60 year old male with c/o dyspnea, cough, sinusitis
- 60 year old male with c/o dyspnea, cough, sinusitis.
- No h/o fever.
- H/o bronchial asthma.
- On examination, Bilateral coarse crepts and wheeze noted.
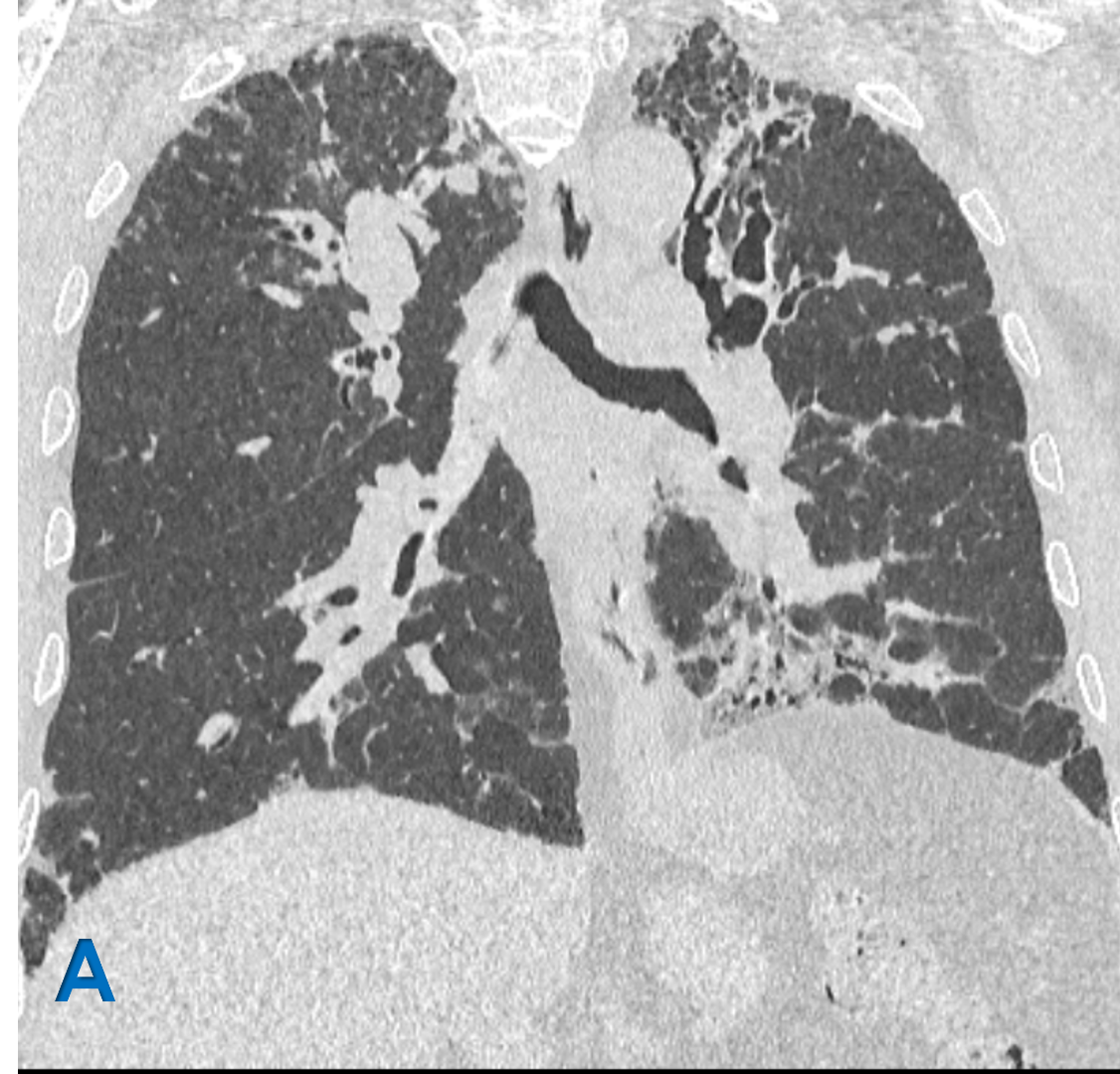
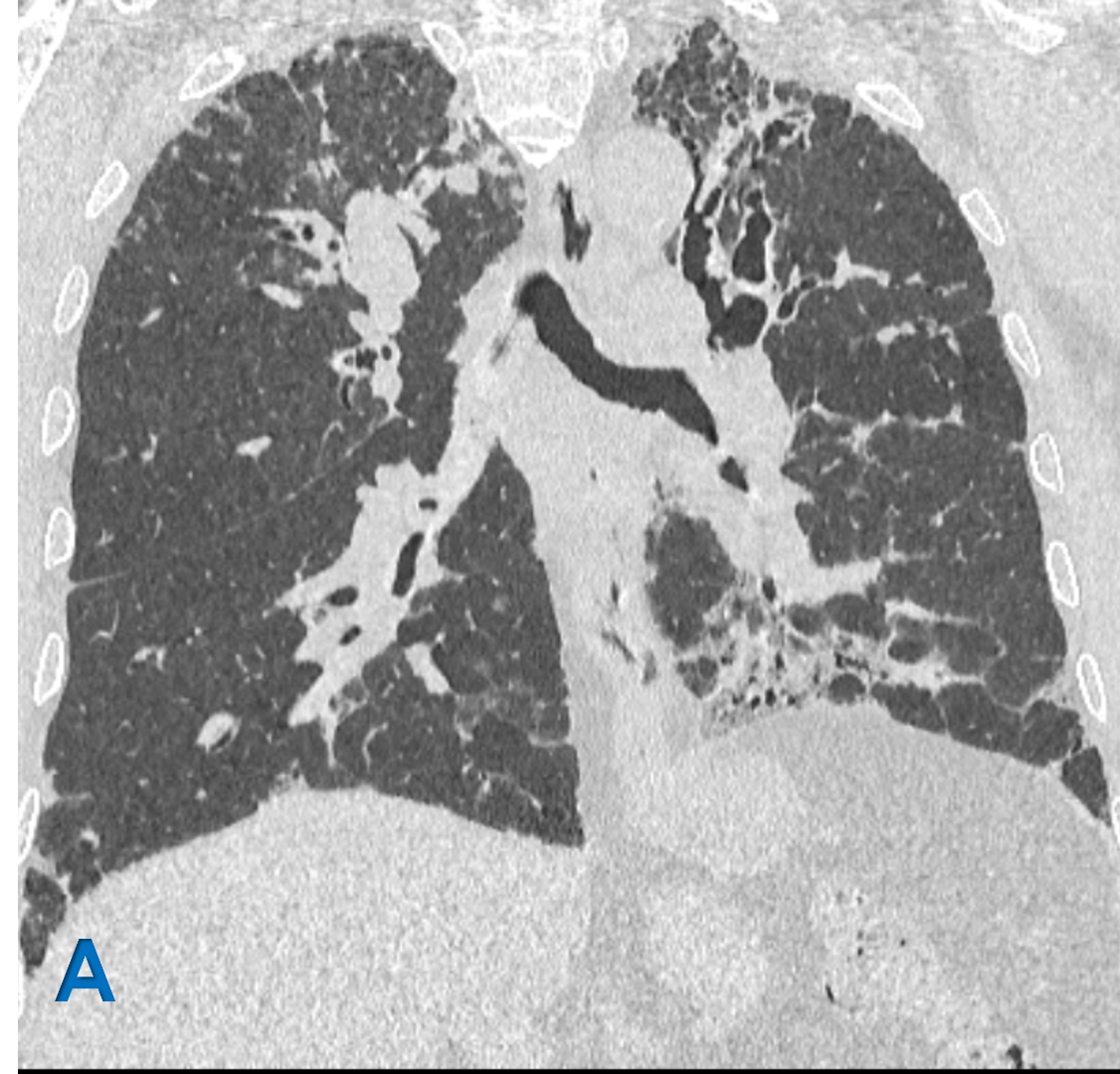
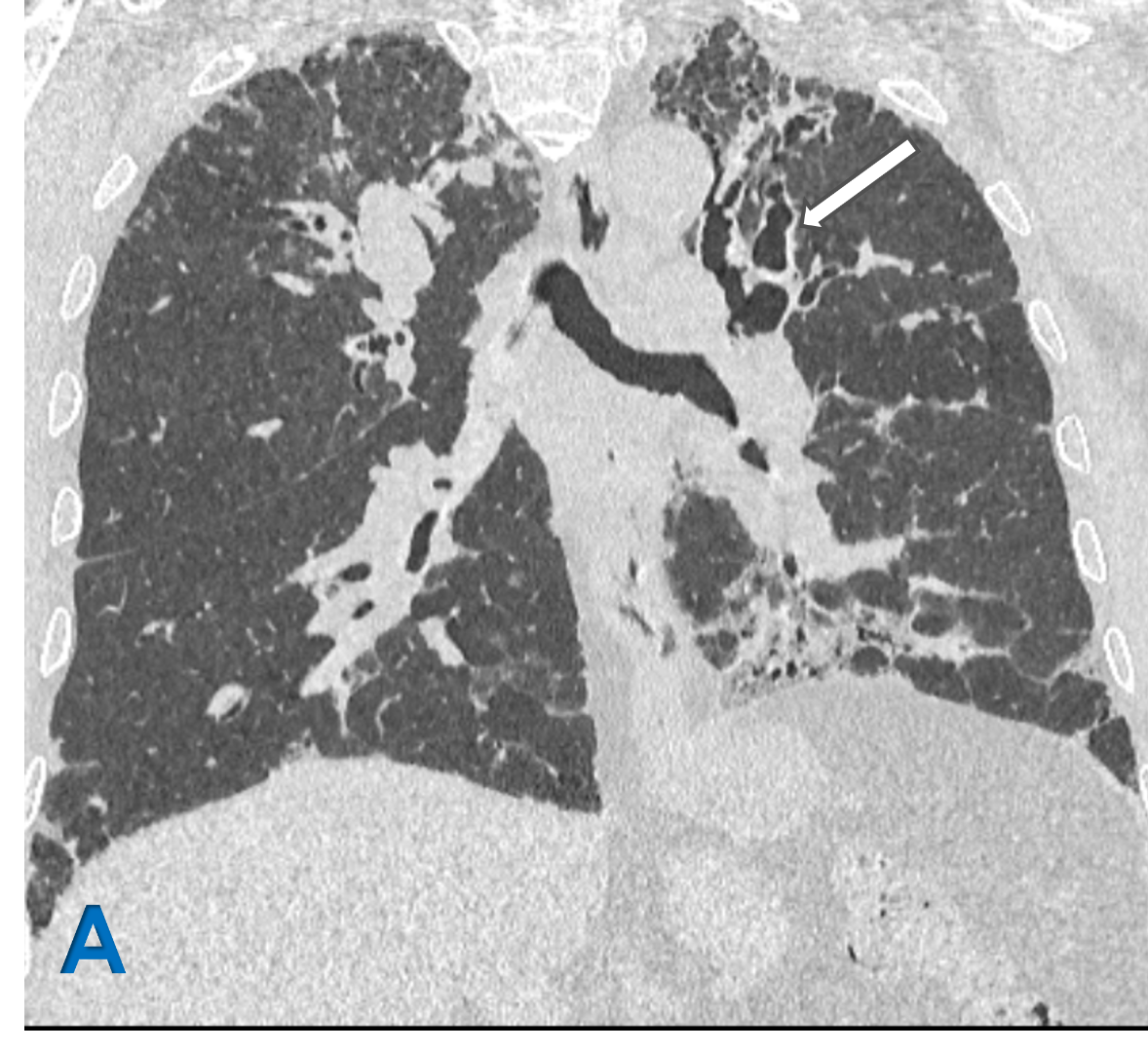
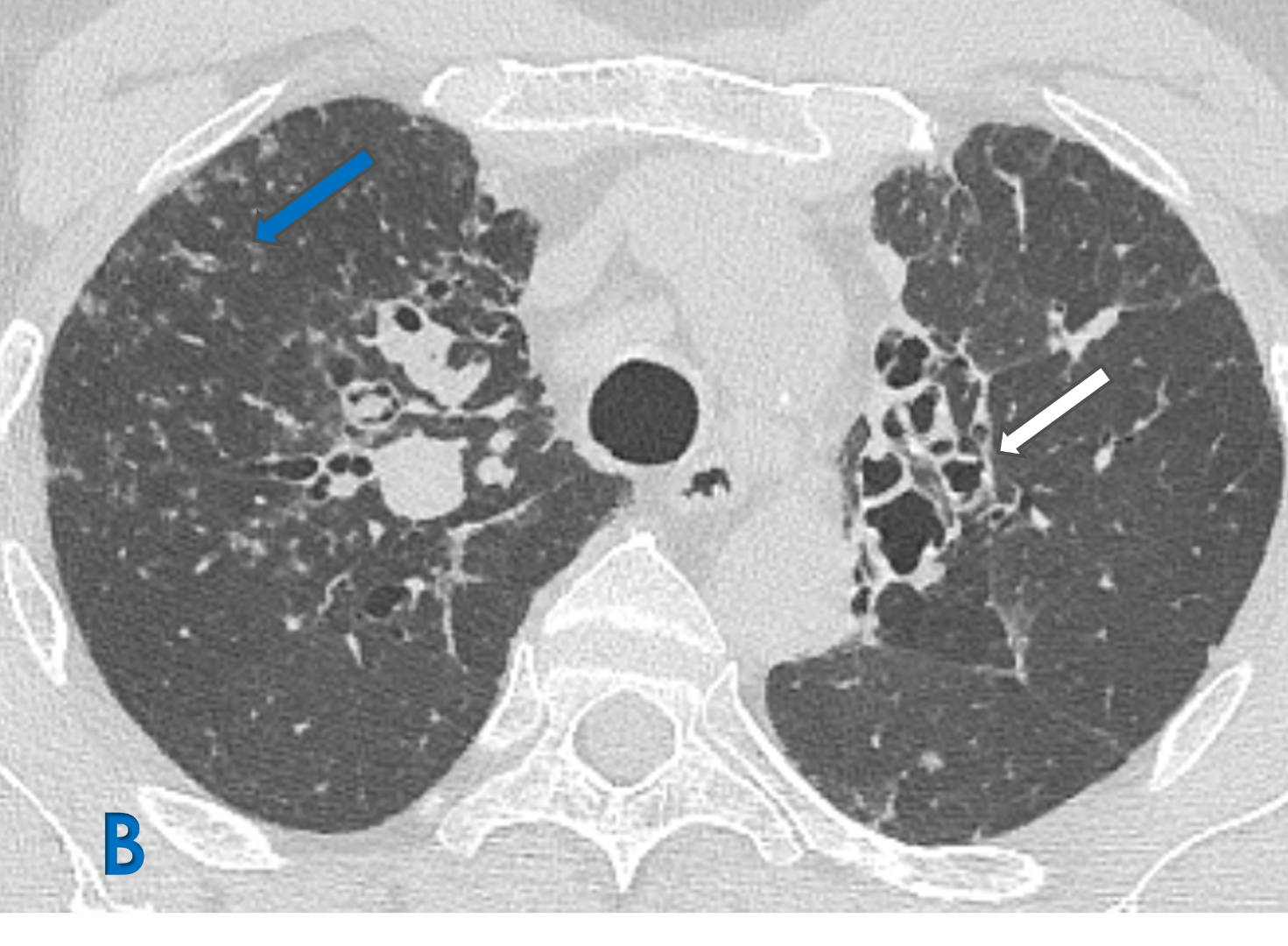
A: Coronal lung window ; B Axial lung window
- White arrow: Upper lobe central bronchiectasis with bronchial wall thickening.
- Blue arrow: Scattered ground glass density centrilobular tree in bud nodules representing Active endobronchial infection.
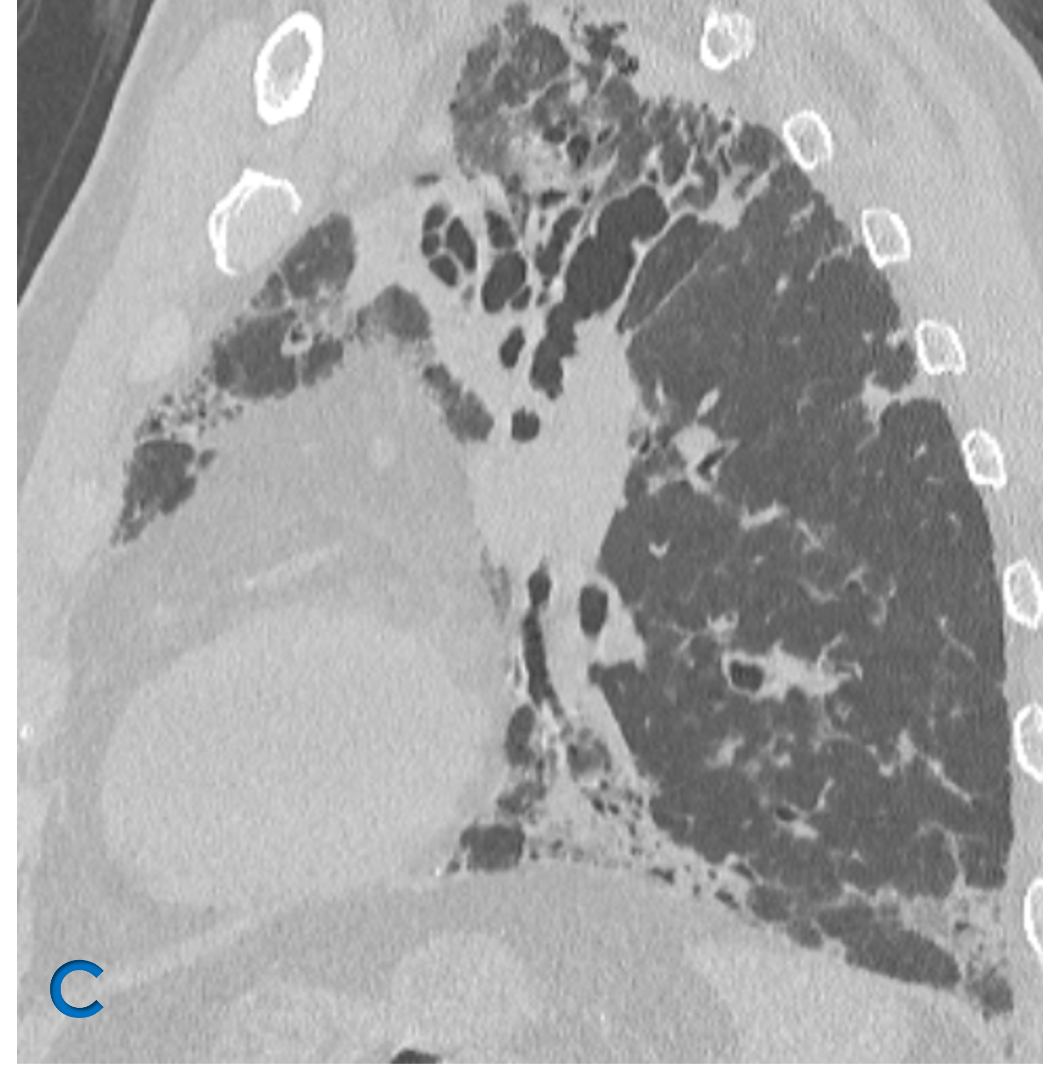
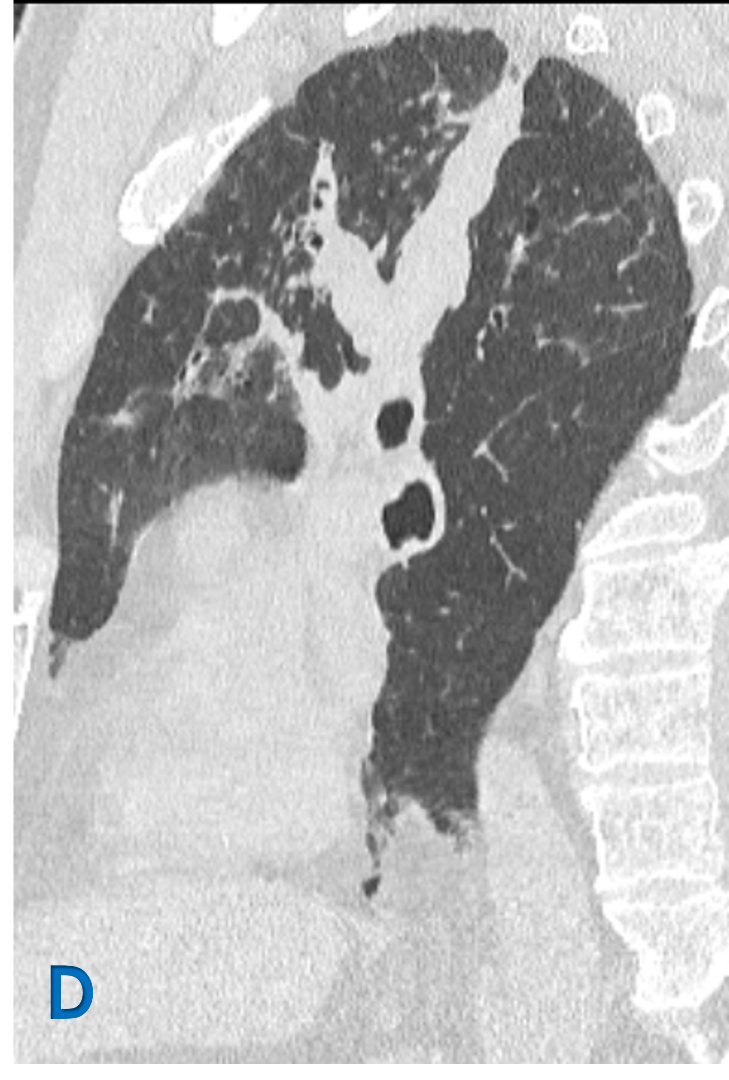
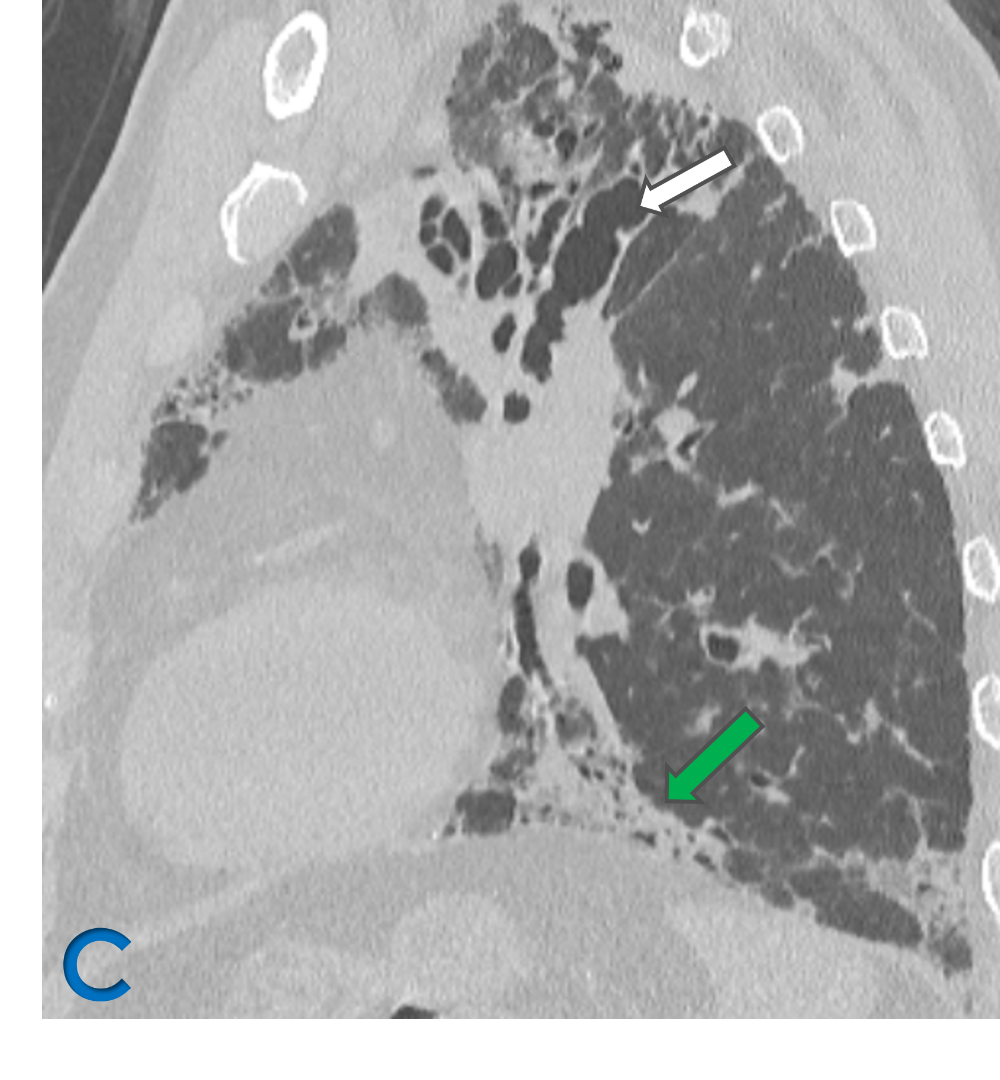
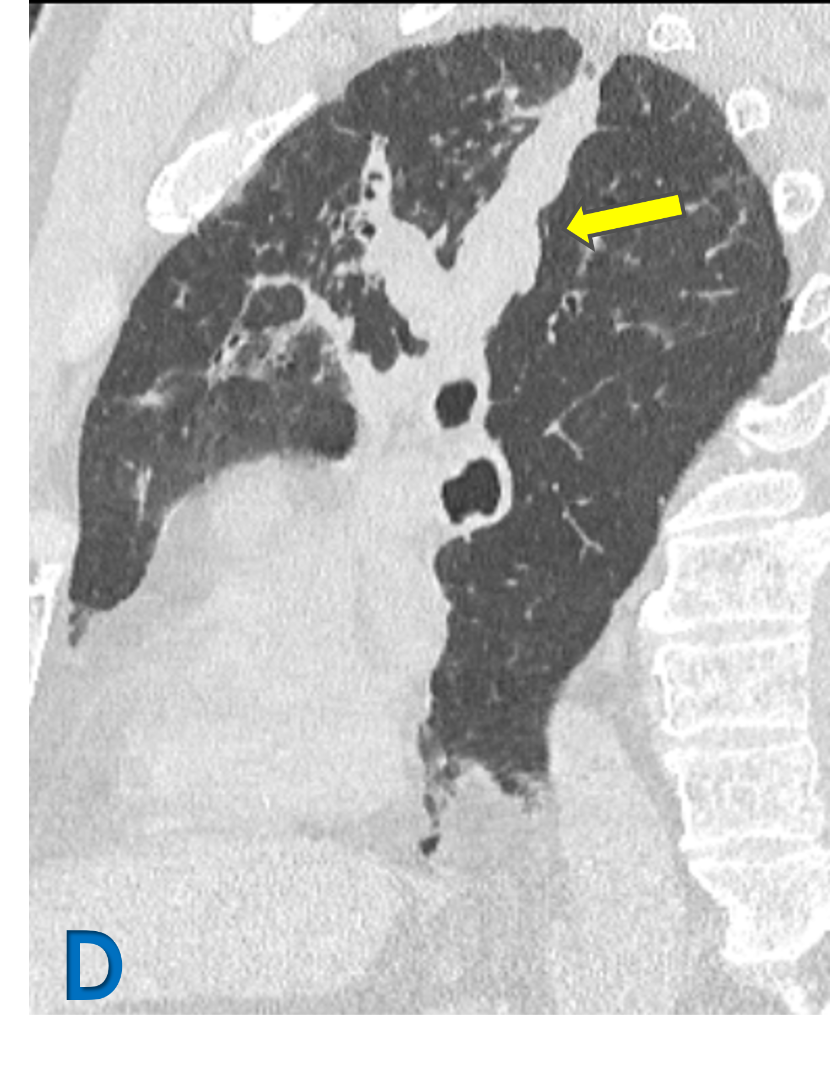
C: Sagittal lung window ; D: Oblique reformat lung window
- White arrow: Upper lobe bronchiectasis (varicoid)with bronchial wall thickening.
- yellow arrow: Mucous impaction in dilated bronchi – Bronchoceles – Finger in glove.
- Green arrow: Fibroatelectatic changes in subpleural region with micro cystic changes
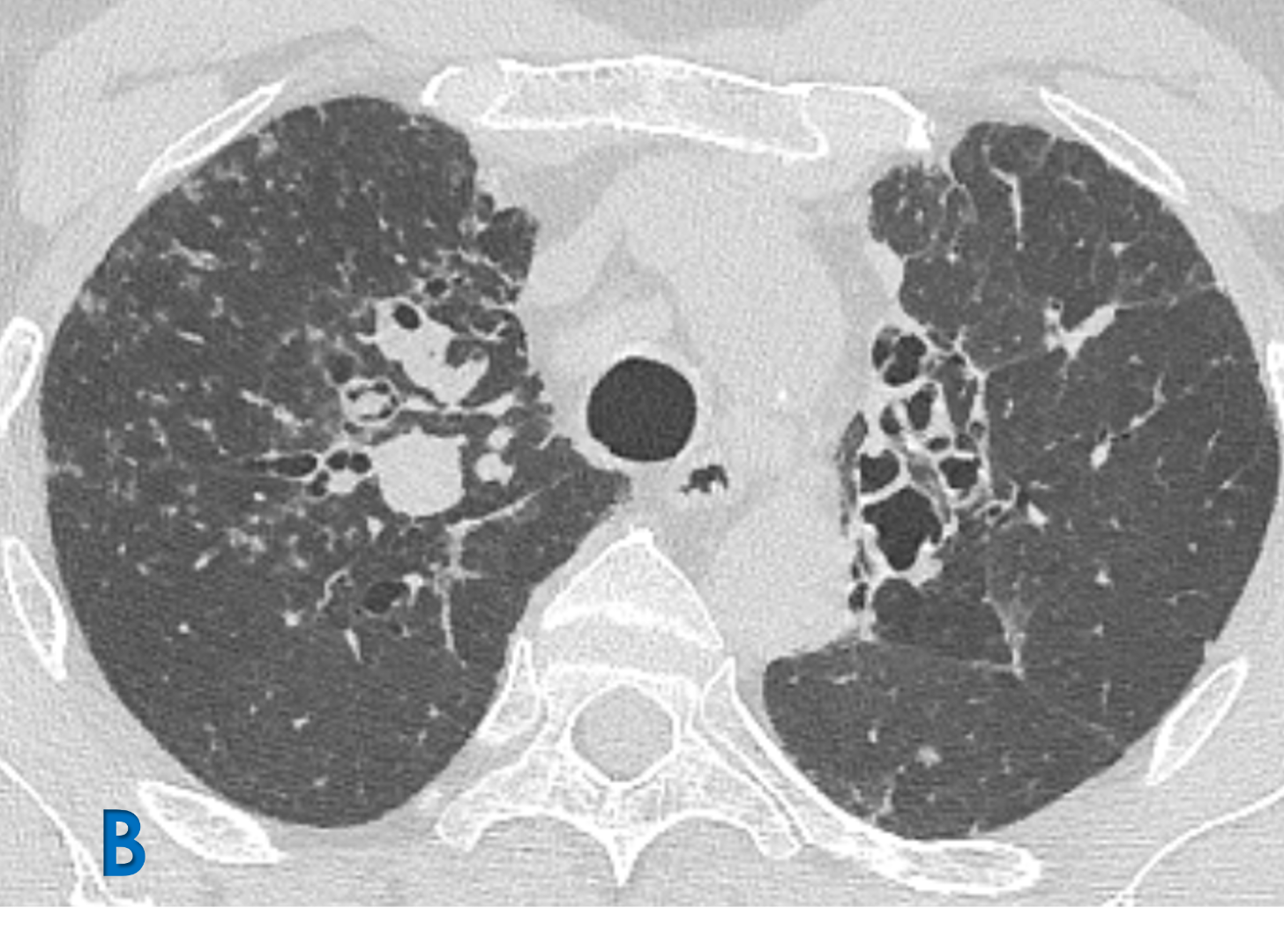
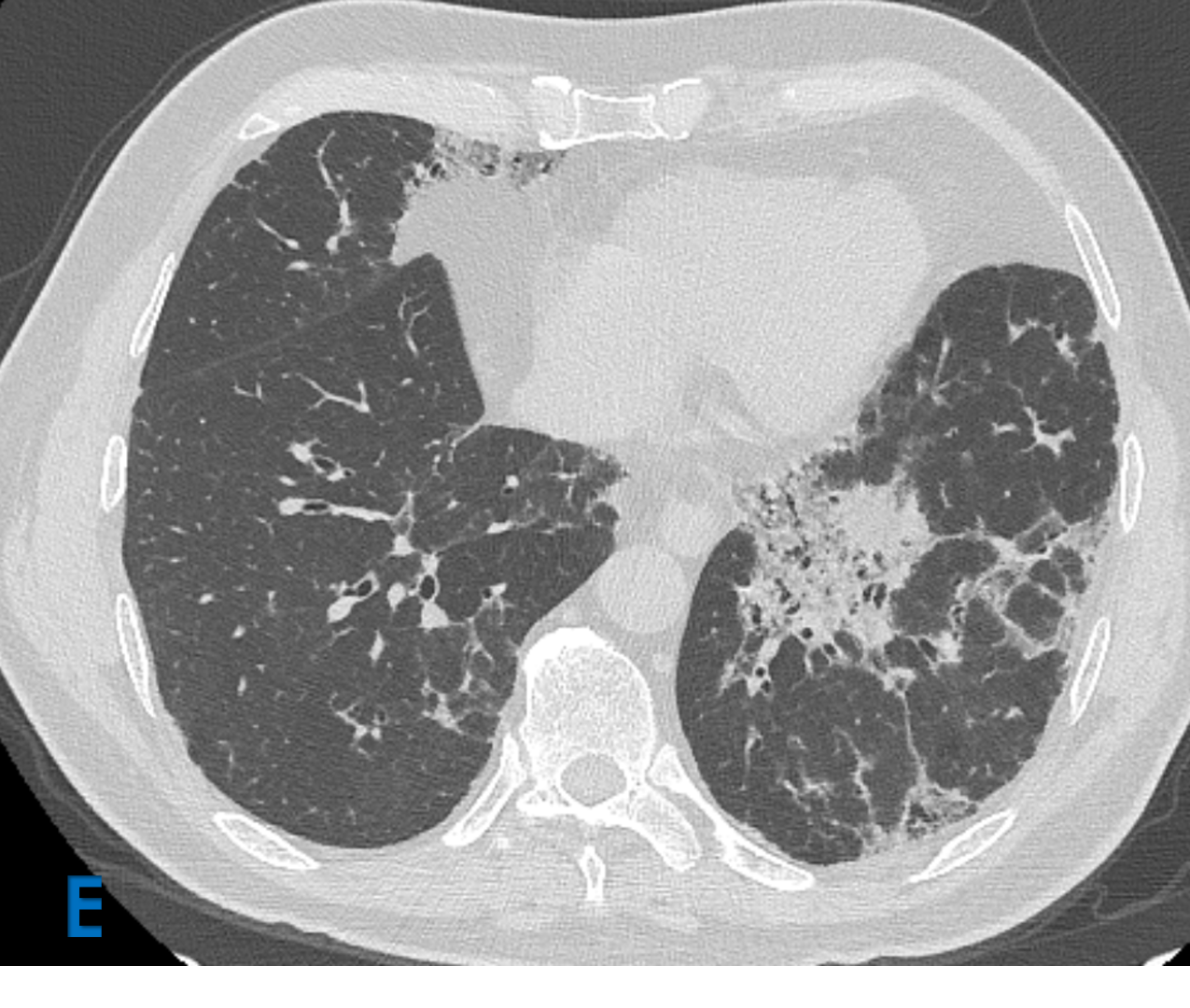
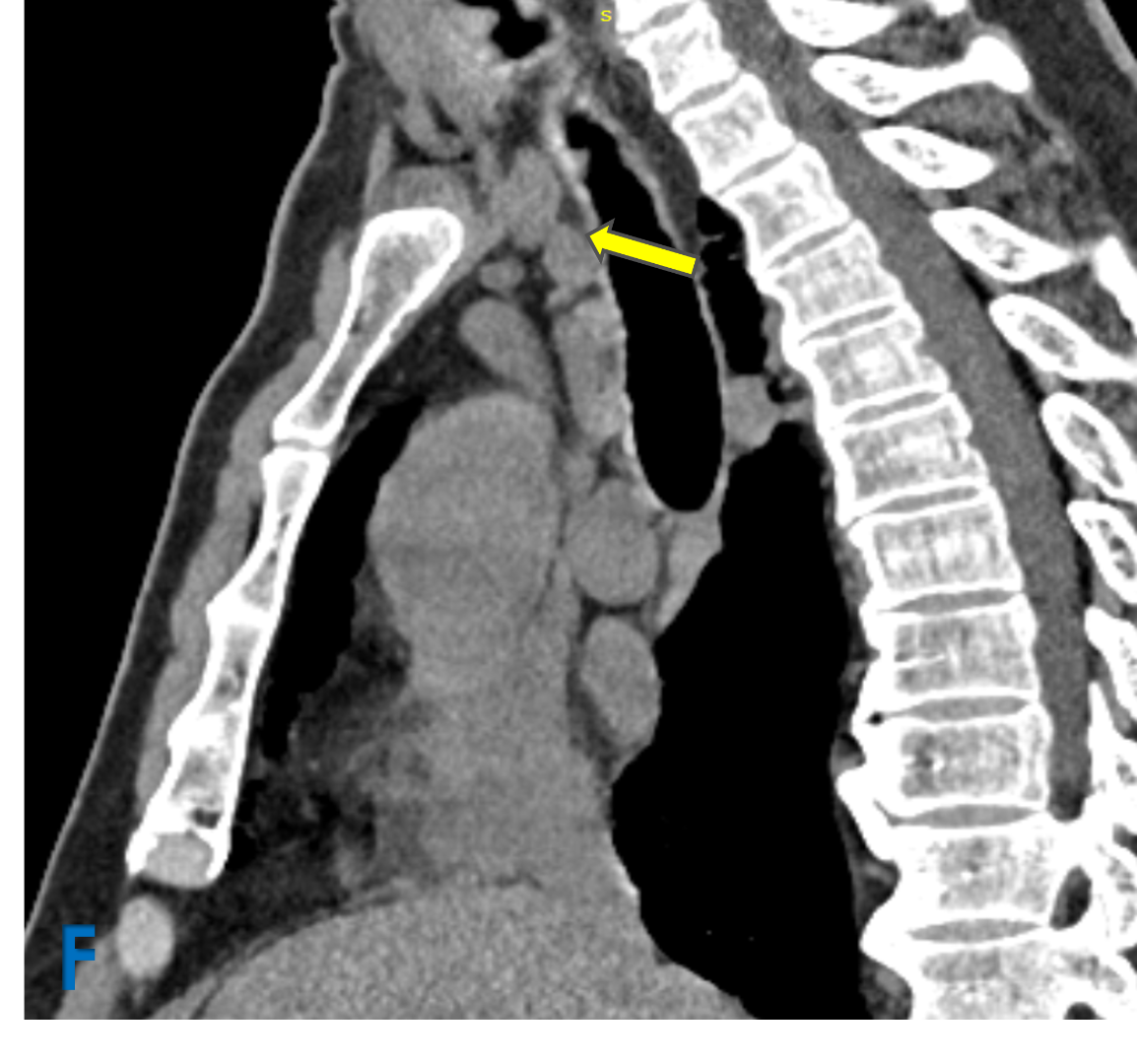
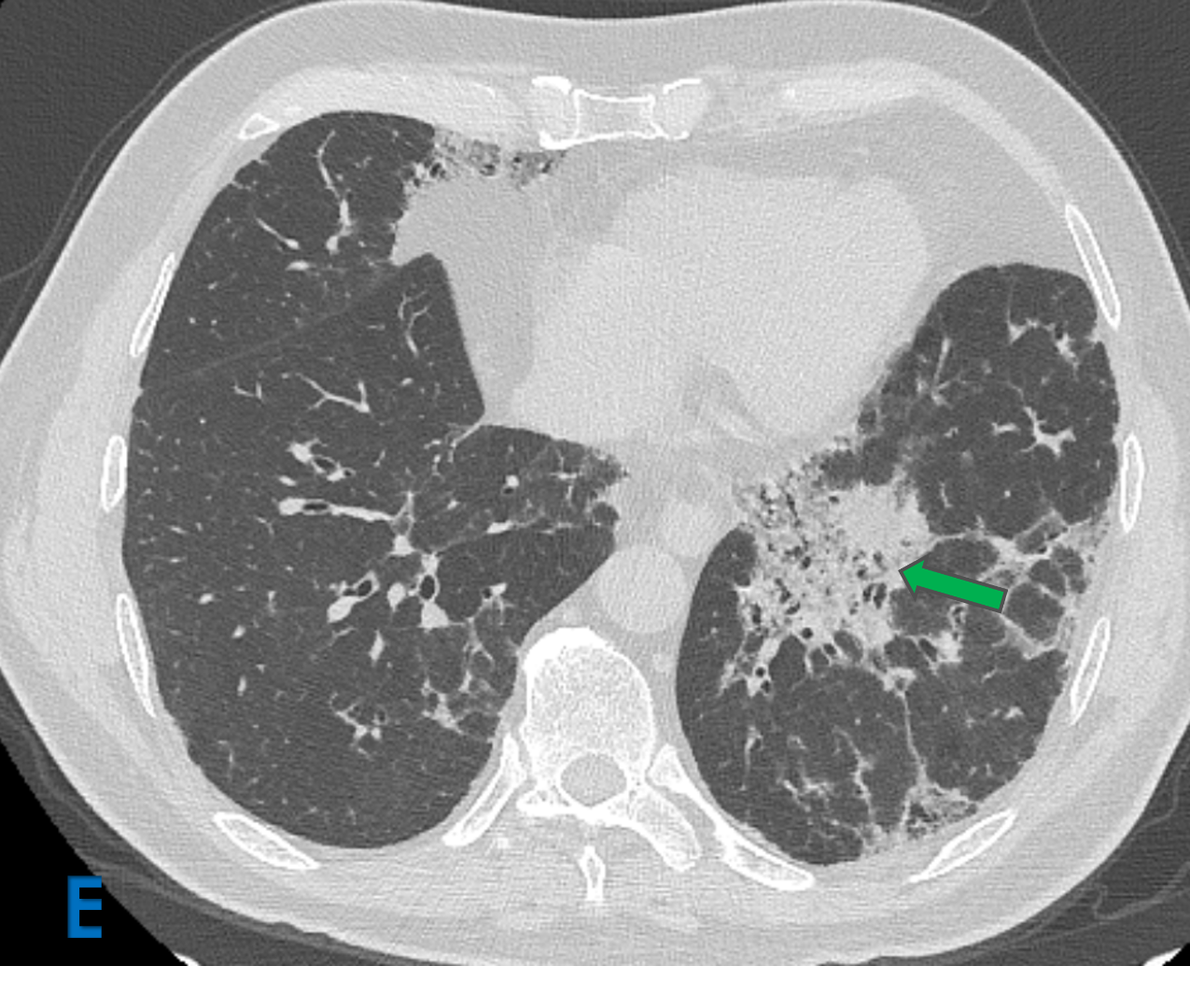
E: Axial lung window ; F: Sagittal mediastinal window
- Yellow arrow: Mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
- Green arrow: Fibroatelectatic changes in subpleural region with micro cystic changes
DIAGNOSIS: ABPA – chronic pleuropulmonary fibrosis
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Common fungal infection in uncontrolled asthmatics, cystic fibrosis patients, and immunocompromised patients.
- Fungal infection of the lung due to a hypersensitivity reaction to antigens of Aspergillus fumigatus after colonization into the airways.
- Predominantly it affects patients with bronchial asthma and those having cystic fibrosis.
- characteristically presents with bronchospasm, pulmonary infiltrates, eosinophilia, and immunologic evidence of allergy to the antigens of Aspergillus species
Radiographic features
- Fleeting pulmonary alveolar opacities: common
- Centrilobular nodules representing dilated and opacified bronchioles
- Bronchiectasis
- central, upper lobe saccular bronchiectasis involving segmental and subsegmental bronchi is characteristic
- mucoid impaction results in a bronchocoele; finger in glove sign
- this may give a Y, V or toothpaste-like configuration
- Centrilobular nodular opacities.
- High attenuation mucus +/- (calcification) in impacted mucus in ~30%
- Bronchial wall thickening: common
- Chronic disease may progress to pulmonary fibrosis, predominantly in the upper lobe
- Cavitation
ABPA – Radiological classification
- Serological ABPA - stage of the disease with normal HRCT chest.
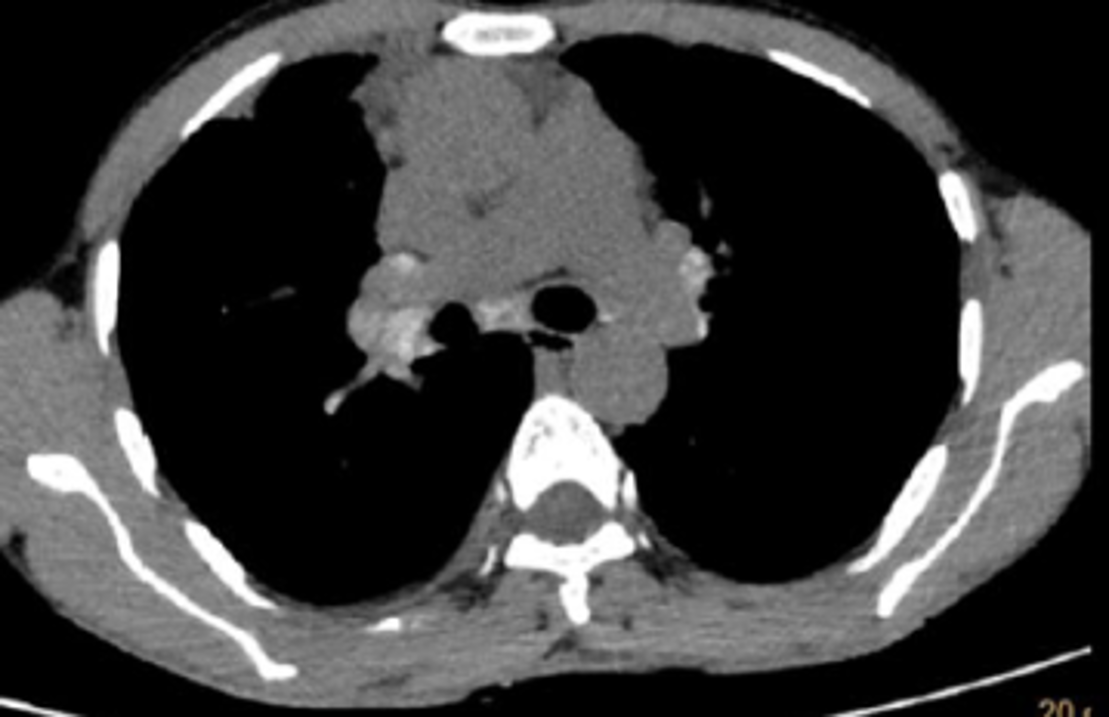
ABPA-High attenuation mucus (HAM)
- All diagnostic features of ABPA with presence of high attenuation mucus
- Aattenuation values greater than the soft tissues (para-spinal muscles) and close to that of calcification is seen in about 20-30% of patients with ABPA.
- high attenuation of the mucus is attributed to the fungal mineral components precipitated within the mucus.
- Presence of HAM represents immunological severity and also indicates higher chances of relapse.
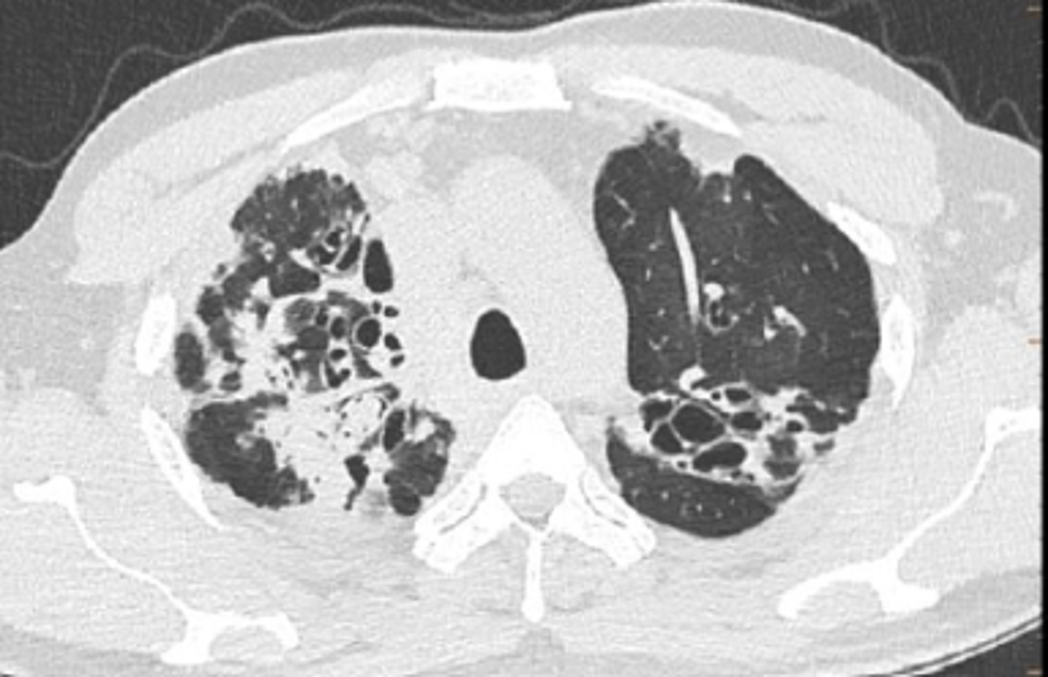
ABPA - Chronic pleuropulmonary fibrosis stage
- Should atleast have two other findings apart from bronchiectasis and HAM:-
- pulmonary fibrosis.
- fibrocavitory lesions
- mycetoma
- thickened pleura
- Chronic stages of the disease may present with atelectasis/collapse of lung, consolidation, fibrocalcific changes, calcific mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy, fibrotic bands, cavities and cicatrical emphysema.
- Maybe difficult to distinguish from chronic pulmonary tb.
References
- Oguma T, Taniguchi M, Shimoda T, Kamei K, Matsuse H, Hebisawa A, Takayanagi N, Konno S, Fukunaga K, Harada K, Tanaka J, Tomomatsu K, Asano K. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in Japan: A nationwide survey. Allergol Int. 2018 Jan;67(1):79-84. [PubMed
- Sehgal IS, Choudhary H, Dhooria S, Aggarwal AN, Bansal S, Garg M, Behera D, Chakrabarti A, Agarwal R. Prevalence of sensitization to Aspergillus flavus in patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Med Mycol. 2019 Apr 01;57(3):270-276. [PubMed]
- Silva CIS, Colby TV, Müller NL. Asthma and associated conditions: high-resolution CT and pathologic findings. Am J Roentgenol 183 (2004): 817-824.
- Agarwal R. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: Lessons for the busy radiologist. World J Radiol 3 (2011): 178.
- Shah A, Panjabi C. Allergic aspergillosis of the respiratory tract. Eur Respir Rev 23 (2014): 8-29.
Dr Deepti H.V.
MBBS, DMRD, DNB , EDiR , Fellowship (Fetal Medicine)
Senior Consultant Radiologist-Level 1 - Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group
Dr K Vishnu Vardhan Reddy
Mbbs, M.D.
Cross section imaging fellow - MHRG