6yrs male child with head ache and visual disturbance
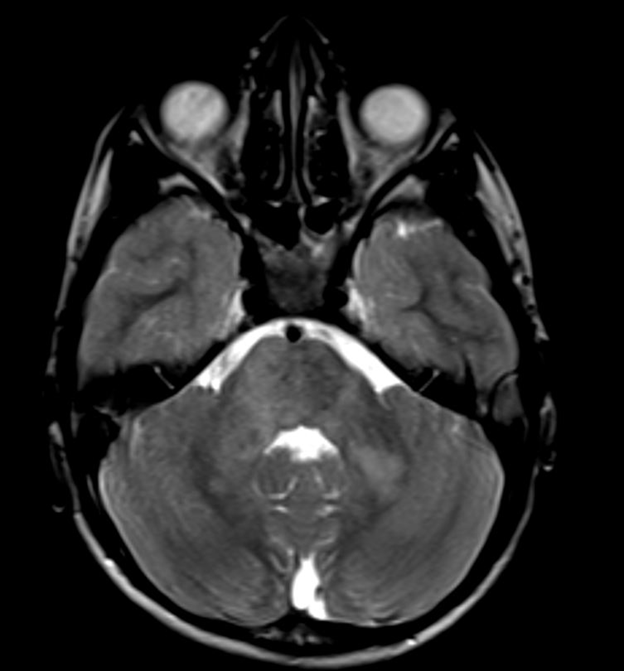
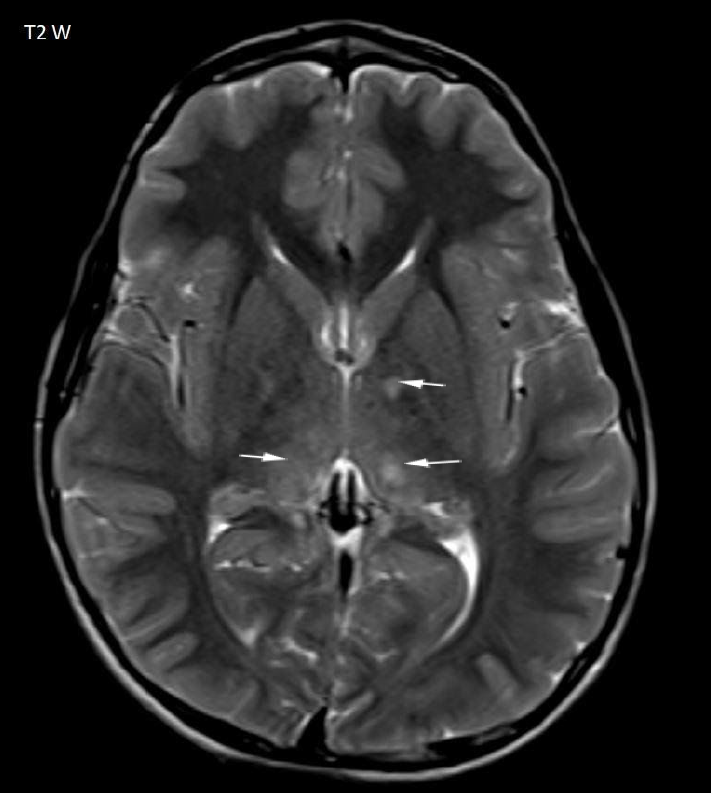
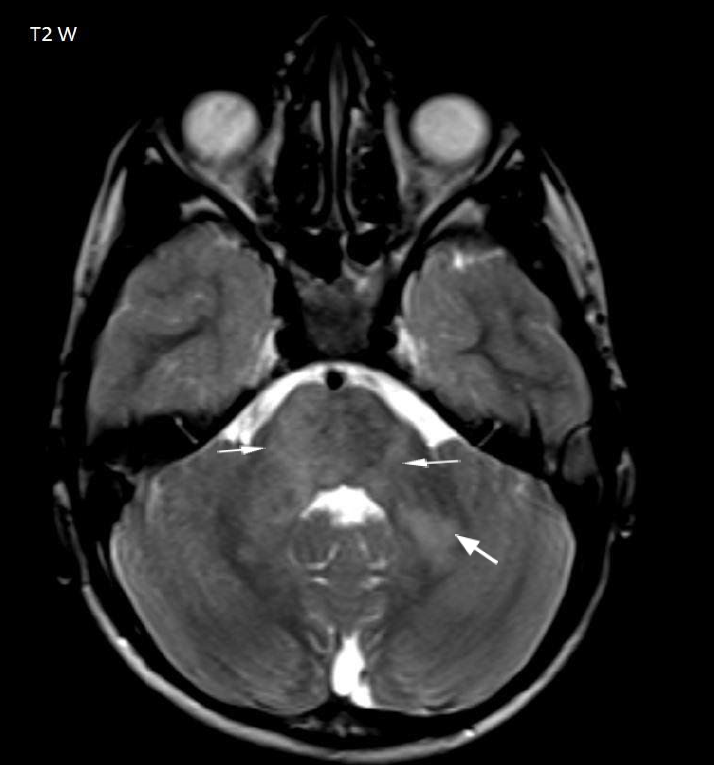
- Multiple T2 hyperintense foci in the left basal ganglia, bilateral thalami, midbrain, pons and bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles (arrows Fig 1-3)
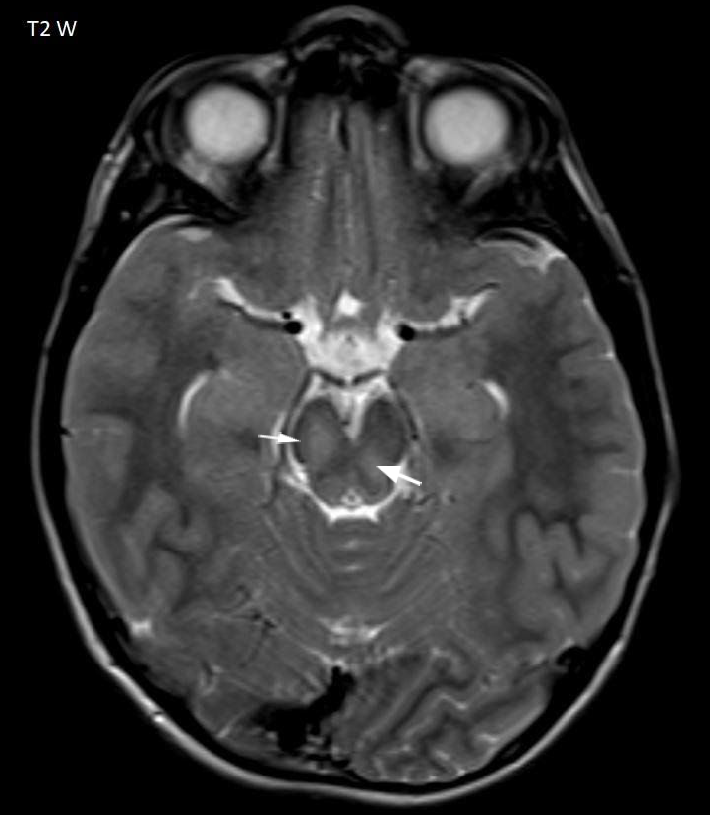
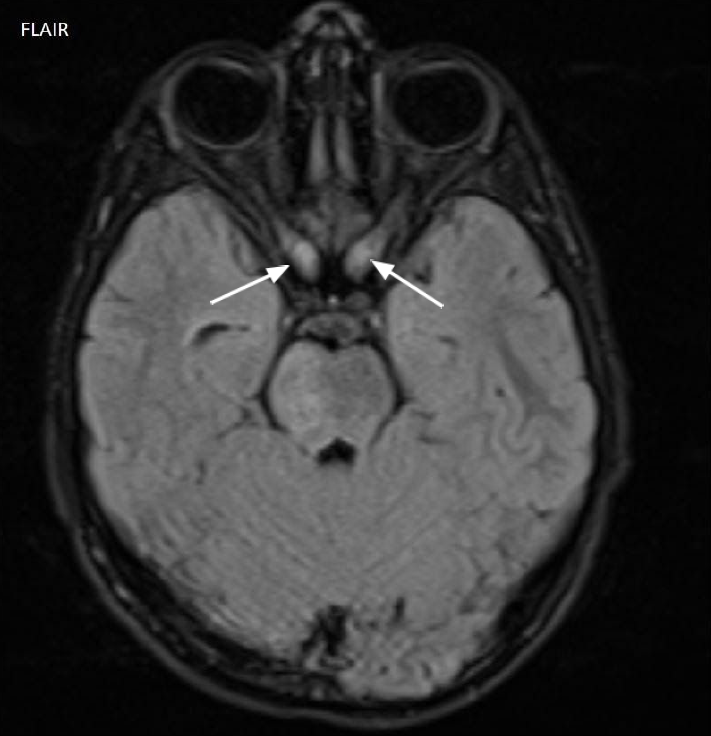
- There is a globular thickening of intracanalicular and intracranial segment of bilateral optic nerves (arrow Fig 4)
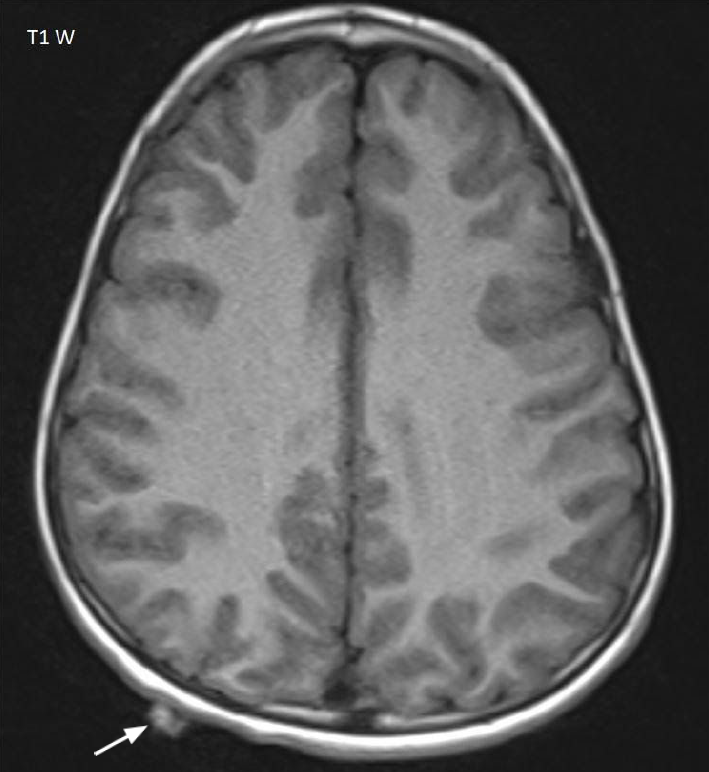
- Focal subgaleal nodule in the right parietal region (arrow Fig 5)
Diagnosis:
Neurofibromatosis type 1
Discussion:
- Multifocal T2 hyperintense foci represent zones of myelin vacuolization suggesting focal abnormal signal intensity (FASI) also called unidentified bright objects (UBO)
- Globular thickening of bilateral optic nerves represent the optic pathway gliomas
- Focal subgaleal nodule represent the neurofibroma
The presence of bilateral optic pathway gliomas and zones of myelin vacuolization is diagnostic of NF1
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as von Recklinghausen disease, is a multisystem neurocutaneous disorder, the most common phakomatosis
It is caused by mutation of NF1 gene on chromosome 17q11.2.
CNS manifestations include
- Dermal neurofibromas, Plexiform neurofibroma, Sphenoid wing dysplasia and Dural ectasia in the region of Scalp/Skull, Meninges, and Orbit
- Hyperintense T2/FLAIR WM foci which zone of myelin vacuolization
- Gliomas in brain – pilocytic astrocytoma , optic pathway glioma, low grade fibrillary astrocytoma, anaplastic and glioblastoma multiformae
- Progressive ICA stenosis causing moyamoya syndrome
References
- Neurofibromatosis: Types 1 and 2: S. Borofsky and L.M. Levy: American Journal of Neuroradiology December 2013, 34 (12) 2250-2251;
- Neuroimaging Manifestations of NF1 — A Pictorial Review- William T. O’Brien et al J Am Osteopath Coll Radiol 2015; Vol. 4, Issue 2
Dr. G. Chennakesava, MD
Cross-sectional imaging fellow
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group