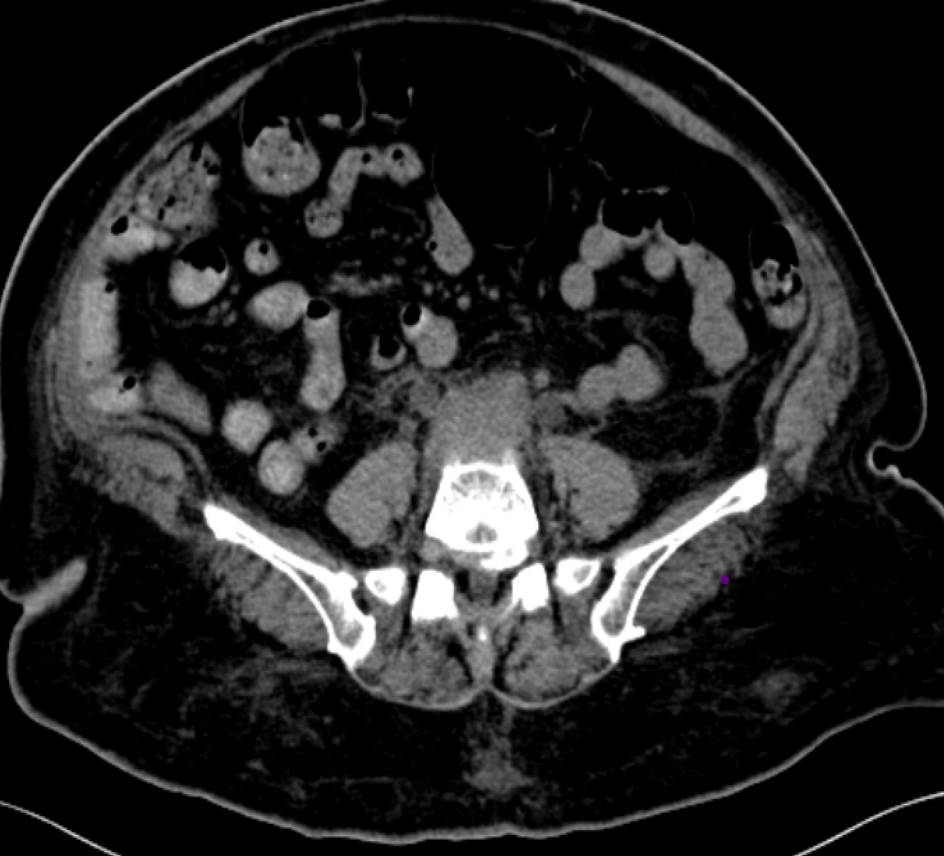
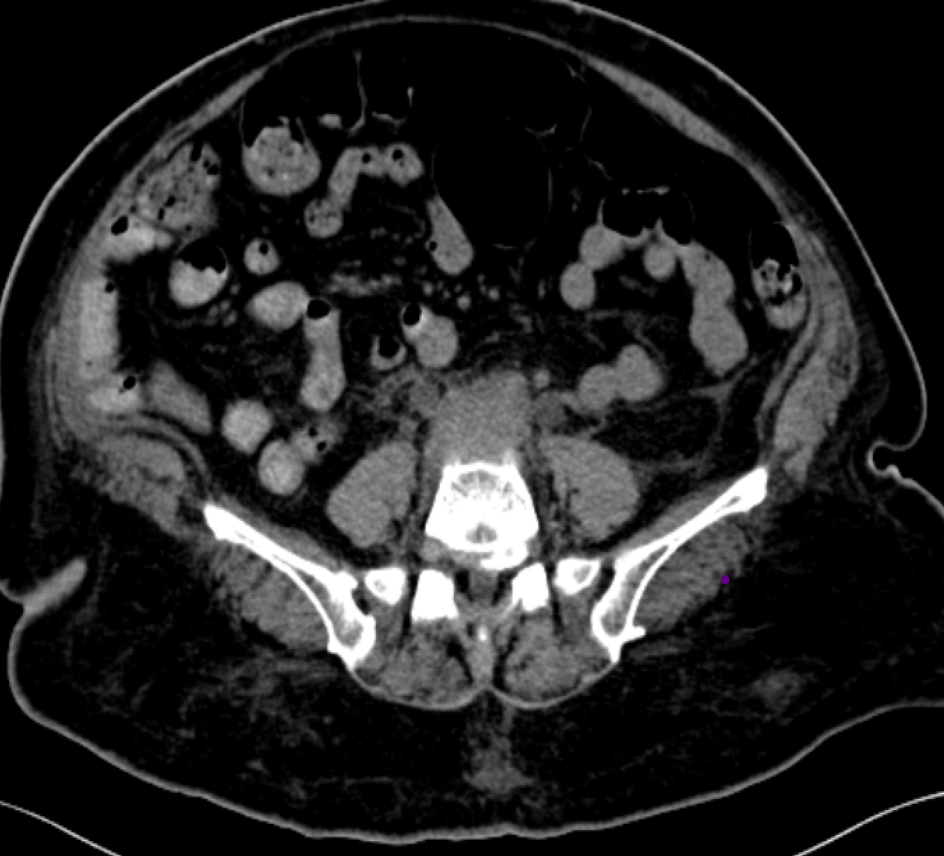
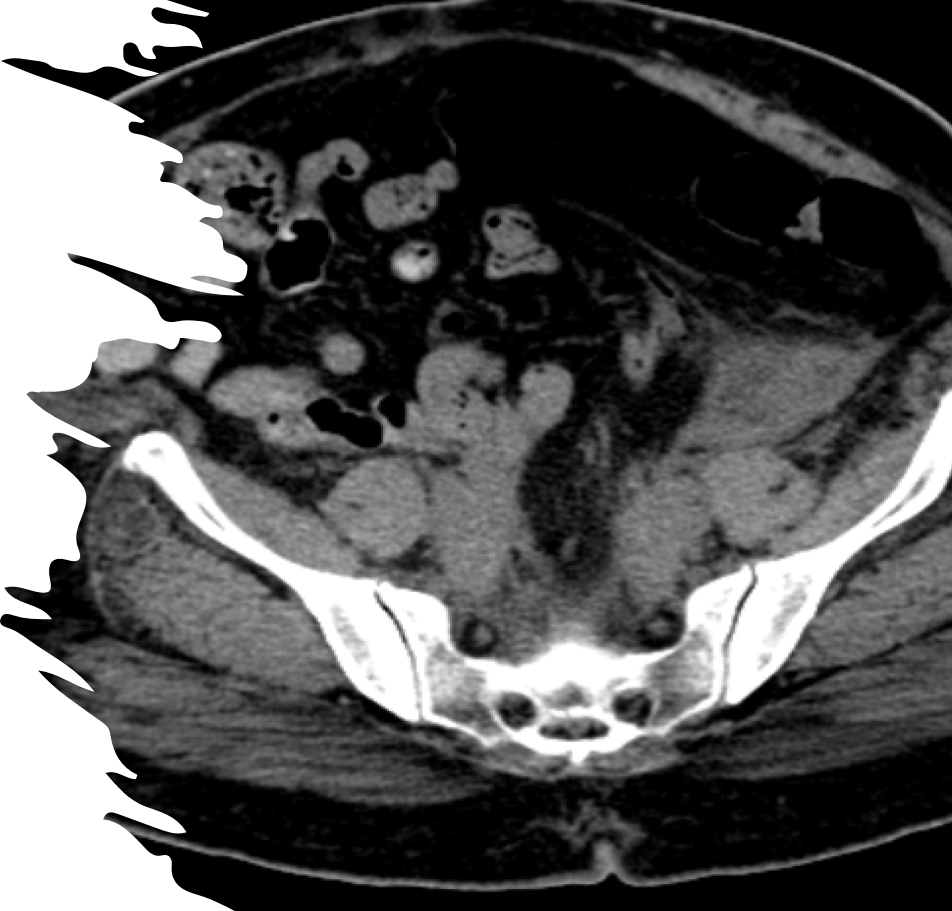
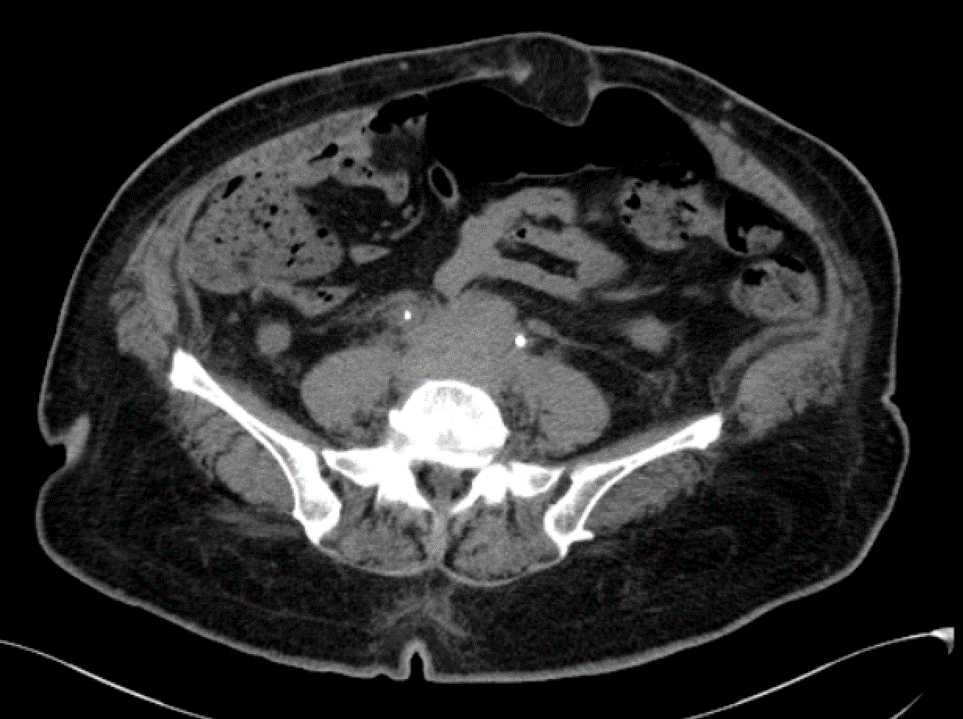
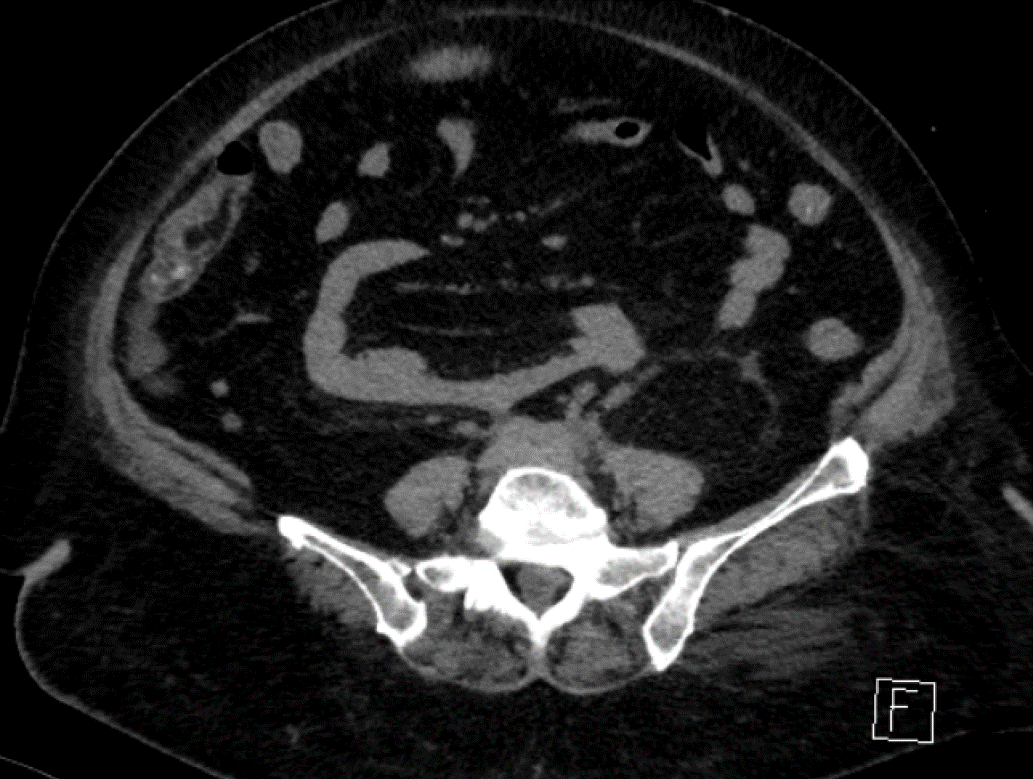
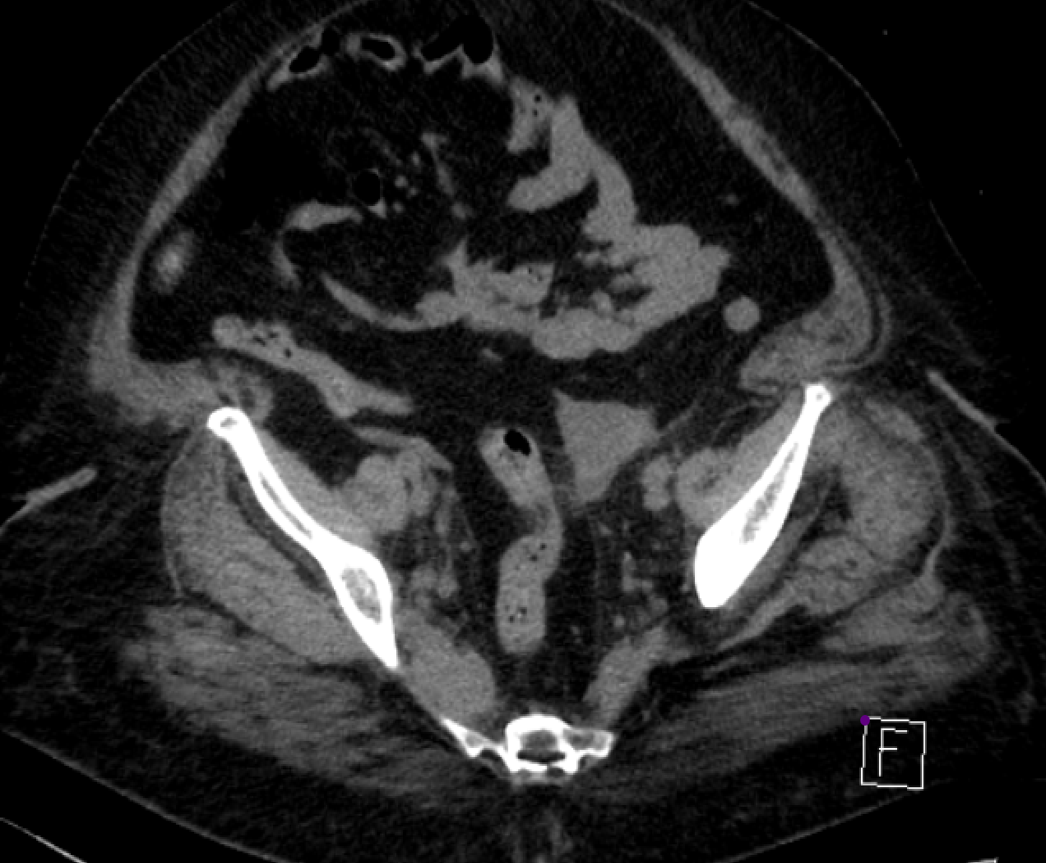
54 year old female came with complaints of urine obstruction
FINDINGS
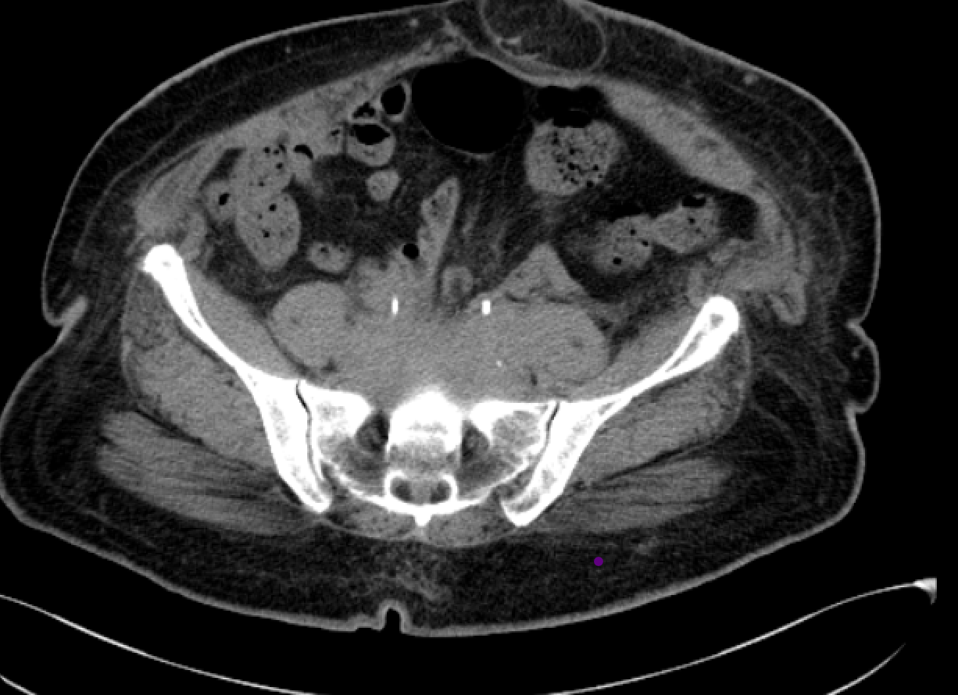
- A ( 3/ 9/ 2018) : CT shows soft tissue density mass lesion noted in the retroperitoneum extending along the iliac vessels encasing and compressing the bilateral distal ureters
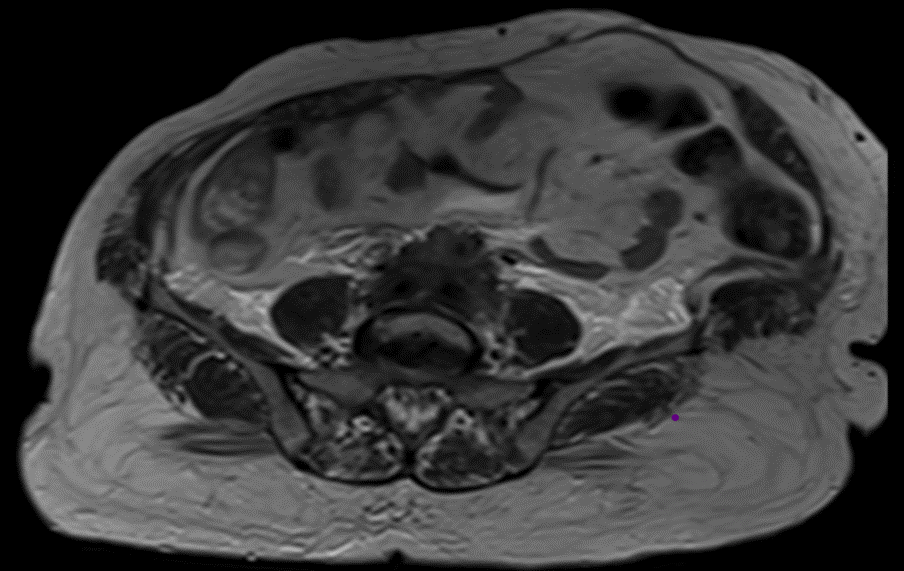
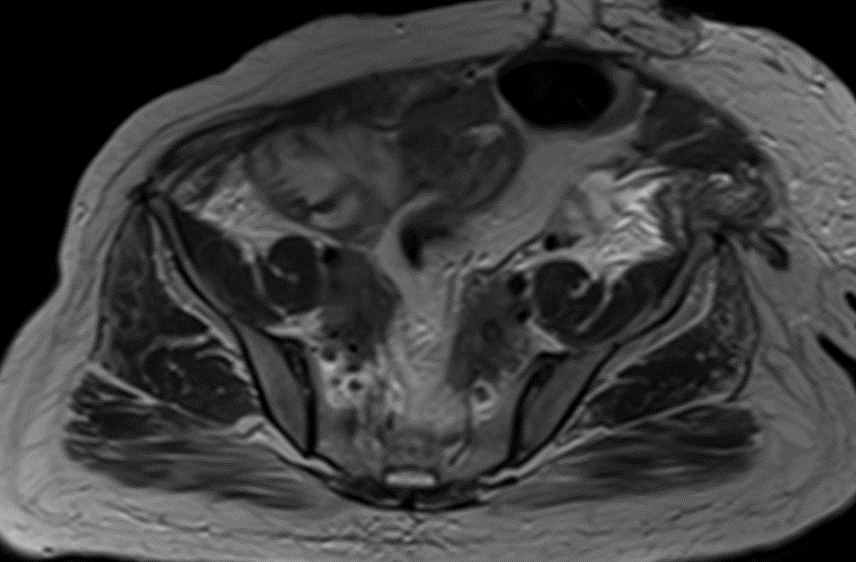
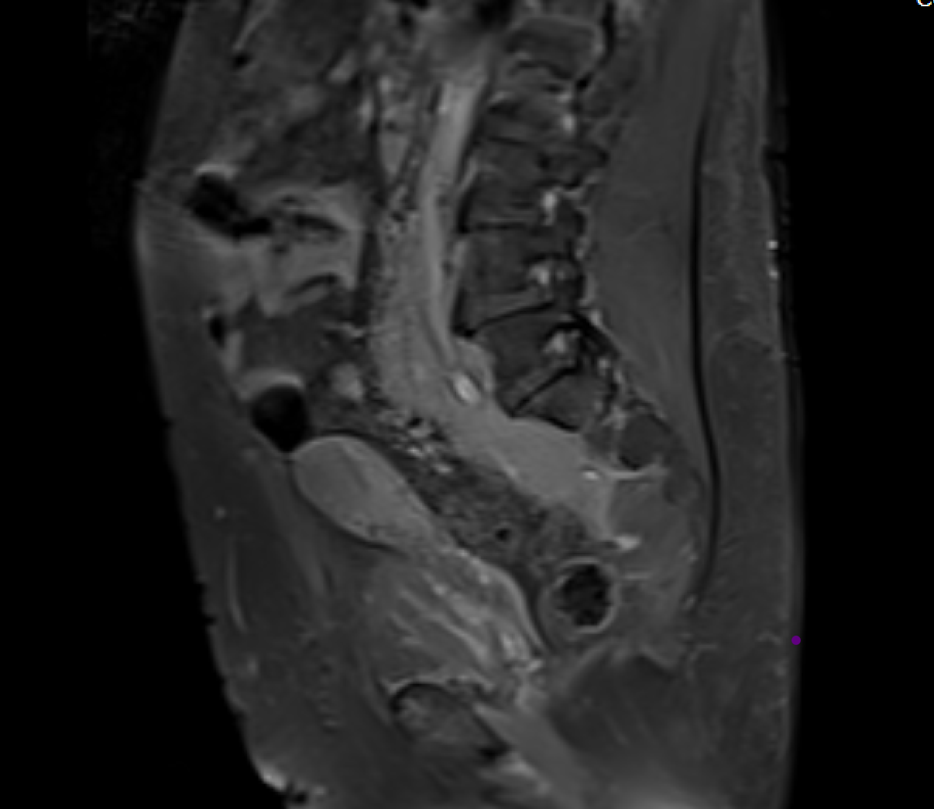
- B & C (22-10-2019) :- CT and MRI shows
The retroperitoneal soft tissue mass lesion noted in the previous scan(2018) has increased in size in 2019 scan encasing the ureters and loss of fat plane with left iliopsoas muscle On correlative MRI images it appears T2 hypointense with intense post contrast enhancement. - D.- 10-2-2022 There is complete resolution of retroperitoneal soft tissue mass.

- Biopsy revealed predominantly of fibrocollagenous tissue,fibroadipose tissue and moderate lymphoplasmacytic cell infiltrate concerning for benign fibroinflammatory lesion
Serum showed raised levels of IgG4
Diagnosis: IgG4 related Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
Discussion:
- Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)–related disease is an increasingly recognized immune-mediated condition that comprises a group of disorders which shows infiltration by IgG4-positive plasma cells and lymphocytes with associated fibrosis, producing tumefactive lesions in one or more organs or organ systems. In addition, elevated serum IgG4 concentrations are found in most patients.
- The Japanese group proposed three major diagnostic criteria for practical use:
(a) clinical examination showing characteristic diffuse or localized swelling or masses in one or more organs; (b) hematologic examination showing elevated serum IgG4 concentrations (≥135 mg/dL); and
(c) histopathologic examination showing marked lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and storiform fibrosis, as well as organ infiltration by IgG4-positive plasma cells. - IgG4-related lesions similar to those of autoimmune pancreatitis have been identified in many extrapancreatic organs, including the bile ducts, gallbladder, lymph nodes, retroperitoneum, mesentery, kidneys, lungs, breasts, prostate gland, and skin. The head and neck may also be involved, with the most commonly affected organs being the salivary and lacrimal glands, orbits, and thyroid gland, as well as the pituitary gland and meninges.
- Clinical symptoms of IgG4-related disease are generally mild, with no fever or elevation of C-reactive protein levels. The disorder is often identified incidentally when organ swelling is detected at radiology. Response to steroid therapy is excellent in most patients, although some patients are refractory to such therapy.
- A few cases of cancer have been reported in patients with IgG4- related disease—mainly, lymphoma and pancreatic carcinoma—but the potential for malignant transformation of the disease is not clear.
RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES:
IVU
- Medial deviation of the middle third of the ureters (maiden waist sign)
- Tapering of the lumen of one or both ureters in the lower lumbar or upper sacral region
- Proximal unilateral or bilateral hydroureteronephrosis with delayed excretion of contrast material
CT
- Soft tissue density mass located around the aorta and iliac arteries.
- Develops around the aortic bifurcation and spreads upwards where it can envelop the renal hila.
- It encases but does not invade or stenose the ureters or vessels. (ureteric obstruction and venous thromboses can occur). Early or active stages: variable enhancement is seen with intravenous contrast
- Quiescent stage: No enhancement is seen
MRI
- The soft tissue mass is usually dark on T1W and T2W unless there is an active inflammation whereby the T2W images can be hyperintense.
- Soft tissue mass shows variable enhancement on post contrast images.
- No specific imaging findings are there to differentiate idiopathic RPF and IgG4 related RPF except for the fact that IgG4 related disease is common in middle and elderly aged males
Conclusion:
IgG4-related disease is an established systemic disease that produces organ infiltration by fibroinflammatory tissue and sometimes mimics other inflammatory or neoplastic processes. This condition comprises a large number of medical disorders previously considered to be confined to single-organ systems. The pancreas is most commonly involved, but the list of extrapancreatic manifestations is continually growing. Radiologists must be familiar with this disorder because patients usually demonstrate a marked response to corticosteroid therapy, and timely recognition may help avoid delays in diagnosis and unnecessary invasive procedures.
REFERENCE:
- Anxo Martínez-de-Alegría , Sandra Baleato-González, Roberto García-Figueiras,I gG4 related disease from head to toe :Oct 16 2015
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2001;344(10):732–738. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
- Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol 2003;38(10):982–984. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
- Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28(9):1193–1203. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
- Cheuk W, Yuen HK, Chu SY, Chiu EK, Lam LK, Chan JK. Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32(5):671–681. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
- Zen Y, Onodera M, Inoue D, et al. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: a clinicopathologic study with respect to immunoglobulin G4. Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33(12):1833–1839. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
Dr. CHANNABASAPPA CHAVADI
Senior Consultant Radiologist
Manipal Hospital, Sarjapur, Bengaluru.
Dr. VINEETHA RAGHU
Senior Consultant Radiologist
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group.
Dr. SHARNITHA JOHNSON
Manipal Hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru.