A 7-month-old infant presented with complaints of abdominal distension, persistent fever spikes and swelling in bilateral lower limbs.
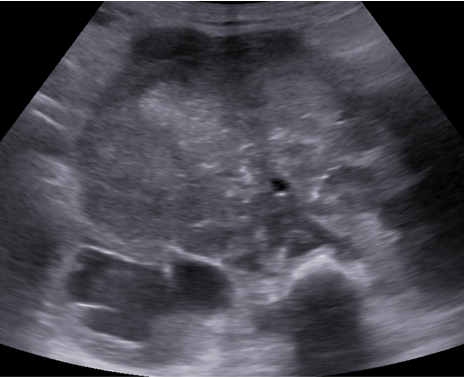
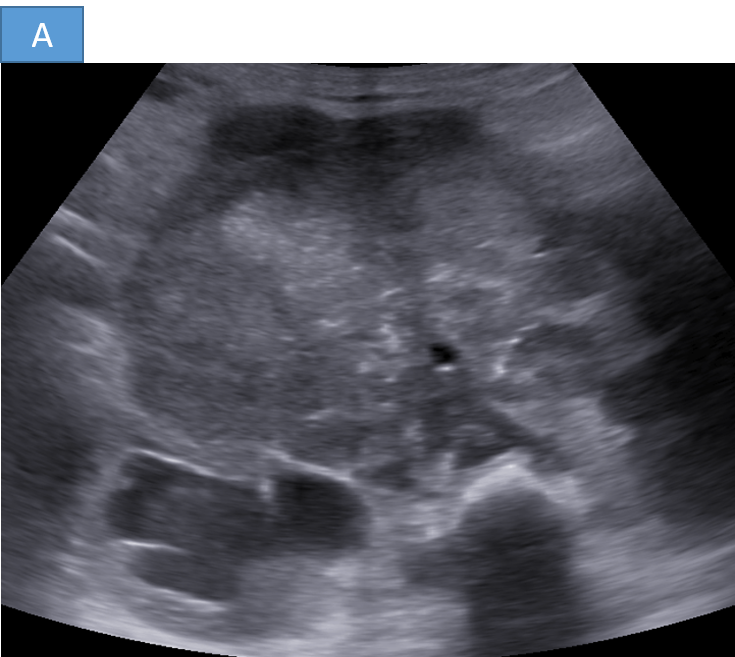
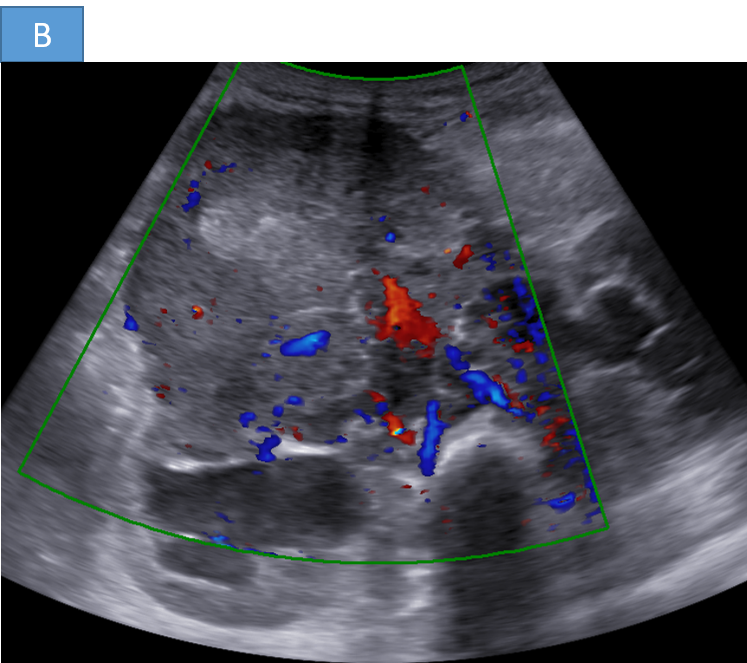
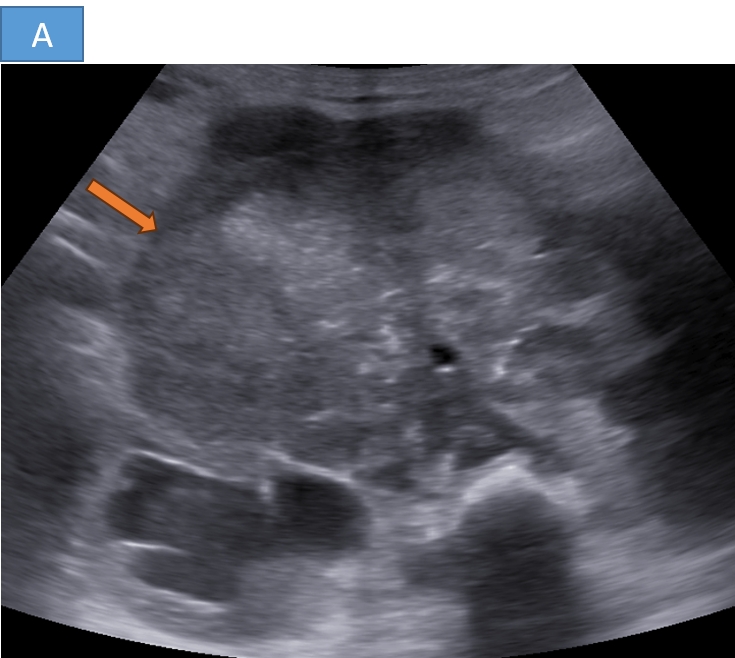
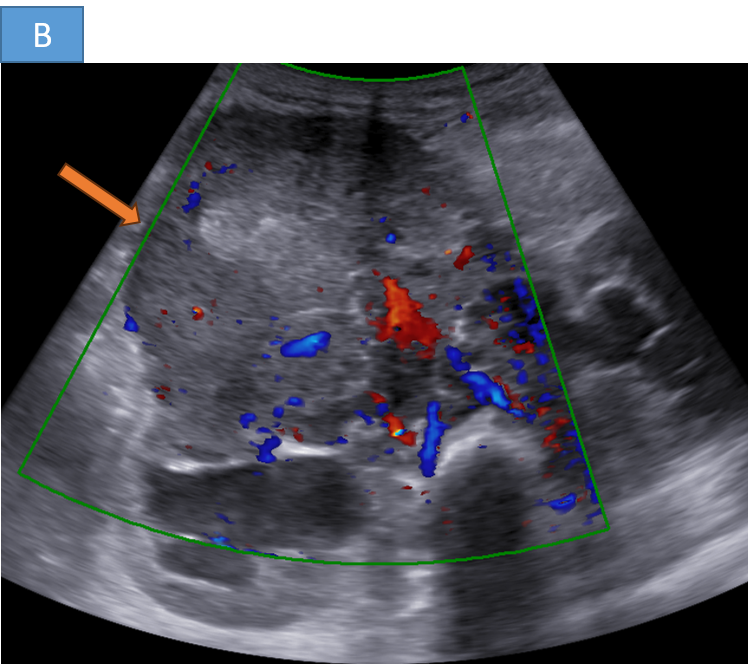
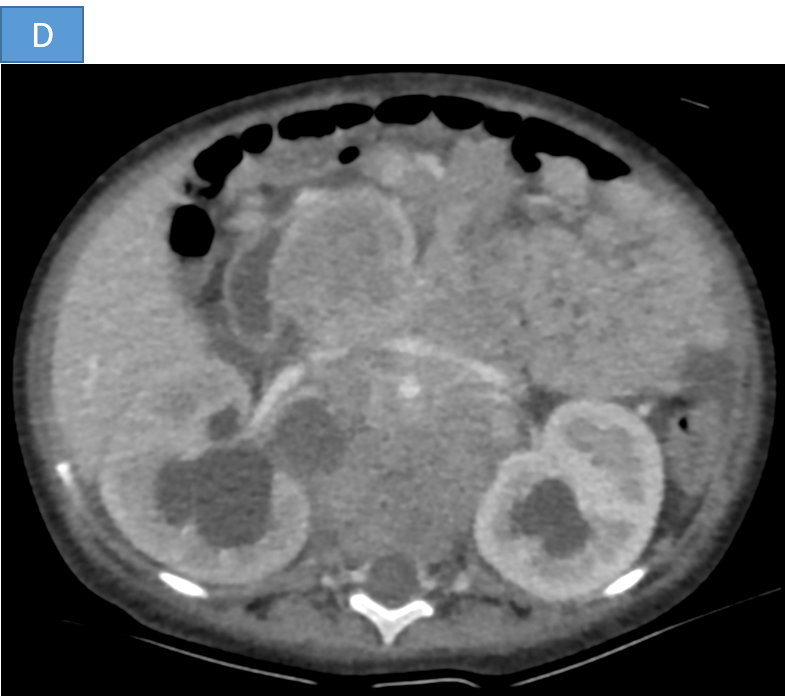
- A. A large hetero-echoic retroperitoneal mass lesion with internal vascularity associated with multiple enlarged retroperitoneal nodes causing bilateral grade III hydronephrosis.
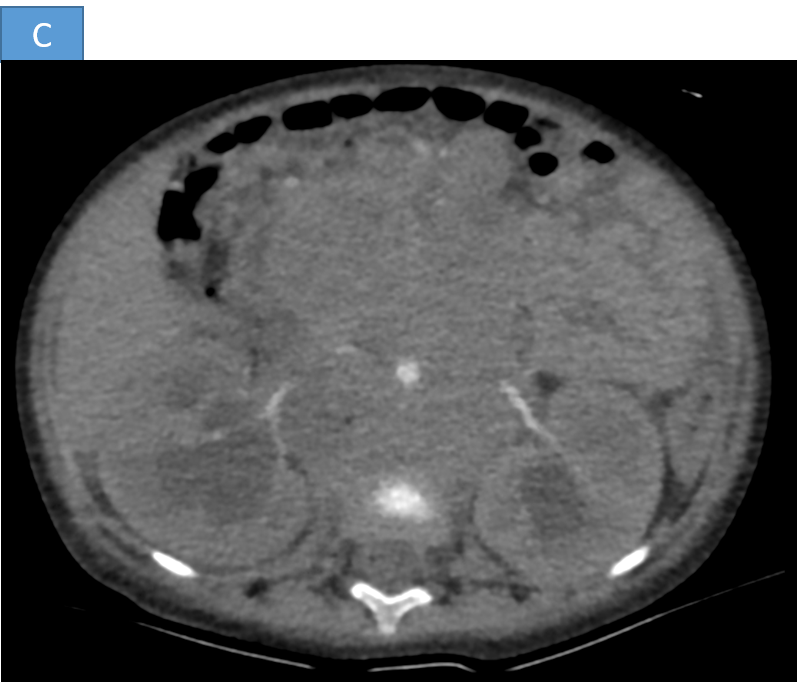
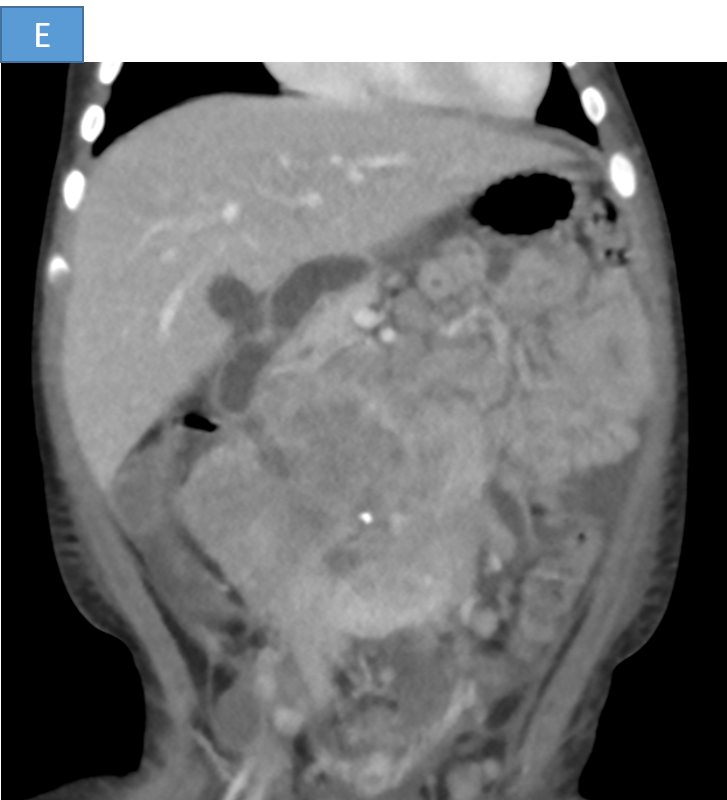
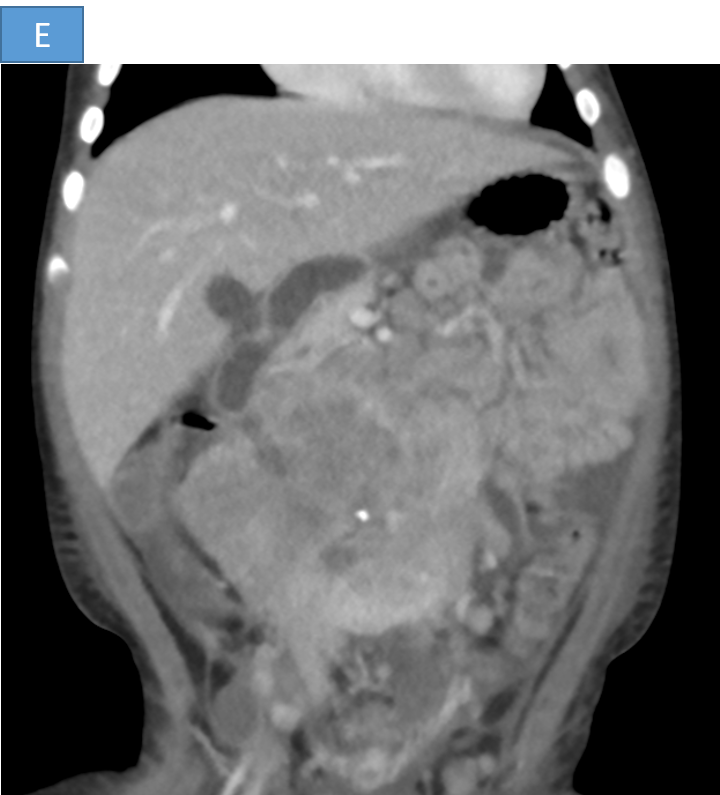
- B. Large heterogeneously enhancing lobulated retroperitoneal mass lesion causing encasement and anterior displacement of abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava and bilateral renal vessels.
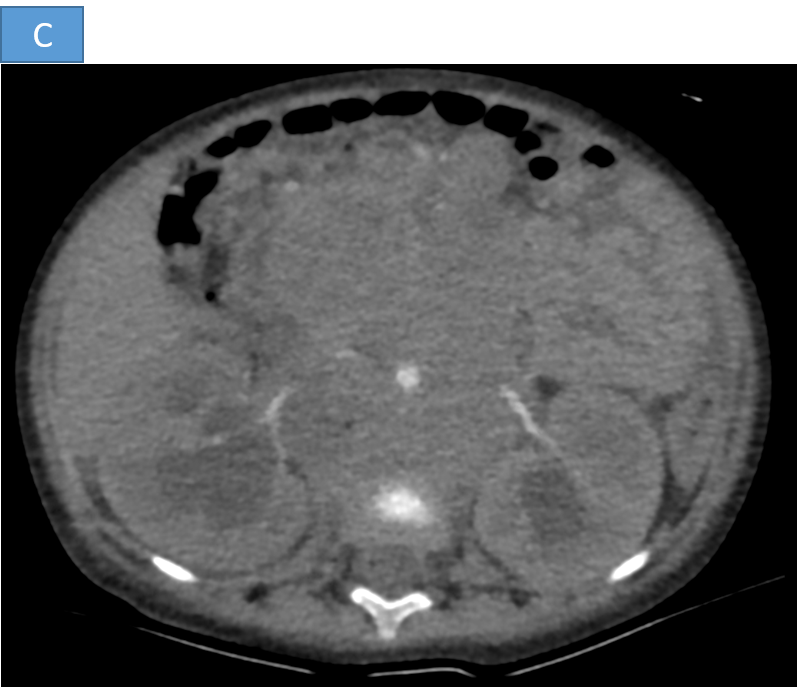
- C. The lesion is reaching up to the anterior abdominal wall and causing displacement of the adjacent bowel loops.
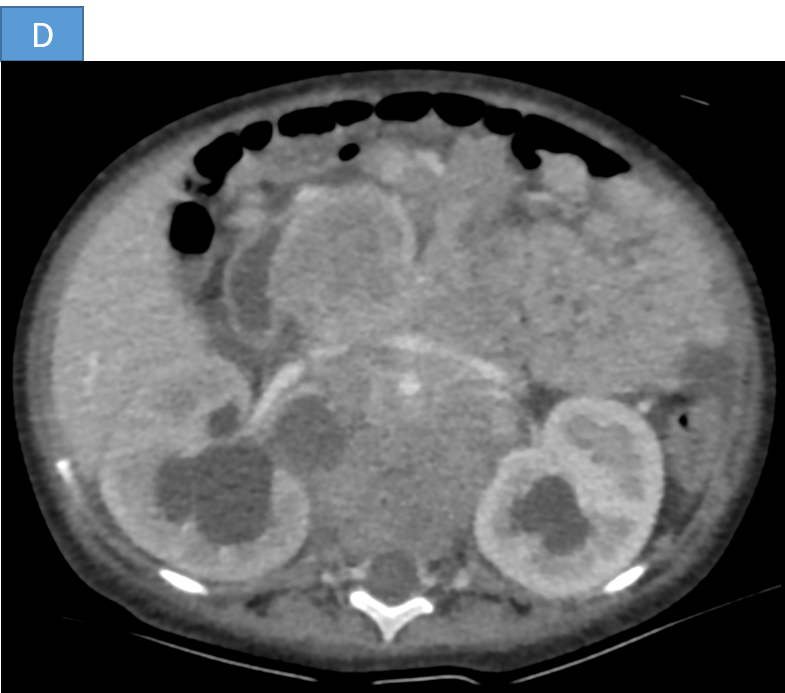
- D. The heterogeneous mass and retroperitoneal lymph nodes are causing compression of bilateral ureters causing upstream grade III hydroureteronephrosis.
- E. Tiny speck of calcification seen within the lesion
DIAGNOSIS :
- Poorly differentiated Neuroblastoma (Histopathology proven)
DISCUSSION :
Neuroblastoma :
- Neuroblastoma is the most common extracranial solid tumor in children and the most frequent cancer in infants before the age of 5.
- It arises from neural crest cells that form the sympathetic nervous system, most commonly originating in the adrenal medulla or paraspinal sympathetic ganglia.
- Derived from primitive sympathetic neuroblasts that fail to differentiate properly.
- Can present as a localized or metastatic disease.
- Mostly sporadic, but 1-2% are familial, associated with ALK and PHOX2B mutations.
- Amplification of MYCN oncogene is a poor prognostic factor.
- Infants (<18 months) with localized disease have excellent outcomes.
Clinical features :
Clinical manifestations vary based on the location of the tumor and metastatic spread:
- General Symptoms: Fatigue, weight loss, fever, irritability
- Abdominal Mass: Firm, irregular, non-tender mass (most common in the adrenal gland)
- Metastatic Symptoms:.
- Bone pain (bone metastases)
- Proptosis, periorbital ecchymosis ("raccoon eyes")
- Hepatomegaly (Pepper syndrome)
- Skin nodules (blueberry muffin rash)
- Paraneoplastic syndromes (e.g., opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome)
- Spinal Involvement: If extending into the spinal canal (dumb bell tumor), it can cause spinal cord compression and neurological deficits.
- Hypertension: Due to catecholamine secretion in some cases elevated urinary vanillymandelic acid/ homovanillic acid
Imaging :
- X-ray:
- Calcifications in the mass (speckled or coarse)
- Bone metastases (lytic lesions or periosteal reaction)
- Ultrasound:
- Heterogeneous mass with possible calcifications
- Useful for initial evaluation in abdominal cases
- CT Scan:
- Heterogeneous, enhancing mass with necrosis
- Calcifications (in 80-90% of cases)
- Local invasion and vascular encasement
- MRI:
- Better for soft tissue and spinal involvement
- T2-hyperintense, heterogeneous mass
- Extension through neural foramina (dumbbell tumor)
- MIBG Scan (Metaiodobenzylguanidine):
- Highly specific for neuroblastoma
- Detects primary and metastatic disease
- Bone Scan & PET-CT:
- Evaluate metastatic spread
- FDG-PET useful in MIBG-negative cases
References :
- Sharp SE, Gelfand MJ, Shulkin BL. Pediatric neuroblastoma: Diagnosis, staging, and therapy response assessment with 123I-MIBG scintigraphy. Radiographics. 2016 Oct;36(1):258-278. doi: 10.1148/rg.2016150086.
- Siegel MJ, Bhalla S. Neuroblastoma: Modern imaging tools for diagnosis and staging. Pediatr Radiol. 2020 Feb;50(2):168-181. doi: 10.1007/s00247-019-04521-2.
- McHugh K. Neuroblastoma: Imaging in diagnosis, staging, and follow-up. Am J Roentgenol. 1998 Sep;171(3):995-1001. doi: 10.2214/ajr.171.3.9725314.
Dr Skanda Prasad Ragi
MBBS, MD
Junior Consultant – MHRG
Dr S Shreya
MBBS, MD
Cross section imaging fellow - MHRG