1 month old boy (2nd to non-consanguinous couple) with c/o abdominal distension, excessive crying, x 7days
- 1 month old boy (2nd to non-consanguinous couple) with c/o abdominal distension, excessive crying, x 7days.
- On examination: Weight:4kg No pallor, icterus Per abdomen: Distended, shiny, prominent veins over abdomen. Liver palpable till RIF with left lobe extending up to LI
- Lab – Raised Lactate and PT. Rest normal
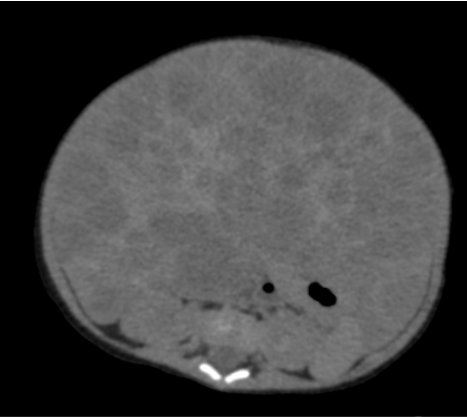
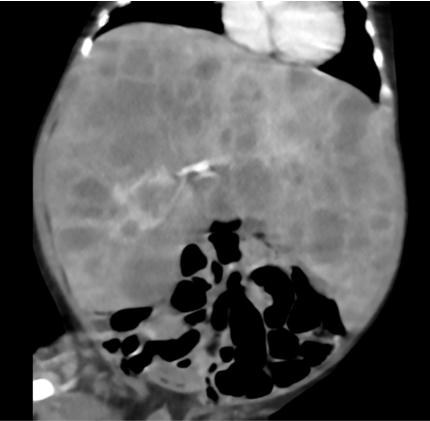
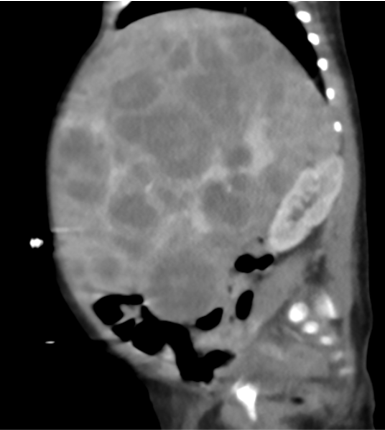
- Grossly enlarged liver numerous hypoenhancing enhancing nodules of varying sizes in both lobes. Some of these nodules are partly exophytic extending to the paraaortic and paracaval regions (horizontal arrow) and compressing stomach (vertical arrow).
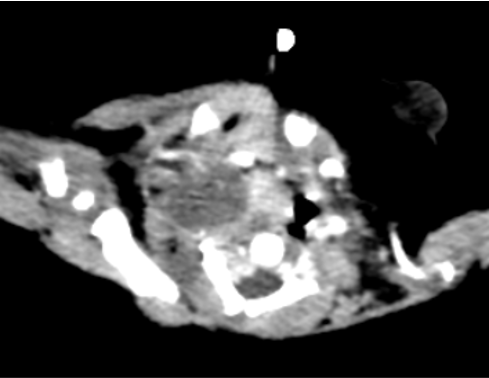
- A – Well-defined hypoenhancing lesion seen in right paravertebral region from C3 to T1 with mild extension into C4/C5 neural foramina.
- B – No calcifications, hemorrhage or bone erosions.
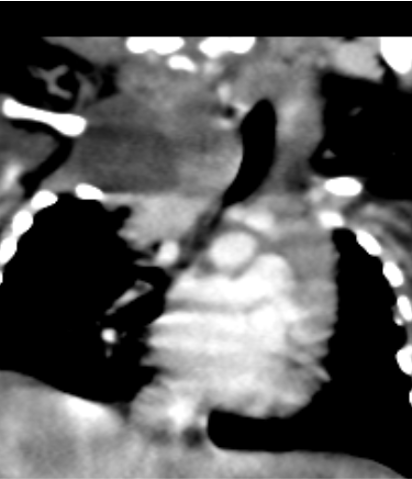
- C – Horizontal arrow: Medially the lesion compresses and displaces the trachea and esophagus towards left.
Vertical arrow: right lower paratracheal solid enhancing mass caudal to the aforementioned lesion.
Diagnosis:
- CERVICOTHORACIC NEUROBLASTOMA WITH LIVER METASTASES.
- USG guided liver biopsy was done.
Discussion:
- Most common extra-cranial childhood malignancy
- Sporadic or syndromic (Beckwith-Weidmann, DiGeorge syndrome, NF1)
- Usually present with abdominal distension and associated syndromes:
- Opsomyoclonus
- Pepper syndrome – hepatomegaly due to liver metastases
- Blueberry muffin cutaneous lesions
- Hutchinson syndrome – bone metastases
- Location – adrenal (most common), retroperitoneal, mediastinal and neck
Radiological features:
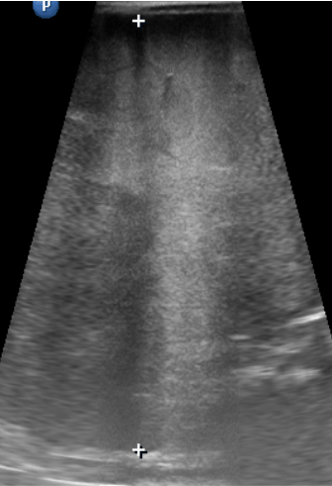
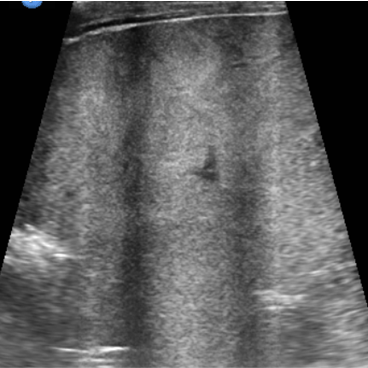
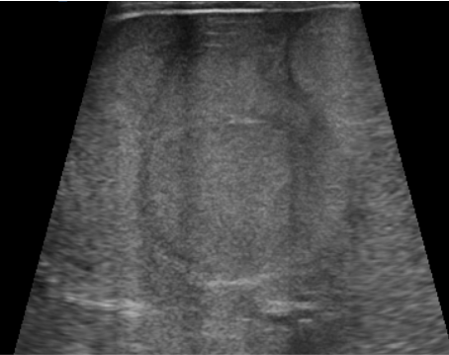
USG
- Solid heterogeneous mass that demonstrates calcification 30%–90% of the time
- If the mass arises from the adrenal gland, there may be inferior displacement of the adjacent kidney
- Doppler: Neuroblastomas tend to encase the surrounding vessels or displace them rather than infiltrate them
- Prenatal – solid/cystic adrenal mass (90% of congenital neuroblastomas arise from the adrenal gland)
CT/MRI – heterogeneously enhancing solid lesion crossing midline, encasing vessels with bone/liver metastases.
- Often, both CT and MR imaging are performed at the initial evaluation, especially if the tumor is paraspinal. For evaluation of all solid tumors in children, whole-body MR imaging has consistently shown sensitivity comparable to or greater than that of skeletal scintigraphy with technetium 99m (99mTc) diphosphonates for detecting skeletal metastases to bone.
- Nuclear – Iodine-123 and 131 –labeled MIBG
- Modified Curie, SIOPEN scoring to assess prognosis
Genetics:
- Common mutations – ALK, PTPN11 ATRX, NRAS and MYCN
- MYCN amplification and ploidy – 20% – advanced stage and poor prognosis
- DNA index >1 (normal=1) – hyperdiploid – lower stage and better prognosis
- Deletion of 1p36, unbalanced gain of 17q, deletion of 11q – poor prognosis
Diagnosis is histological
- Histologically- malignant small round cell tumors – called “blue” because of large hyperchromatic nuclei and a thin rim of cytoplasm.Cells may be separated by a fibrillar matrix forming pseudorosettes -Homer-Wright rosettes.
- IHC markers – Neuron specific enolase, S-100 protein and chromogranin
Treatment
- Congenital – observation
- Other low risk – Surgical resection
- Intermediate risk – Surgery and chemotherapy
- High grade – Aggressive multimodality approach -neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgical resection, adjuvant high dose chemotherapy with hematopoietic stem cell rescue, and radiation therapy
Newer techniques:
- Immunotherapy – Dinutuximab (Anti-GD2)
- Targeted therapy – MIBG labeled with I-131 , Lutetium 177-DOTATATE in refractory cases are under trial
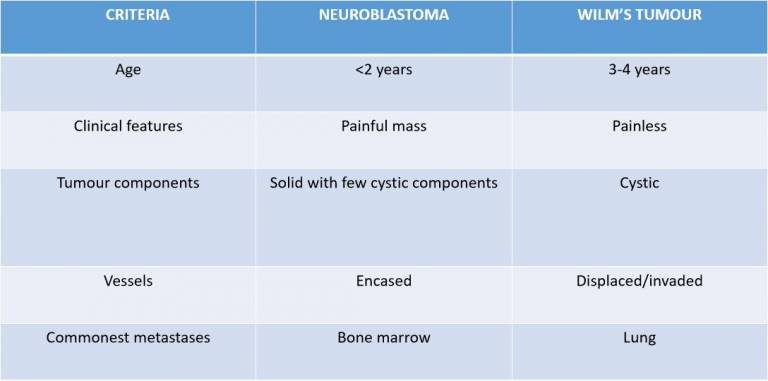
Dilemma : Neuroblastoma vs Wilm’s tumour
REFERENCE:
- Swift, C. C., Eklund, M. J., Kraveka, J. M., & Alazraki, A. L. (2018). Updates in Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment of Neuroblastoma. RadioGraphics, 38(2), 566–580.
- Dumba M, Jawad N, McHugh K. Neuroblastoma and nephroblastoma: a radiological review. Cancer Imaging. 2015 Apr 8;15(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40644-015-0040-6. PMID: 25889326; PMCID: PMC4446071.
Dr Rajesh V. Helavar
Senior Consultant , Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology
Manipal Hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru
Dr Anagh Vishnu Narayanan
Radiology Resident
Manipal Hospital, Yeshwanthpur, Bengaluru