7 months child with bilateral sensorineural hearing loss and delayed development
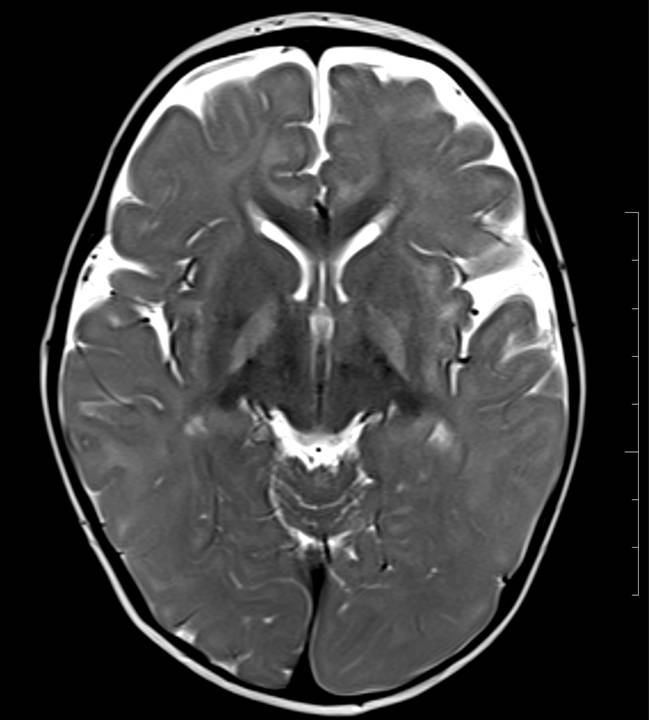
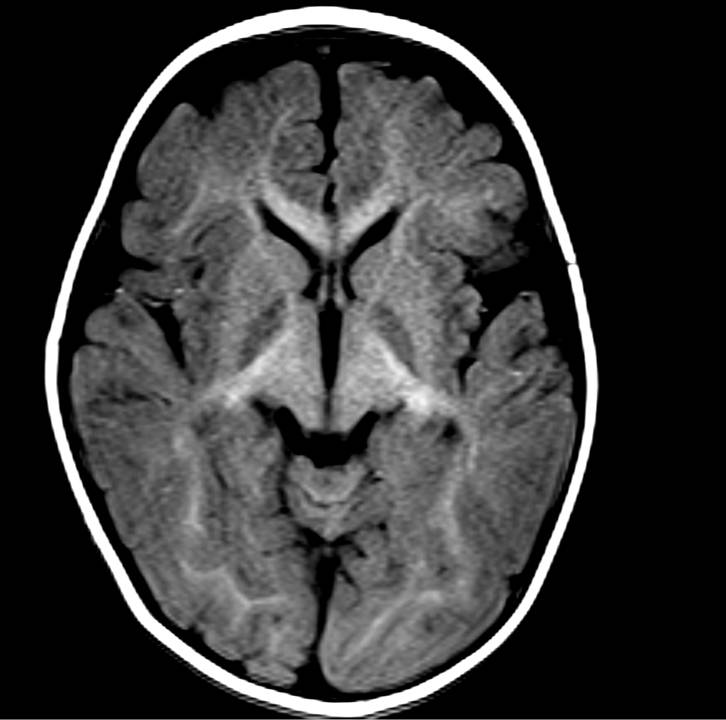
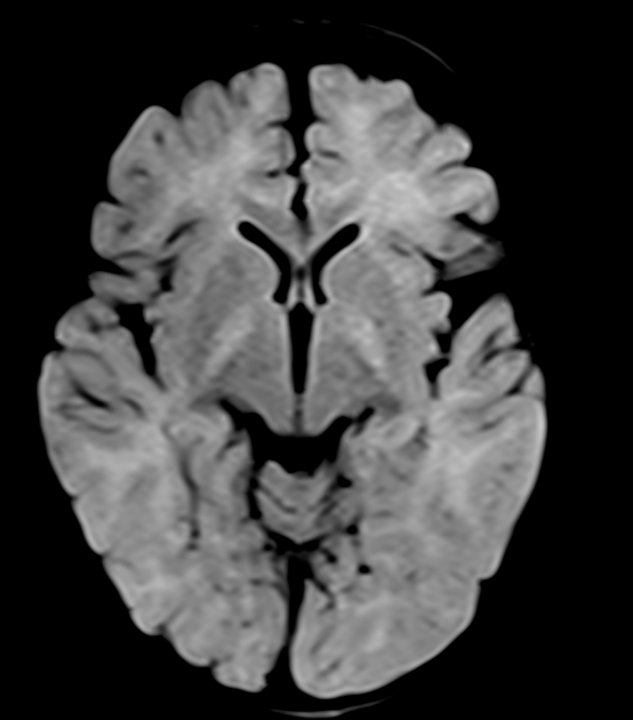
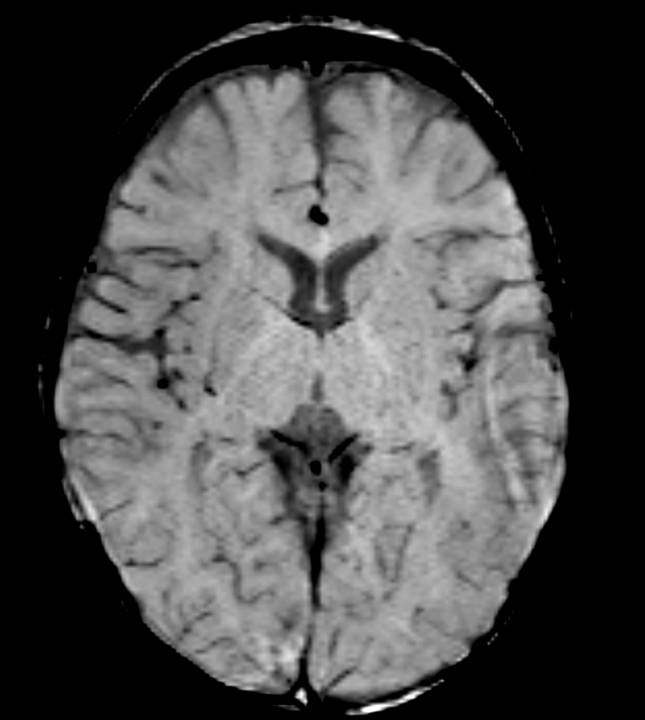
There is symmetrical T2/FLAIR hyperintensity and T1 hypointensity seen in bilateral globus pallidus. No evidence of diffusion restriction (not shown). No evidence of blooming on SWI. The rest of the bilateral cerebral hemispheres and deep grey matter structures are unremarkable. On reviewing the post-natal history, there was severe neonatal jaundice with an unconjugated bilirubin level of 30mg/dl.
Diagnosis:
Kernicterus
Discussion:
- Kernicterus (chronic bilirubin encephalopathy) results from neurotoxicity of excessive unconjugated bilirubin affecting the neonatal brain.
- Acute phase – the neonate presents with jaundice, lethargy, somnolence, hypertonia and opisthotonos. MRI shows symmetrical T1 high signal in bilateral globus pallidus and sometimes in subthalamic nuclei.
- Chronic phase – neurological manifestations include choreoathetoid cerebral palsy, neuropathies (SNHL), intellectual disabilities, ataxia and dental dysplasia. MRI done in chronic phase demonstrates symmetrical T2 hyperintensity and T1 hypointensity in bilateral globus pallidus. The other affected sites include subthalamic nuclei, hippocampus and putamen.
- No specific treatment is available, and the prognosis is poor. Early management of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, with phototherapy and exchange transfusions, is necessary to prevent kernicterus
Dr. Sriram Patwari
MD, PDCC (Neuroradiology)
Consultant Radiology, Co-lead Neuroradiology
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group