22 year old male with history of Road traffic accident -sustained subdural haemorrhage with 6 mm midline shift, craniofacial injuries, Pneumothorax, and pneumomediastinum
- 22 year old male with history of Road traffic accident -sustained subdural haemorrhage with 6 mm midline shift, craniofacial injuries, Pneumothorax, and pneumomediastinum.
- Decompressive craniotomy was performed and VP shunt was placed.
- Follow up CT demonstrated worsening hydrocephalus.
- Blocked VP shunt suspected.
- USG abdomen was performed.
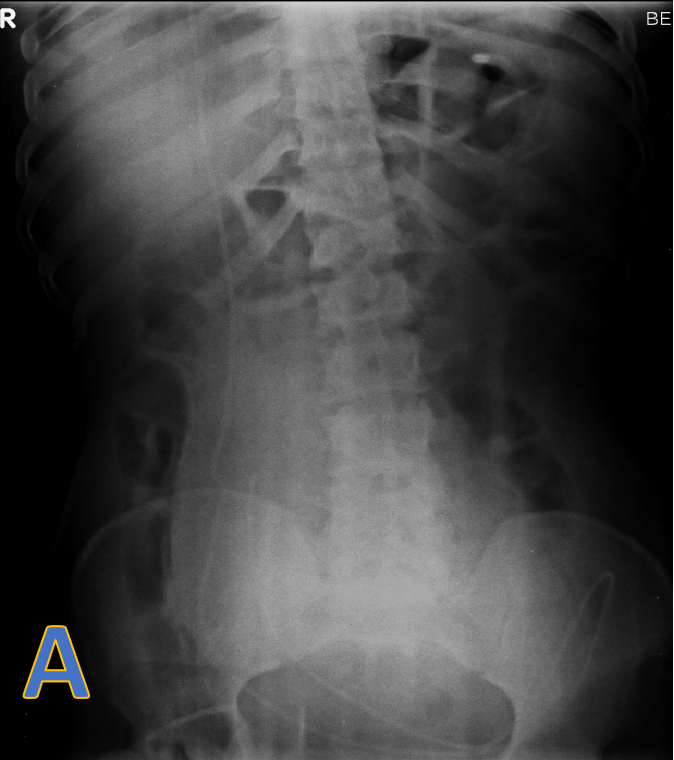
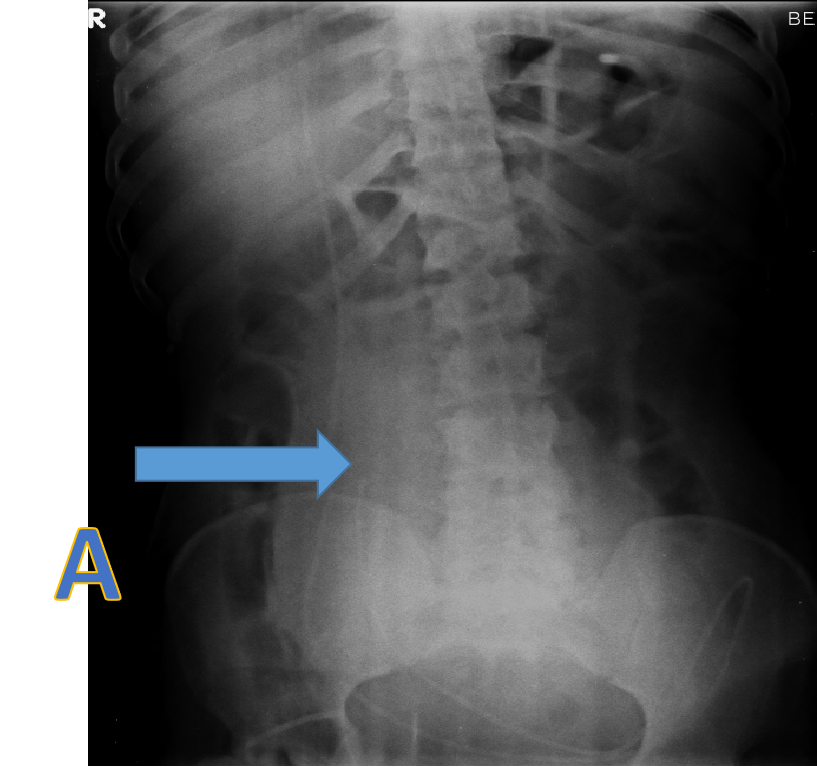
- A: X ray erect abdomen demonstrating tip of the VP shunt and paucity of gas shadows in the abdomen.
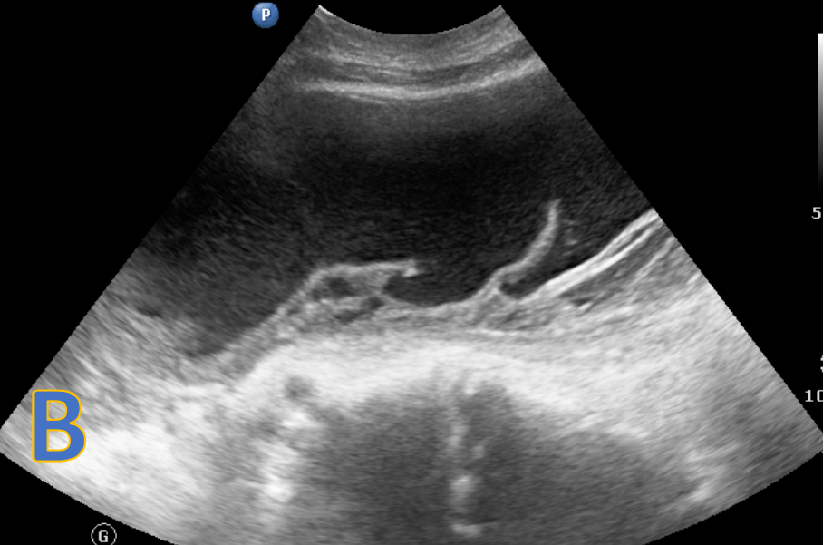
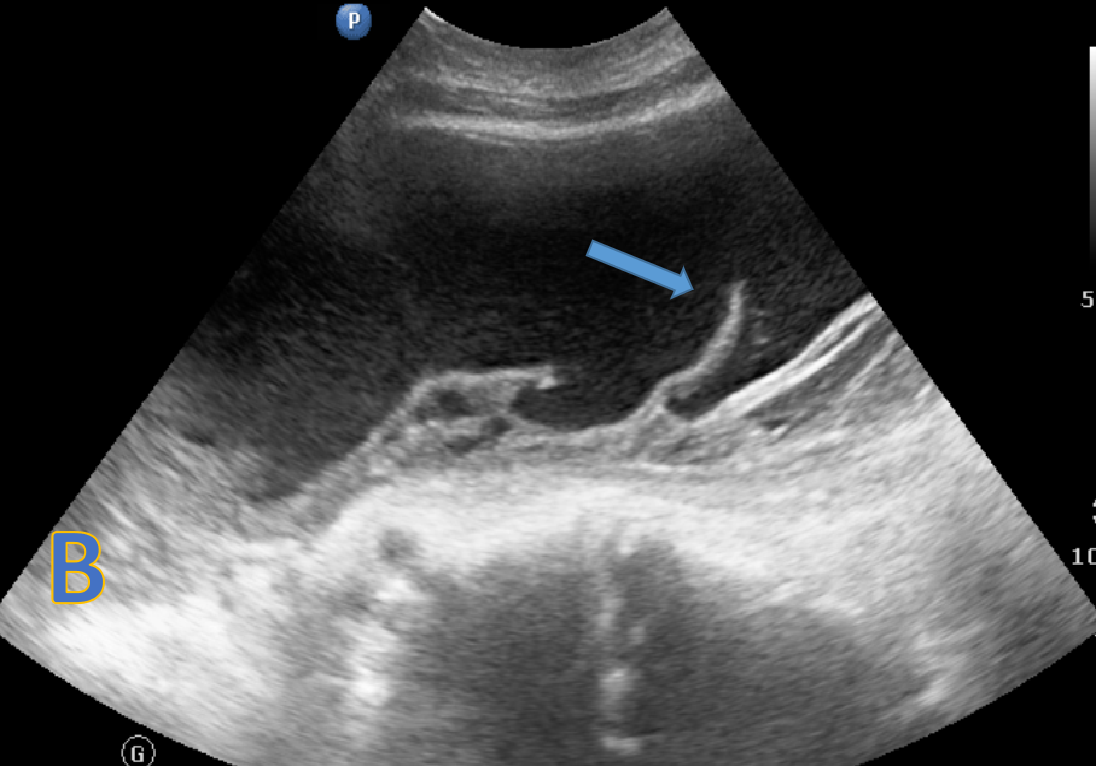
- B: USG abdomen: large abdominopelvic loculated collection with internal echoes and septations and VP shunt tip within.
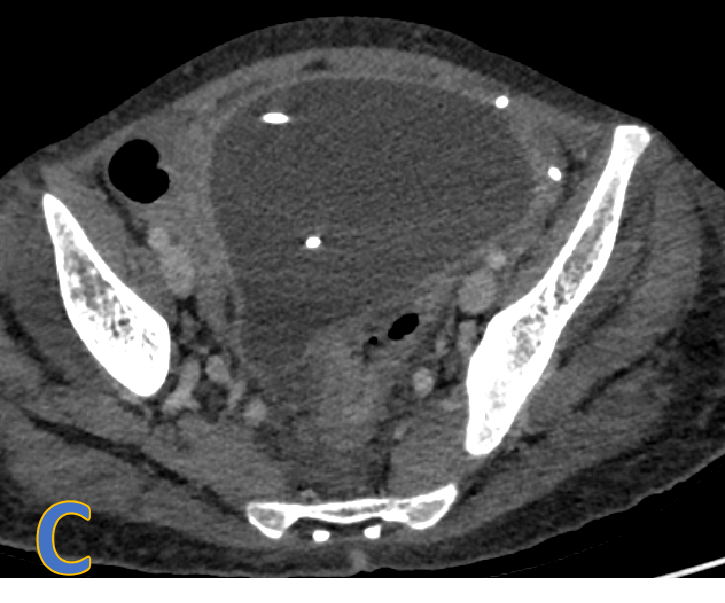
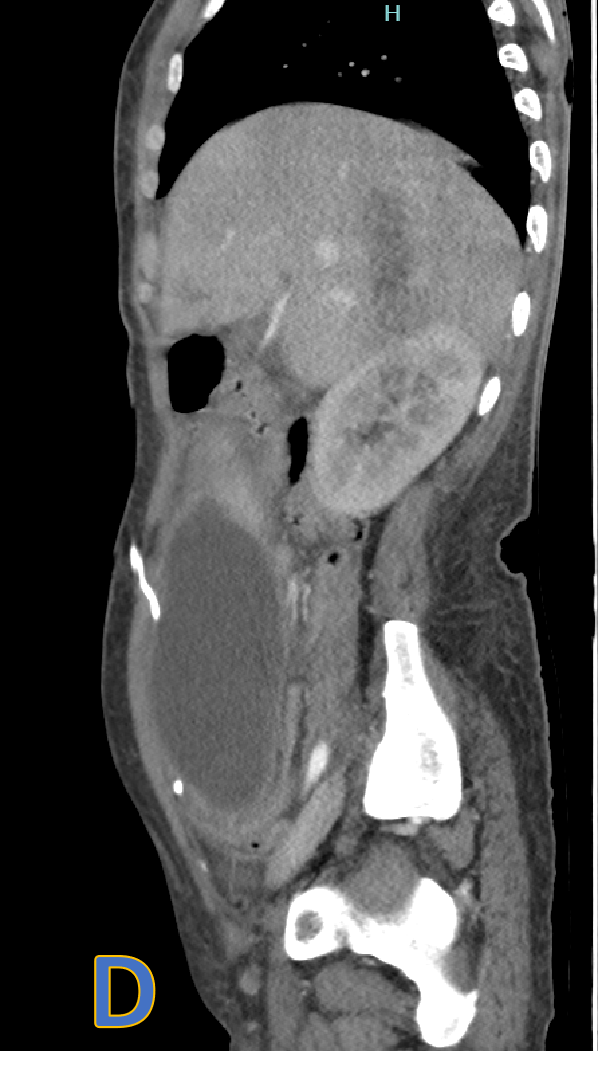
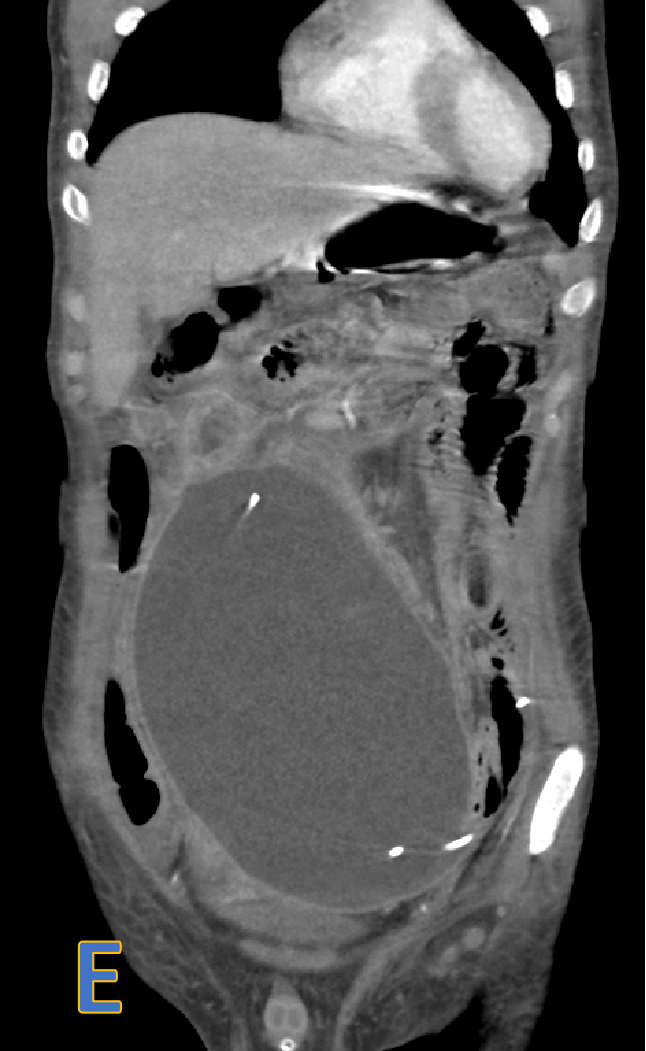
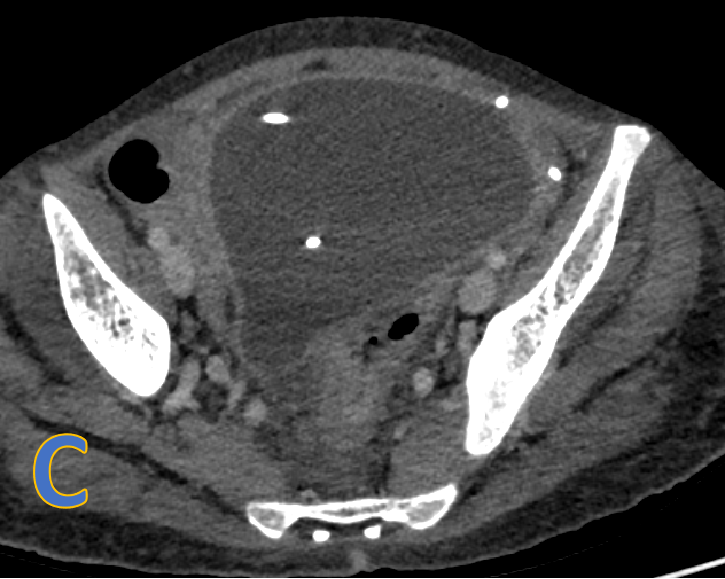
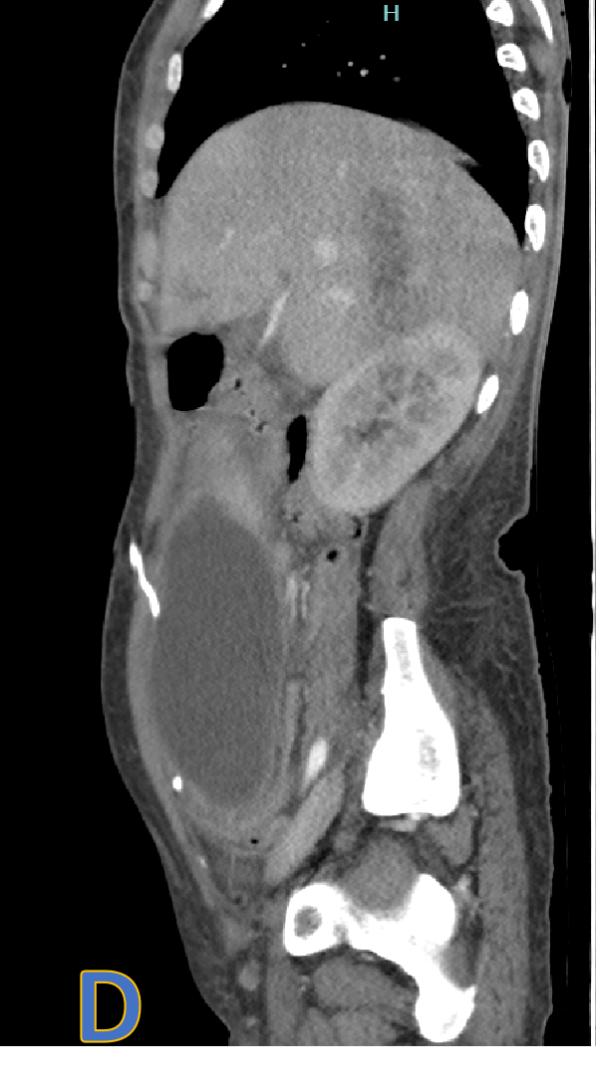
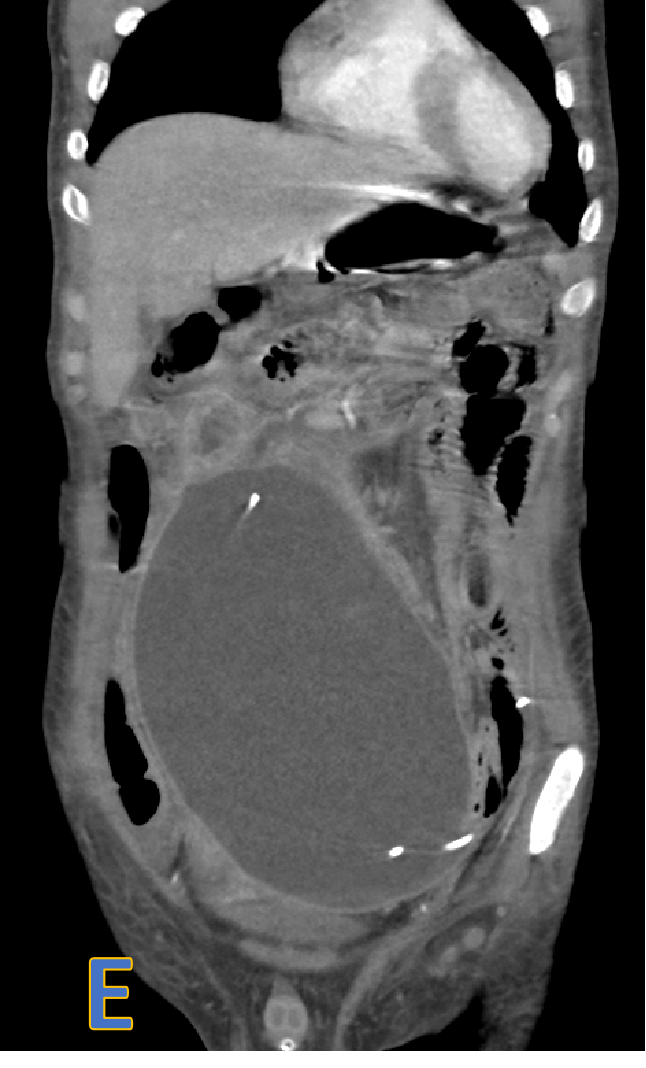
- C, D, E: axial, sagittal and coronal CECT.
- Large, welldefined intra- peritoneal fluid density collection with peripheral rim enhancement displacing bowel loops with VP shunt within.
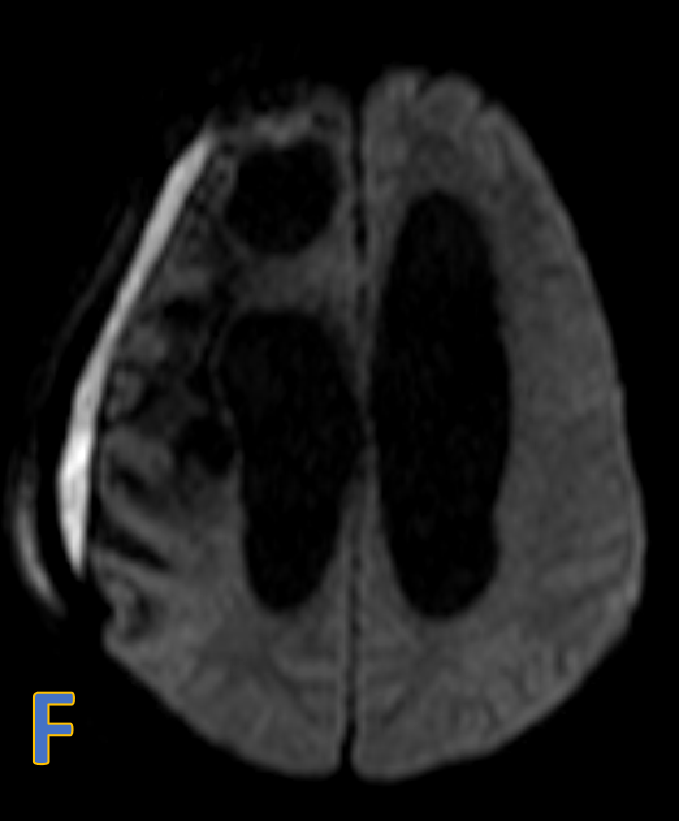
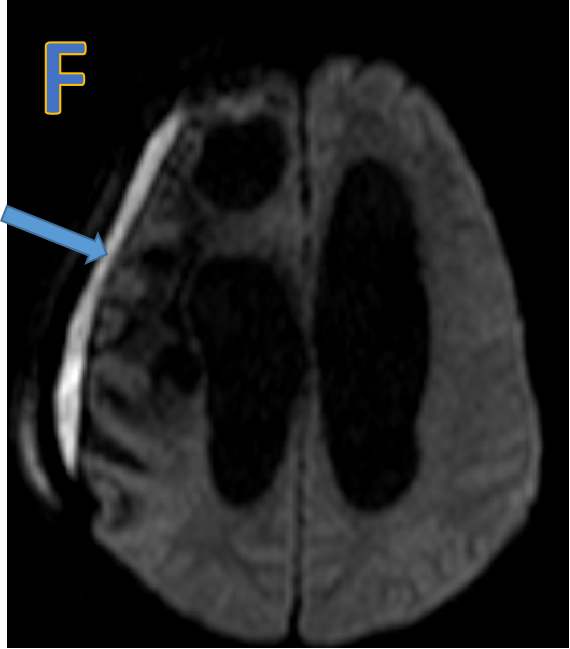
- F: Subdural collection with restricted diffusion.
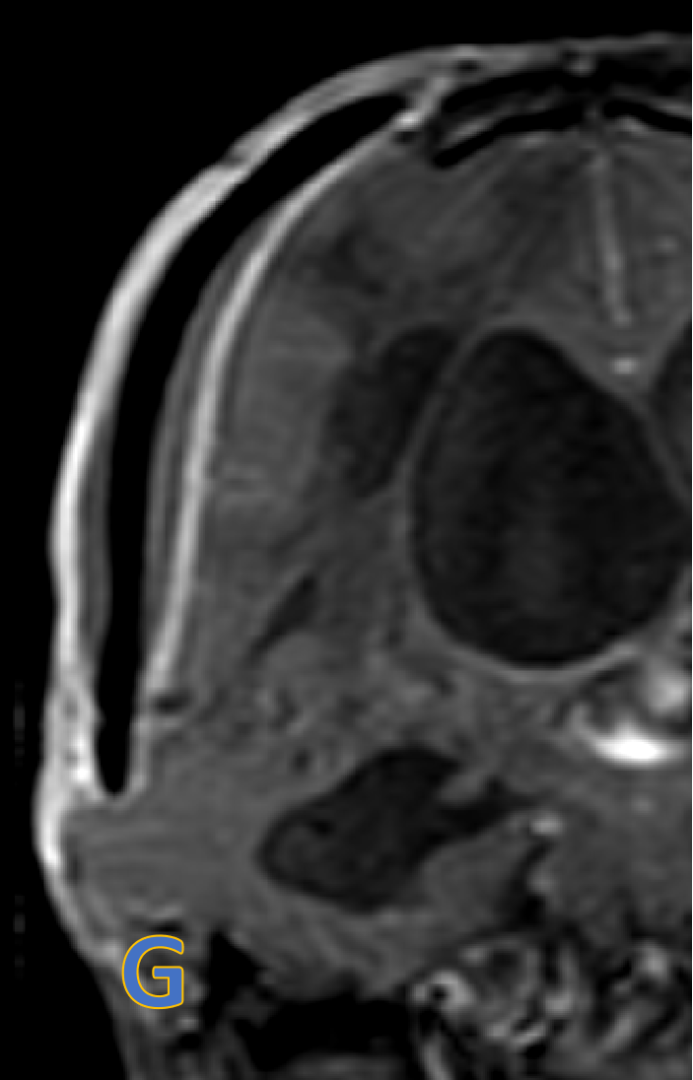
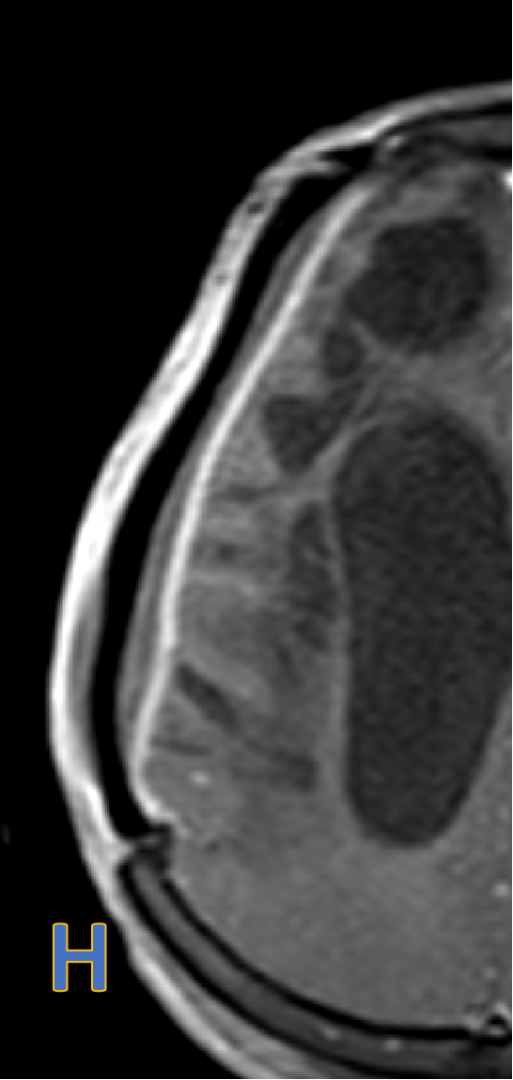
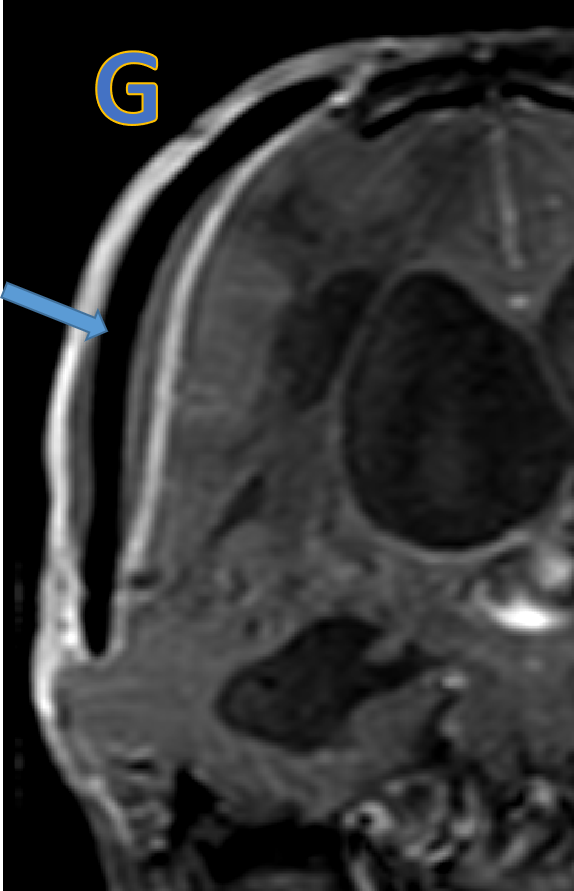
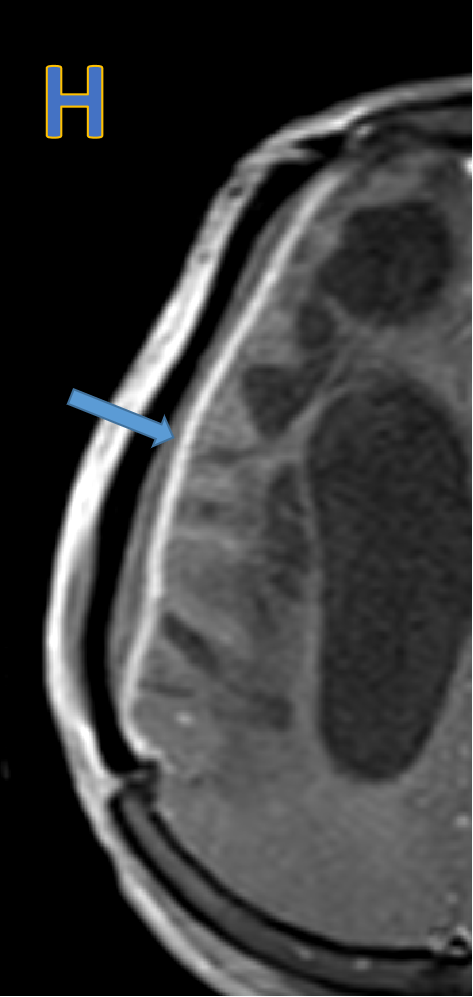
- G&H: Subdural collection with dural enhancement at cranioplasty site - likely subdural empyema.
PERITONEAL CSF PSEUDOCYST
- Rare complication of VP shunt placement resulting in a CSF filled cyst without epithelial lined cyst wall.
- The time from the last shunting procedure to the development of an abdominal pseudocyst ranges from 3 weeks to 5 years.
- CSF shunts may be placed in :-
- Abdomen (peritoneal cavity)
- Heart (right atrium)
- Chest cavity (pleura)
- Rarely into the ureter or the bladder.
- Peritoneal CSF pseudocyst - rare complication of VP shunt catheter placement. Incidence: 1% to 4.5%
- CSF pseudocysts - caused by peritoneal adhesions or migration of the greater omentum over the shunt tip.
- They can move freely within peritoneal cavity or adhere to small-bowel loops, serosal surfaces, parietal peritoneum or small-bowel loops.
- Pediatric patients commonly present with symptoms of elevated intracranial pressure and abdominal pain.
- Adults predominantly present with abdominal signs only.
- Subdural collection with restricted diffusion & dural enhancement at cranioplasty site - likely subdural empyema.
Radiological investigations: USG and CT are routinely enough to diagnose.
USG:
- Well defined hypoechoic / anechoic cystic mass with tip of VP shunt within it
- Pressure effects on adjacent organs.
- Multiple septations in chronic cases.
- Debris and internal echoes - if the mass is infected.
CT:
- Small to massive, loculated hypodense cyst-like structure in the peritoneal cavity at the distal tip of the VP shunt.
Nuclear medicine:
- Radioisotopes injected into shunt reservoir should normally distribute freely through the abdomen.
- Loculation of tracer within an abdominal collection – S/o pseudocyst formation.
Management
- Percutaneous aspiration/drainage of the pseudocyst can be both diagnostic and therapeutic.
- If the fluid is sterile, the existing shunt is re-implanted or converted to a different site.
- If infection is present, the pseudocyst should be excised and the shunt tube should be removed.
References
- Pernas JC, Catala J. Case 72: Pseudocyst around ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Radiology. 2004 Jul;232(1):239-43. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2321011976. PMID: 15220507.
- Bryant MS, Bremer AM, Tepas JJ et-al. Abdominal complications of ventriculoperitoneal shunts. Case reports and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1988;54 (1): 50-5. Am Surg (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- Birbilis T, Kontogianidis K, Matis G et-al. Intraperitoneal cerebrospinal fluid pseudocyst. A rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2008;103 (3): 351-3. Chirurgia (Bucur) (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- Chick JF, Chauhan NR, Mullen KM et-al. Teaching NeuroImages: massive abdominal CSFoma. Neurology. 2013;80 (13): e146. Neurology (abstract) - doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318289705e - Pubmed citation
Dr. Pravin Kumar M
Senior Consultant Radiologist – Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group
MBBS, DMRD, DNB
Dr. K Vishnu Vardhan Reddy
Fellow In Cross Sectional Imaging
Manipal hospital , Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru