25-year-old with clicking and deviation of jaw for 2 years.
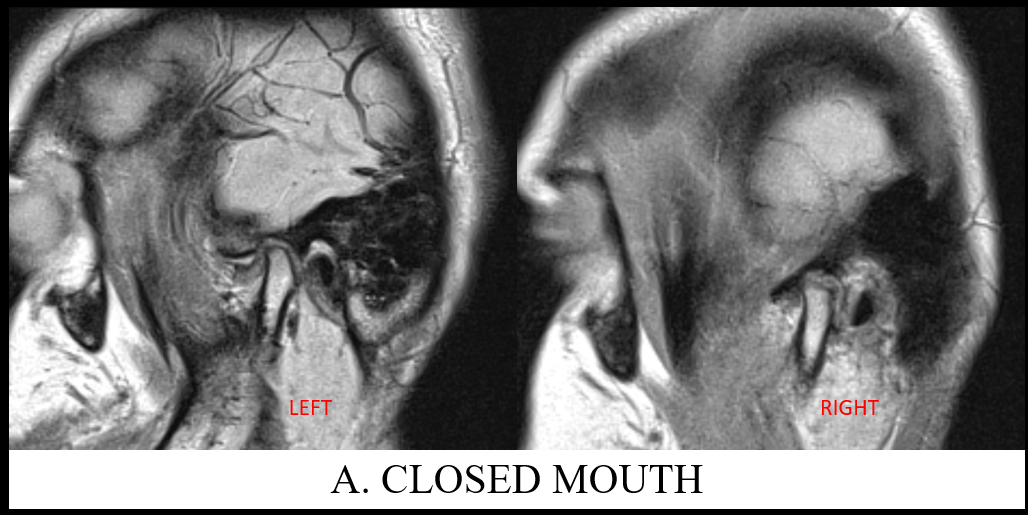
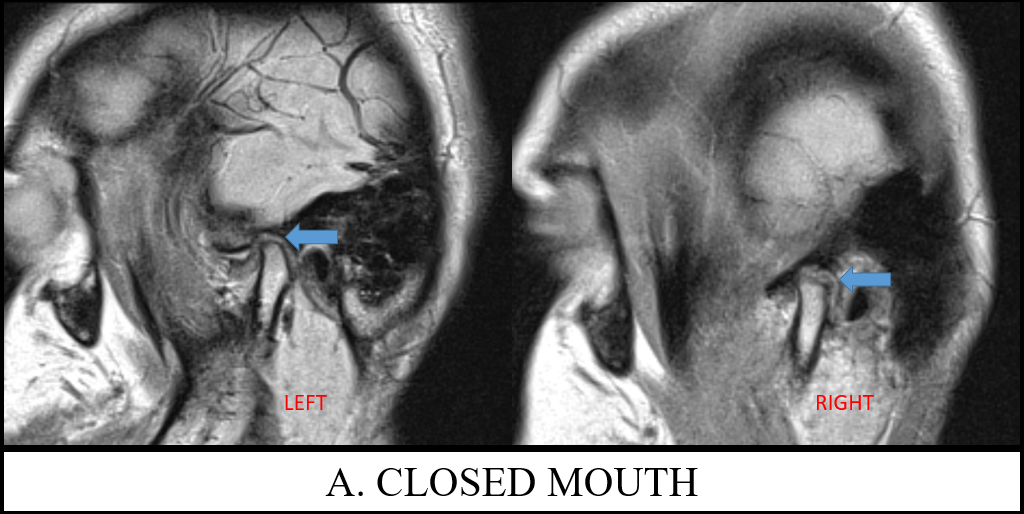
A. Images of closed mouth TMJ PD sequence of left and right joints demonstrates anteriorly displaced bilateral meniscus. The intermediate zone is not located between the articular surfaces of the condyle and eminence. The left disk is thickened and with hyperintense signal. No evidence of disk perforation or retroviral tear.
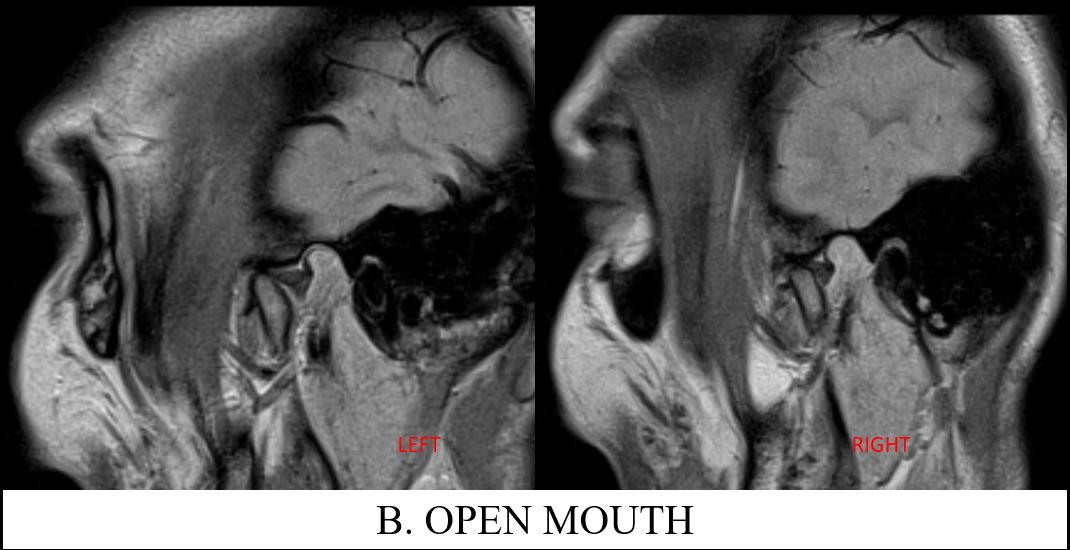
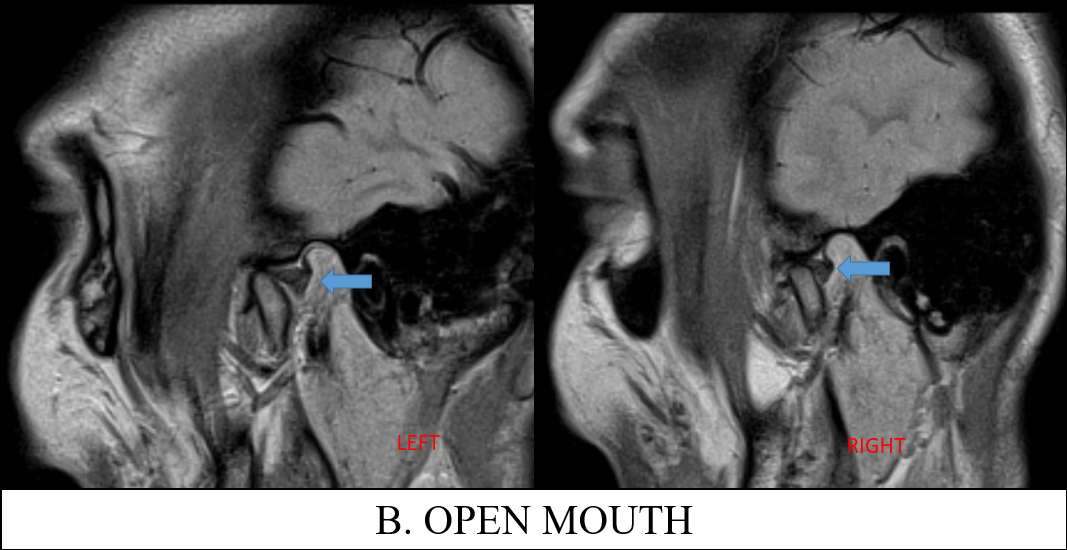
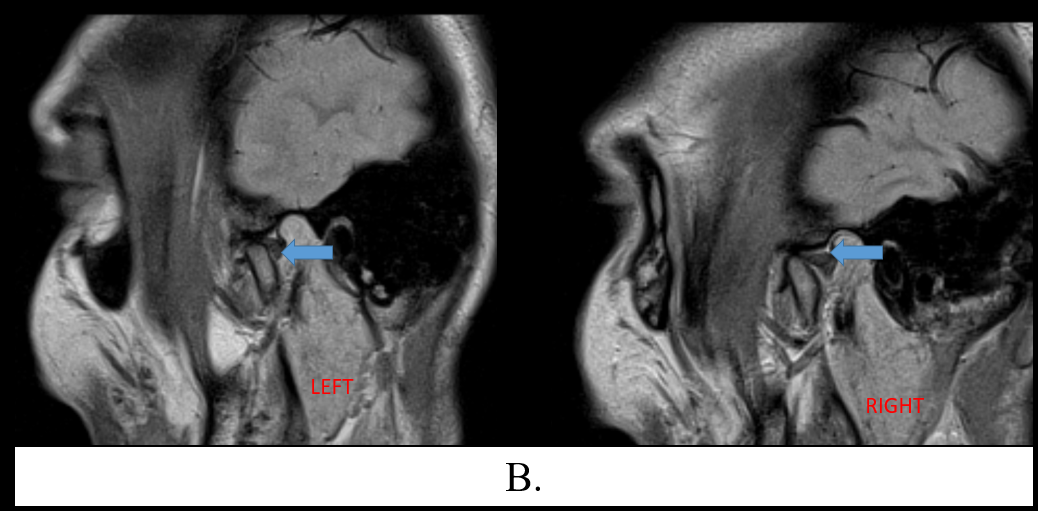
B. Images of open mouth TMJ PD sequence of left and right joints demonstrates the reduced articular disc which are now normally located. Anterior translation of the condyle is slightly reduced as the condylar head still lies slightly posterior to the articular eminence.
DIAGNOSIS AND DISCUSSION:
Bilaterally anteriorly displaced disks with reduction on open mouth
Discussion:
- The most common intra-articular abnormality of the TMJ is internal derangement, which has been defined as an abnormal position of the disc in relation to the mandibular condyle and temporal eminence.
- Internal derangement is a progressive process. Initially, anterior, medial, or lateral displacement of the disc may be evident in the closed mouth position that reduces with mouth opening.
- The following features should be assessed on MR evaluation of the TMJ: the position and morphology of the articular disc, disc deformity or perforation, joint effusion and marrow edema, osteoarthrosis, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the retrodiscal tissues.
Categorization of internal derangement on imaging from least severe to most severe as follows:
- Anterior disc displacement with reduction with mouth opening.
- Anterior disc displacement without reduction with mouth opening.
- Chronic anterior disc displacement with disc perforation and features of degenerative joint disease.
References:
https://radsource.us/internal-derangement-of-the-temporomandibular-joint/
Senior Consultant Radiologist
Manipal Hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru.
Dr Akshay K
Radiology resident
Manipal Hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru.