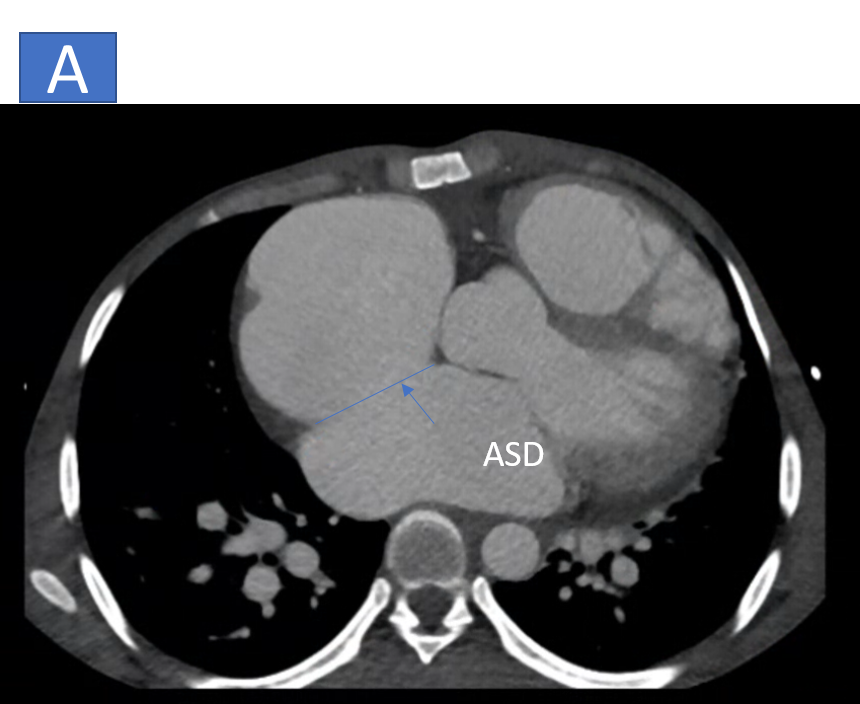
- A: Ostium secondum ASD with defect measuring ~3.8cm in axial diameter and 3.9cm in length.
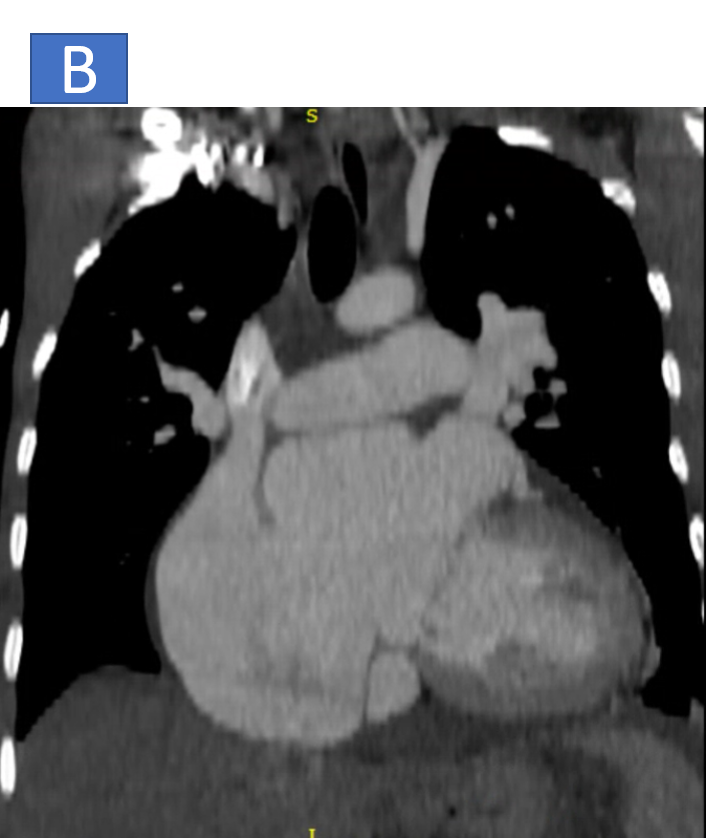
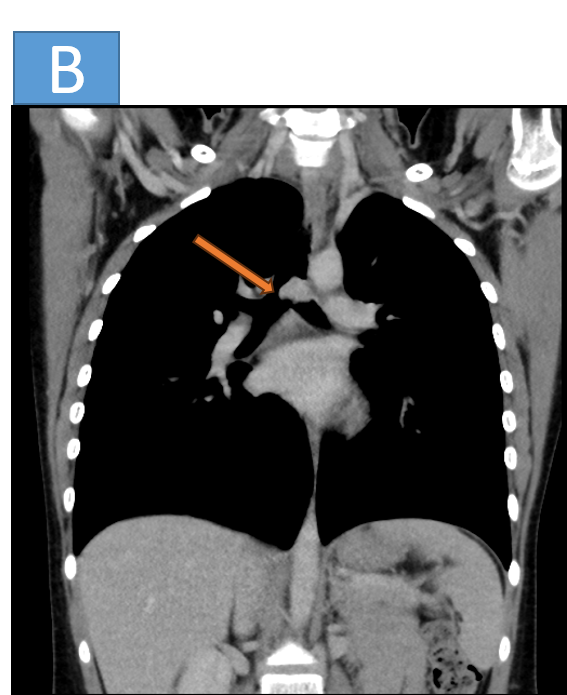
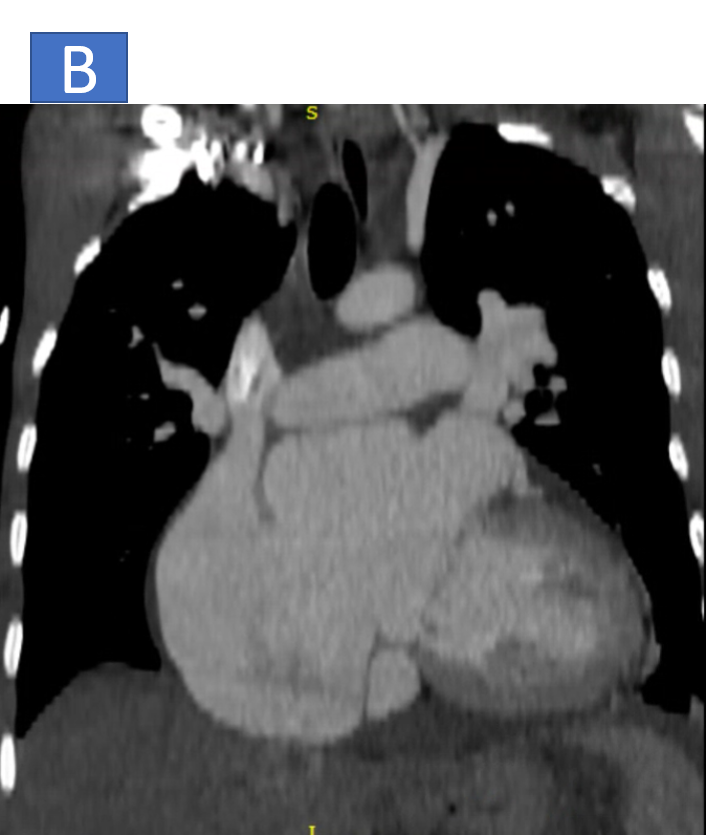
- B: Moderate dilatation of right and left atrium.
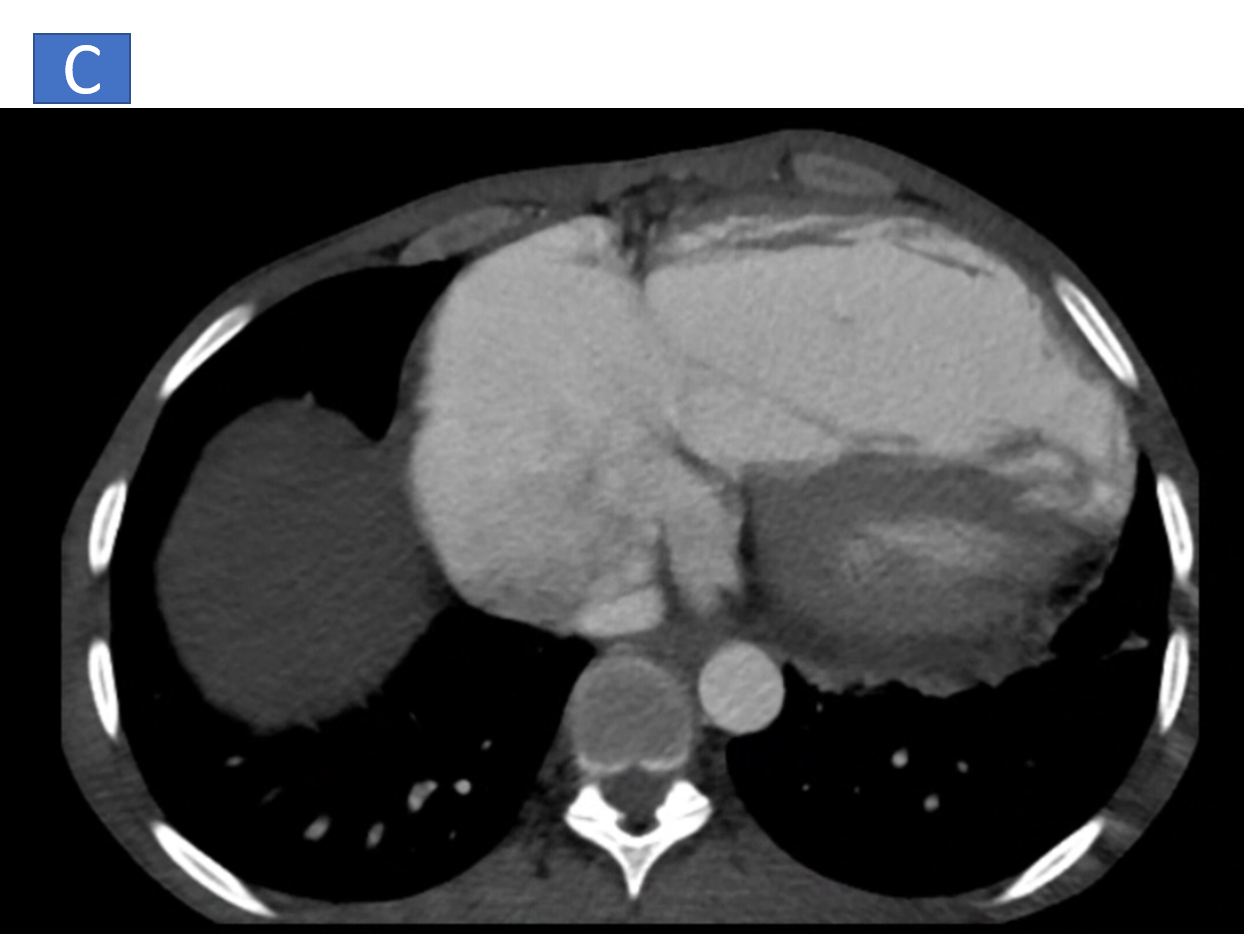
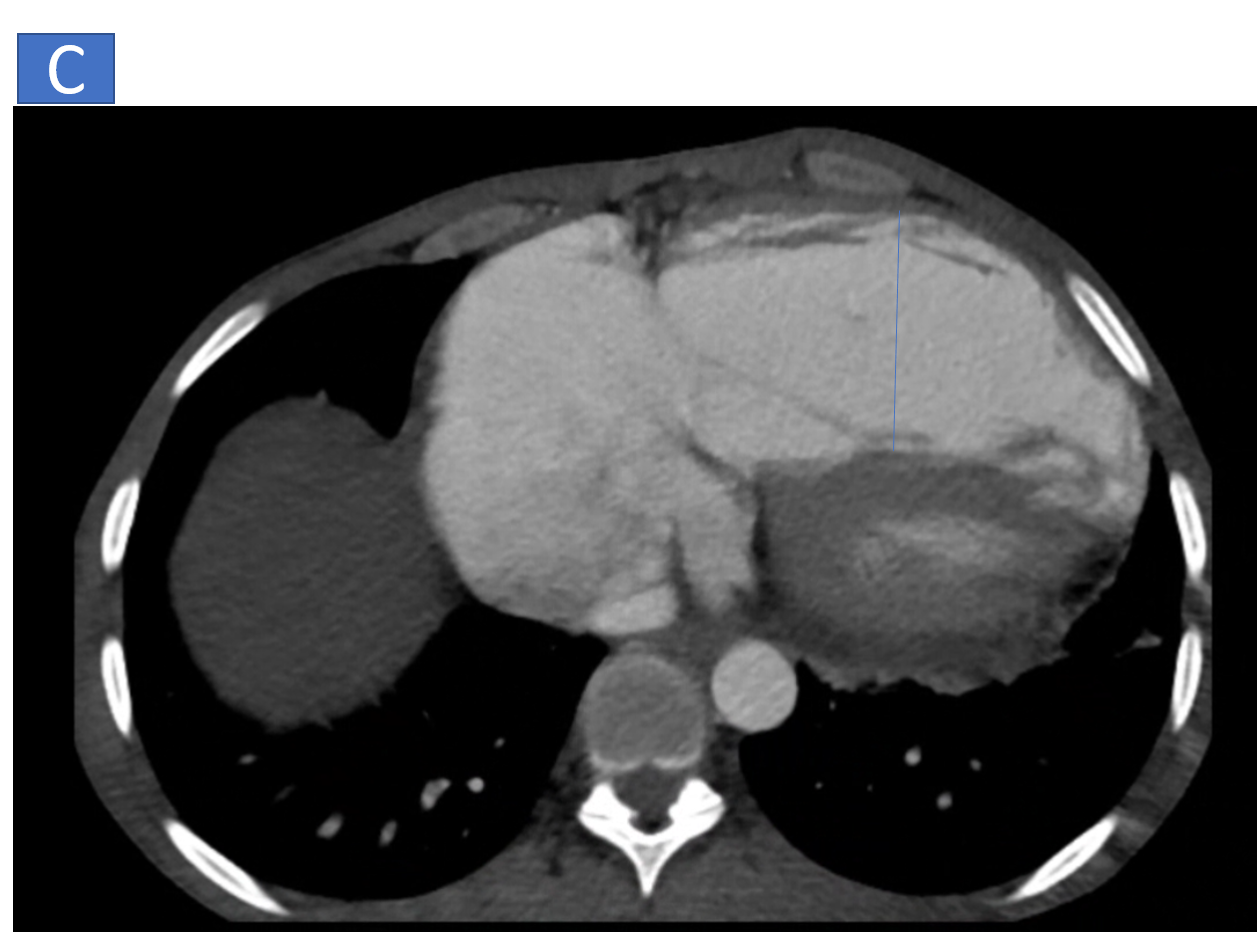
- C: Right ventricle is dilated with right ventricular hypertrophy.
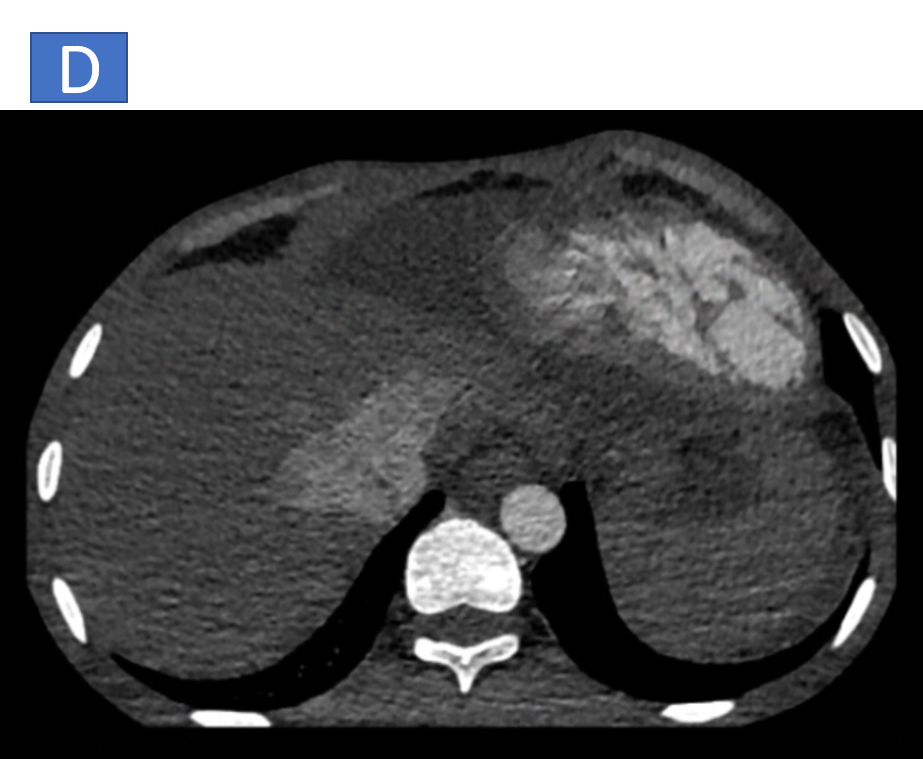
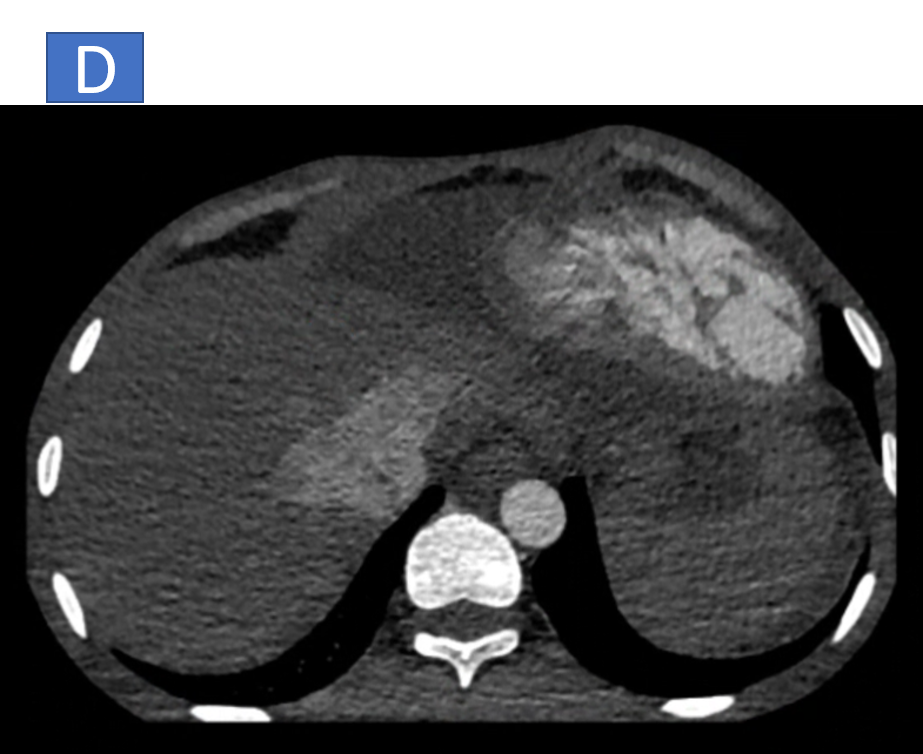
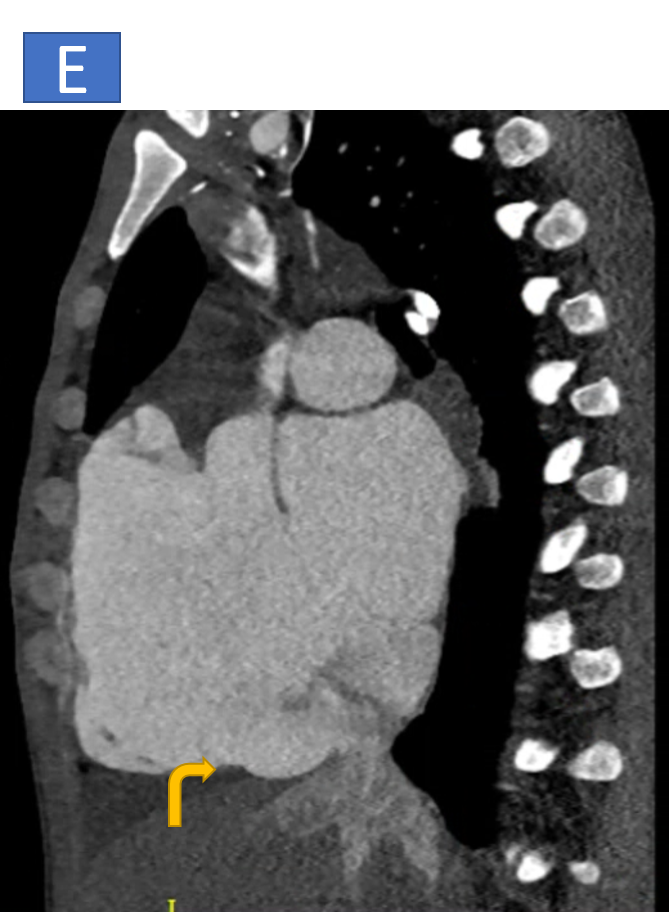
- D & E: Dilated IVC and hepatic veins.
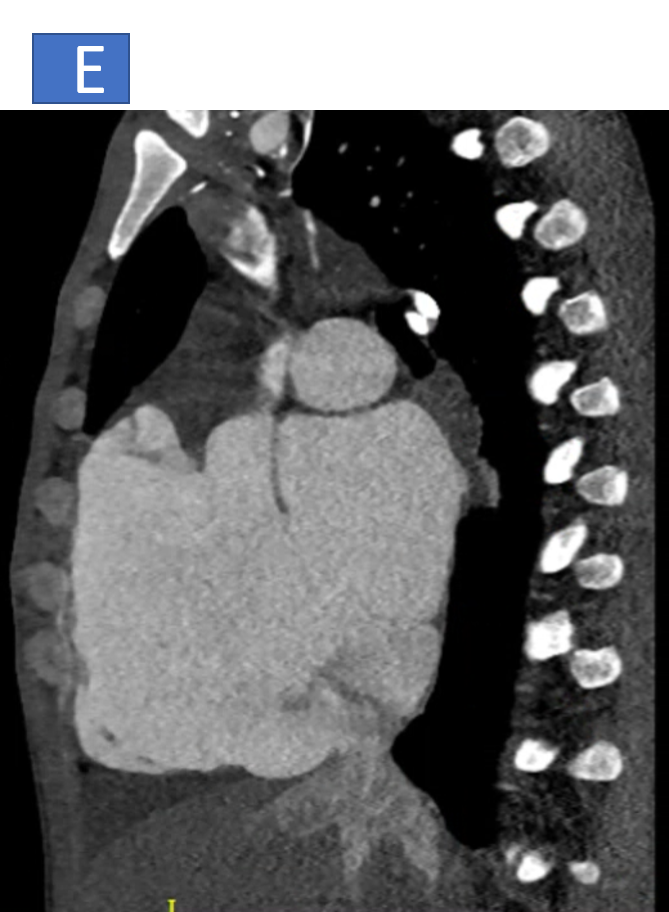
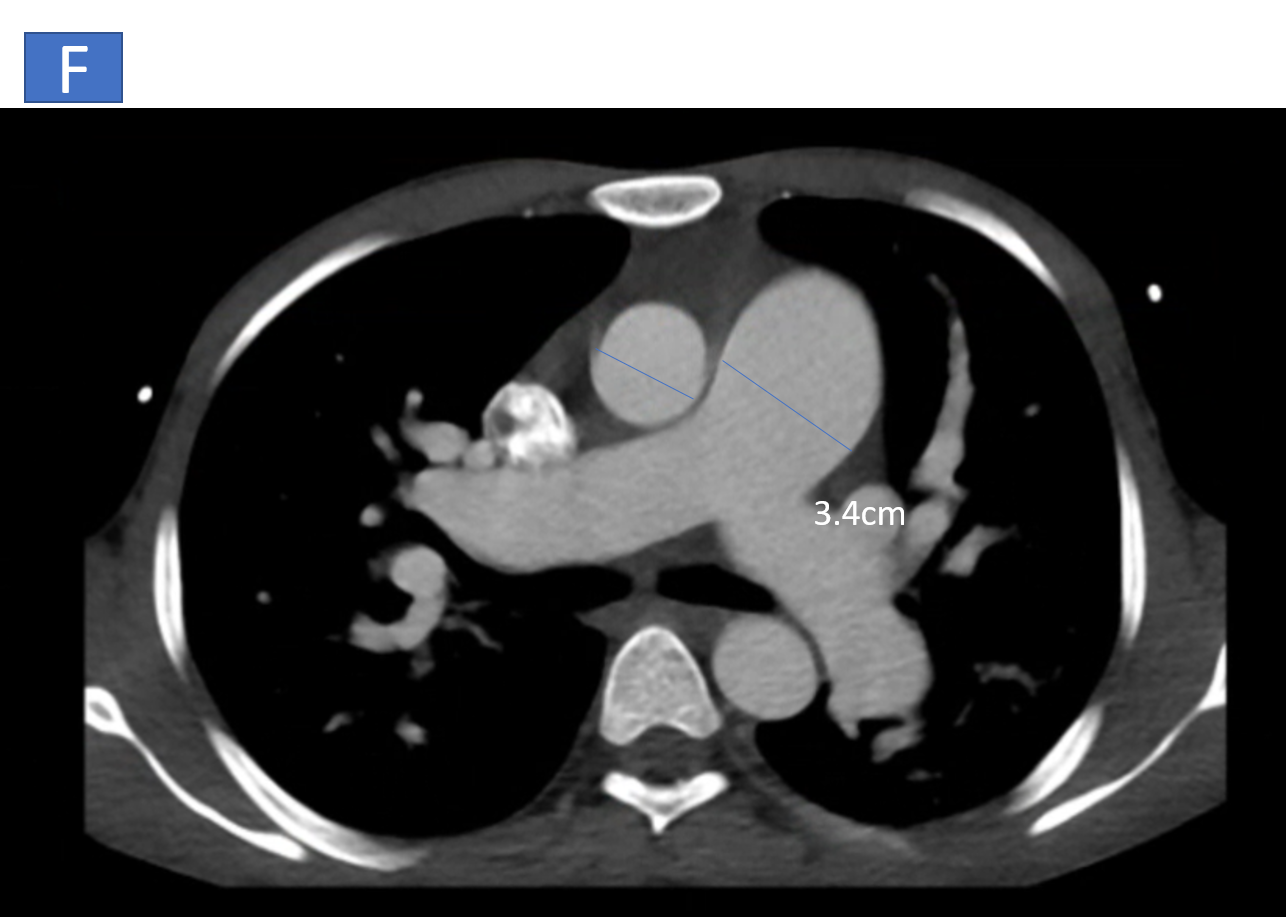
- F: Pulmonary arteries are confluent and dilated, MPA-34mm, right PA is 21 mm and left PA is 26mm.
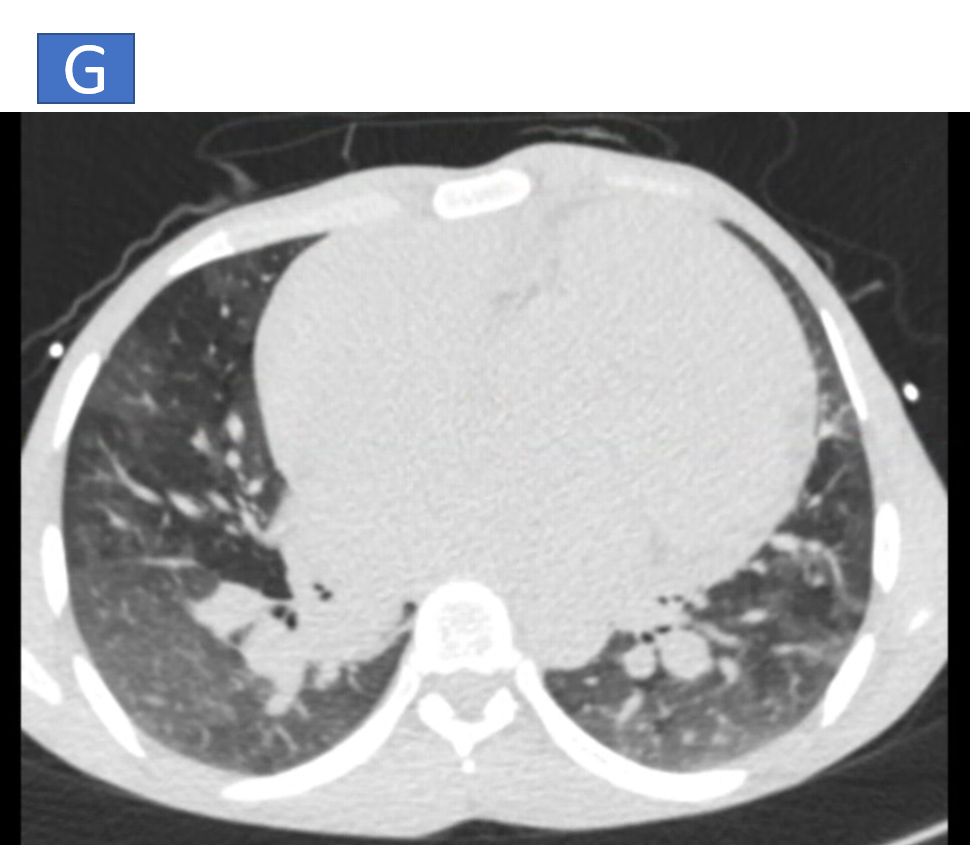
- G: Diffuse ground glass opacities noted in bilateral lungs with smooth interlobular septal thickening.
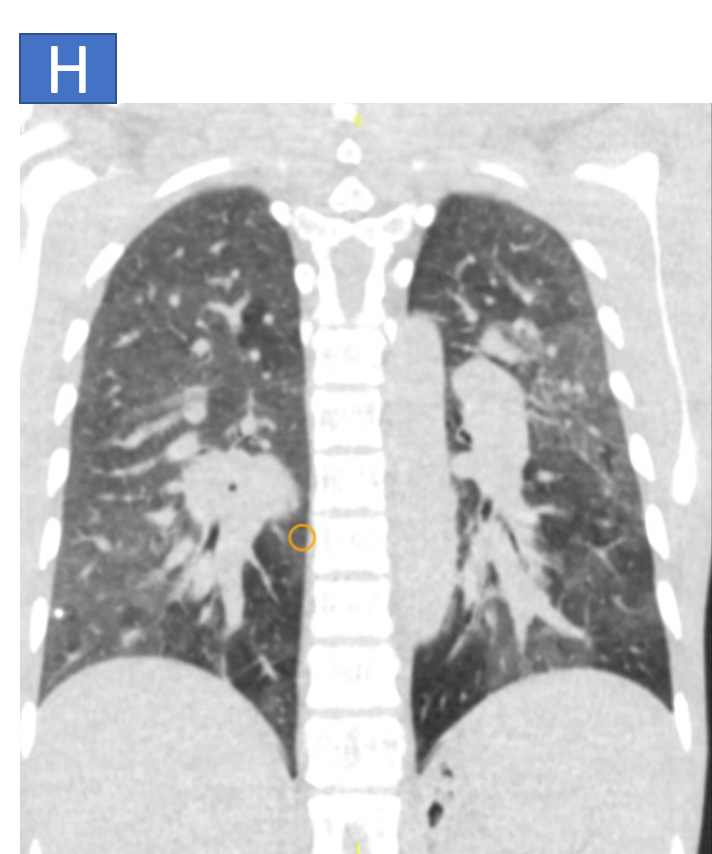
- H: Suggestive of pulmonary edema.
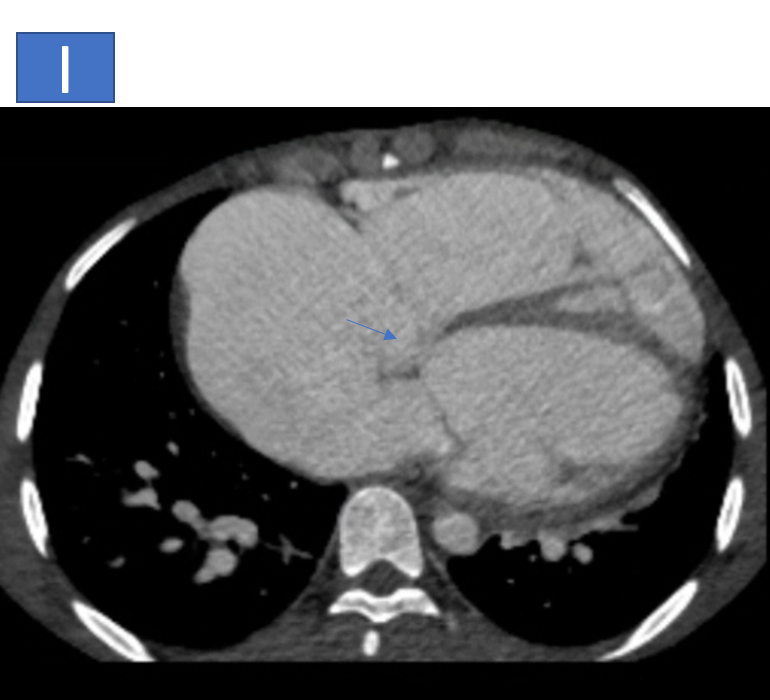
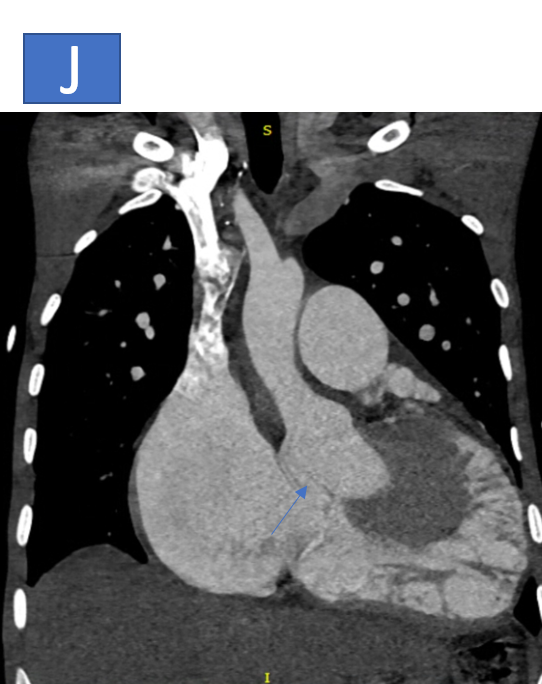
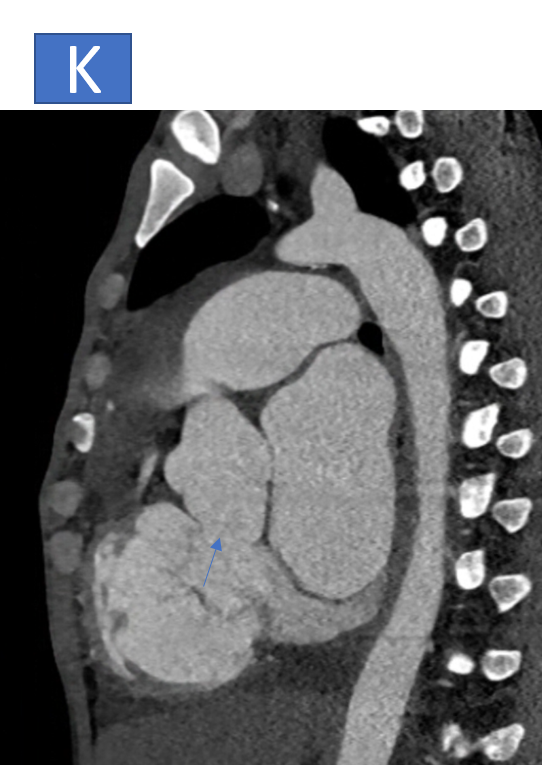
- I, J & K: The aortic root is prominent measuring ~3.8cm at the level of sinus of Valsalva, there is defect noted at the level of posterior coronary sinus with communication seen with the right atrium.
DIAGNOSIS:
- Large Ostium Secundum ASD with moderate biatrial dilatation.
- Dilated Pulmonary Artery (likely PAH), with measurements indicating increased pressure.
- Diffuse Ground Glass Opacities in bilateral lungs, with smooth interlobular septal thickening—likely due to pulmonary edema.
- Prominent Aortic Root (~3.8 cm at the sinus of Valsalva), with a defect at the posterior coronary sinus and communication with the right atrium, suggestive of a Ruptured Sinus of Valsalva.
- CADRADs 0.
DISCUSSION:
- A ruptured aneurysm of the aortic sinus is a major cardiovascular event that requires prompt diagnosis and intervention.
- The right sinus of Valsalva is the most common site for aneurysmal dilatation, followed by the non-coronary sinus.
After rupture, a fistulous tract forms—typically to the right ventricle in the former and to the right atrium in the latter. - A radiologist's comprehensive evaluation is essential for early recognition of these signs.
Etiology:
Congenital Causes (most common):
- Associated with connective tissue disorders, including Marfan syndrome, Loeys-Dietz syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
- Found in defects of the aortic media or a lack of elastic tissue.
Acquired Causes:
- Infective endocarditis, which weakens the sinus.
- Syphilitic aortitis, trauma, degenerative changes, or post-surgical/catheter complications.
Ruptured Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm:
- Caused by congenital defects or infection (endocarditis) leading to weakening of the aortic wall, or trauma.
Signs of Pulmonary Hypertension:
- Main Pulmonary Artery Dilation (>33 mm)
- Right Ventricular Enlargement/Hypertrophy
- Right ventricle diameter > left ventricle diameter.
- Bowing of the interventricular septum toward the left ventricle.
- Lung Parenchymal Changes:
- Scarring from prior pulmonary infarctions (e.g., wedge-shaped opacities, pleural thickening).
- Mosaic lung attenuation.
Main pulmonary artery dilation (> 33 mm)
- Ratio of main pulmonary artery diameter to ascending aorta diameter >1.1:1
Right ventricular signs:
- Enlargement and hypertrophy
- Ratio of right ventricle diameter to left ventricle diameter >1:1
- Bowing of the interventricular septum toward the left ventricle
Lung parenchymal signs:
Scars from prior pulmonary infarctions
- Bands, irregular peripheral linear opacities
- Wedge-shaped opacities with pleural thickening
Mosaic lung attenuation
Treatment and Management:
Surgical intervention is the traditional treatment for rupture of the Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm:
- Direct suture or patch closure depending on the rupture size.
- Percutaneous closure can be performed using devices like umbrella occluders or duct occluders.
Immediate treatment is critical to prevent further complications, such as heart failure or arrhythmias.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
- Aortic root or ascending aortic aneurysms
- Coronary arterio-venous fistulas
- Prolapsed aortic cusps
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Spontaneous coronary dissection
- Early atherosclerosis
- Rheumatic valvular heart disease
- Acute myocarditis
- Infective endocarditis
- Chagas disease
REFRENCES:
- Doost A, Craig JA, Soh SY. Acute rupture of a sinus of Valsalva aneurysm into the right atrium: a case report and a narrative review.
- Marfan Syndrome and other connective tissue disorders—Journal of Cardiovascular Genetics, 2022.
- Aneurysms of the Sinus of Valsalva—European Journal of Cardiology, 2023.
- Pulmonary Hypertension and its Diagnosis—American Journal of Respiratory Medicine, 2021.
Dr. A Faizel
Consultant Radiologist
Manipal Hospital, Varthur road, Bengaluru.
Dr. Pooja Sethi
Junior Resident
Manipal Hospital, Varthur road, Bengaluru.