10 yrs old with seizures, motor developmental delay and unsteadiness of gait.
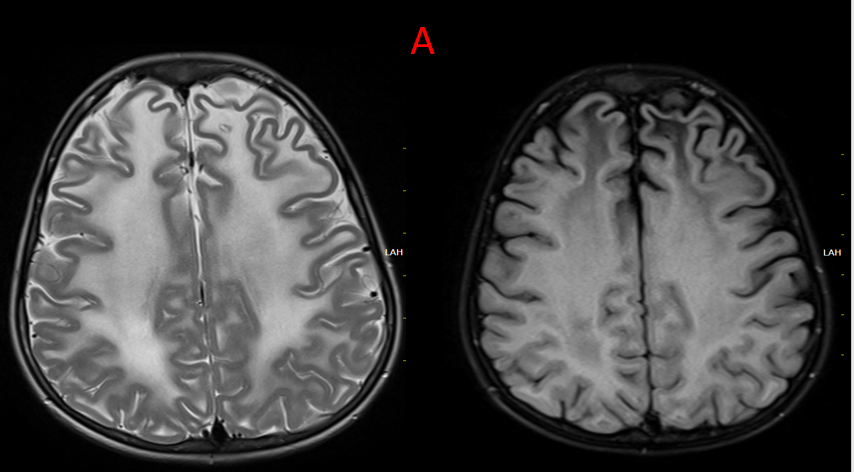
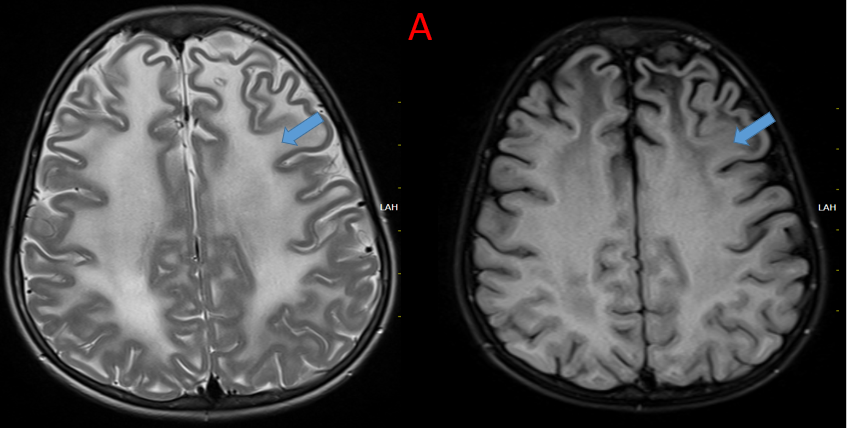
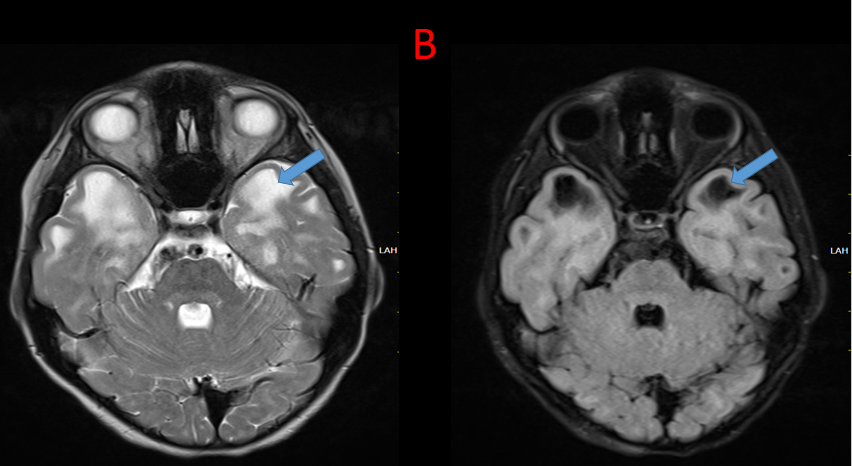
A.
Symmetrical confluent T2/FLAIR hyperintensity seen throughout the deep and subcortical white matter in bilateral cerebral hemispheres.
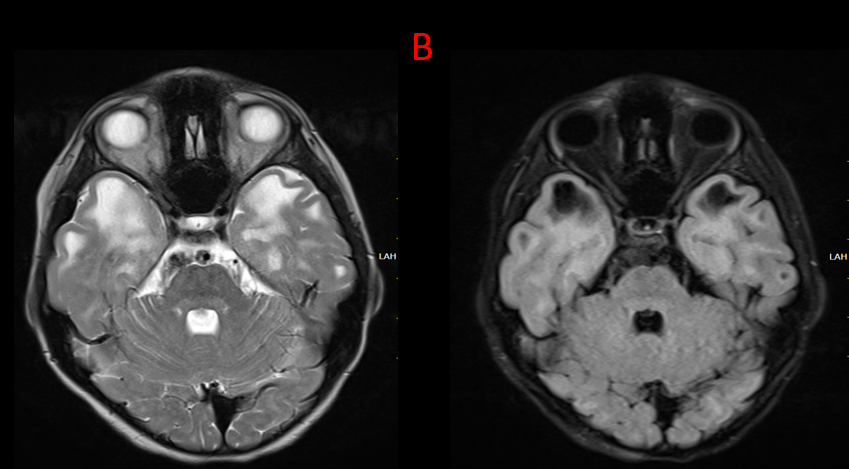
B.
Multiple subcortical cysts are seen in bilateral temporal and frontal lobes characterized by T2 hyperintensity with suppression on FLAIR.
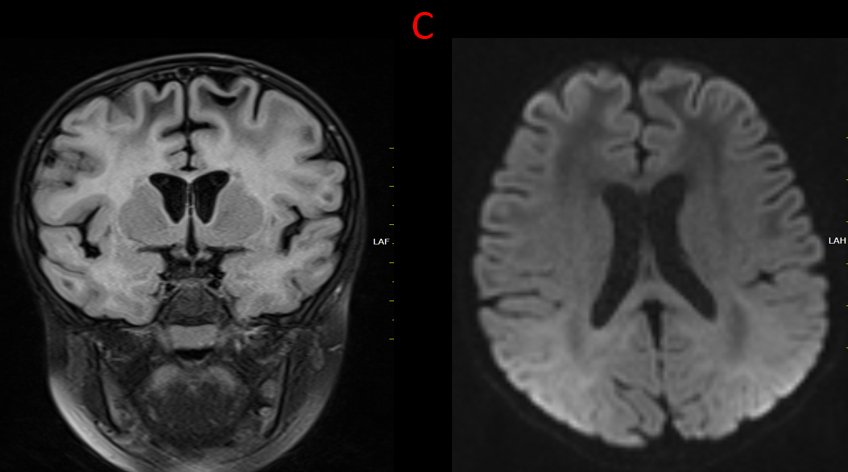
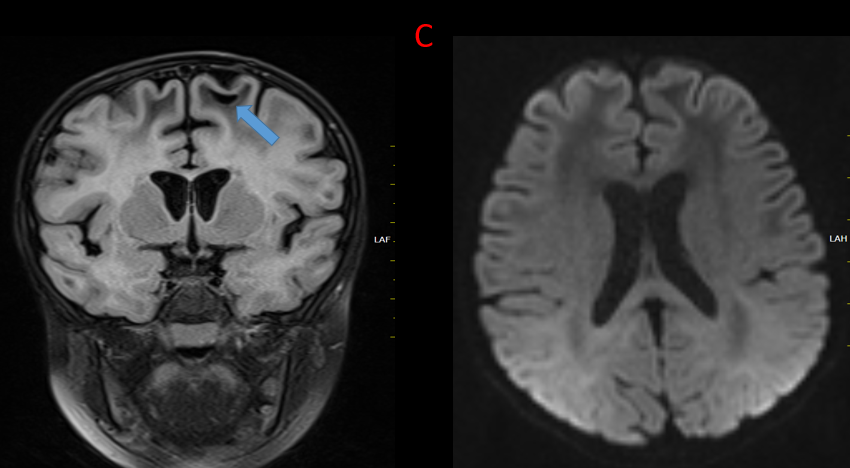
C.
Subcortical cyst in the left parietal lobes.
Diffusion weighted images demonstrates no abnormality.
DIAGNOSIS AND DISCUSSION:
MEGALENCEPHALIC LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY WITH SUBCORTICAL CYST
Discussion:
- Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts was first described by van der Knaap et al. in 1995.
- The disease has a high incidence in Aggarwal community in India and Jewish community with consanguinity being a high risk factor.
- MLC is an autosomal recessive disorder due to mutations in MLC 1 gene7 which has its locus in chromosome 22qtel.
- MLC is known for its mild neurological signs and symptoms in the setting of very abnormal MR findings. The age at onset of symptoms varied from birth to 25 years.
- Macrocephaly is present at birth or, more commonly, develops within the first year of life. Seizures from an early age.
- Early development is normal or mildly delayed with slow deterioration of motor functions with cerebellar ataxia.
MRI Demonstrates :
- Macrocephaly
- Swollen white matter’ and diffuse supratentorial symmetrical white matter changes in the cerebral hemispheres with relative sparing of central white matter structures like the corpus callosum, internal capsule, and brain stem.
- Subcortical cysts are almost always present in the anterior temporal region and are also frequently noted in the frontoparietal region.
- Grey matter is usually spared.
- Gradually the white matter swelling decreases and cerebral atrophy may ensue.
- The subcortical cysts may increase in size and number.
MLC must be included in differential diagnosis of macrocephaly with early onset leukoencephalopathy.
Differential diagnosis of MLC includes:
- Alexander disease – shows frontal lobe white matter involvement with post contrast enhancement is seen and also parietal white matter, internal and external capsules and basal ganglia may be involved.
- Vanishing white matter disease – shows extensive symmetric CSF-isointense white matter changes and radiating cystic degeneration would be seen.
- Cystic leukoencephalopathy without megelencephaly – shows no megalencephaly bilateral temporal subcortical cysts and multifocal lobar white matter lesions showing hypointensity on T1W and hyperintensity on T2W and FLAIR with central white matter sparing will be seen.
- Canavans disease – shows diffuse involvement (including subcortical U fibers) of white matter with markedly increased NAA on MR spectroscopy noted.
- Glutaric aciduria type 1 – frontotemporal atrophy, “bat wing” dilatation of Sylvian fissures, increased T2W intensity in bilateral caudate nuclei, putamen and delay in myelination is seen.
References:
- Van der Knaap MS, Barth PG, Stroink H, et al. Leukoencephalopathy with swelling and a discrepantly mild clinical course in eight children. Ann Neurol1995; 37:324-34. PMID:7695231
- Singhal BS, Gursahani RD, Udani VP et al. Megalencephalic leukodystrophy in an Asian Indian ethnic group. Pediatr Neurol 1996; 14:291-6. PMID:8805171
- Gorospe JR et al Indian Agarwal megalencephalic leukodystrophy with cysts is caused by a common MLC1 mutation Neurology. 2004 Mar 23;62(6):878-82 PMID 15037685
- Leegwater FA, Boor PK, Yuan BQ, et al. Identification of novel mutations in Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy with Subcortical Cysts responsible for megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Hum Genet 2002; 110: 279-83.
- KV Rajagopal et al. Van der Knaap Disease, A Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy. Ind J Radiol Imag 2006; 16:4:733-734.
- Gangadhar, K., Patwari, S., Verma, A., & Kaviyarasy, .-. (2013). Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy with Subcortical Cyst: A Case Report. Nepalese Journal of Radiology, 2(2), 76–80. https://doi.org/10.3126/njr.v2i2.7691
Dr. SRIRAM PATWARI
Senior Consultant Radiologist
Manipal Hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru.
Dr. VAIBHAV BHANDARI
Senior resident
Manipal Hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru.