35 years old male Presented with neck pain and headache with Odynophagia since 5 days
- 35 years old male Presented with neck pain and headache with Odynophagia since 5 days
- On examination torticollis.
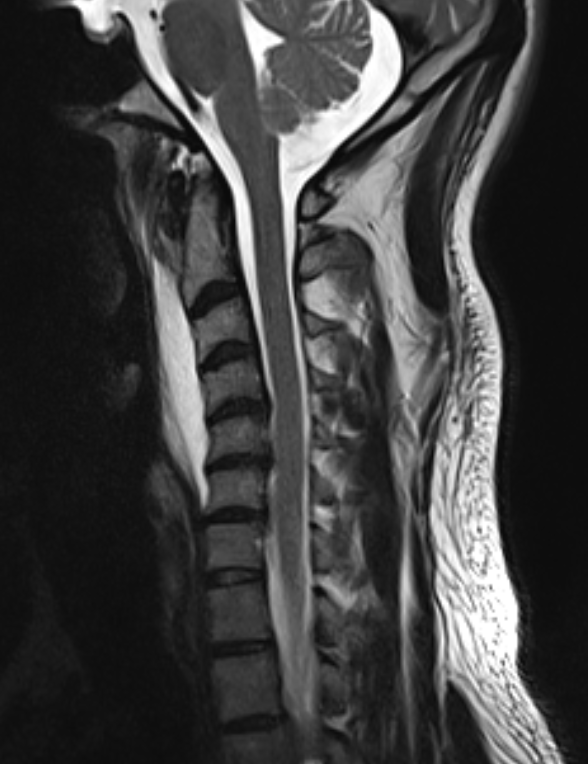
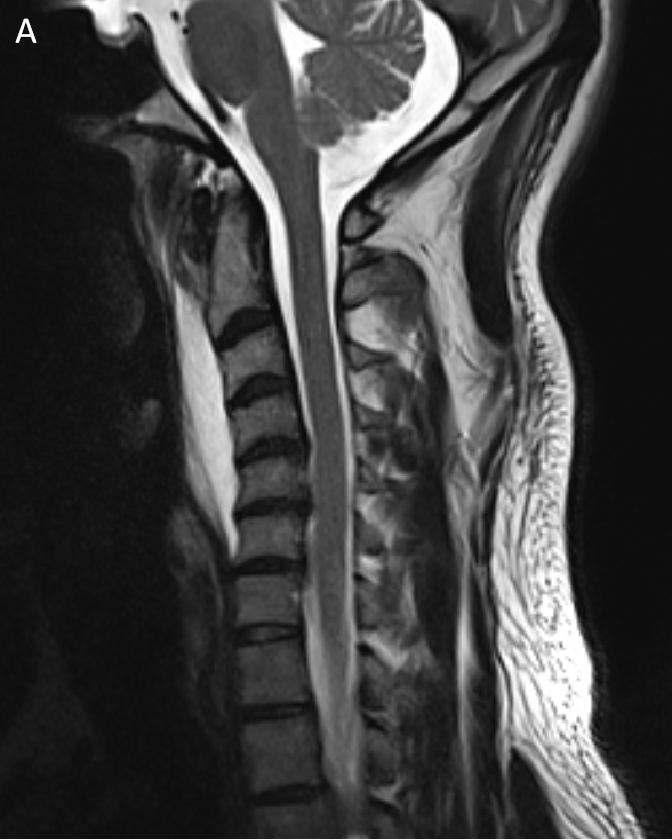
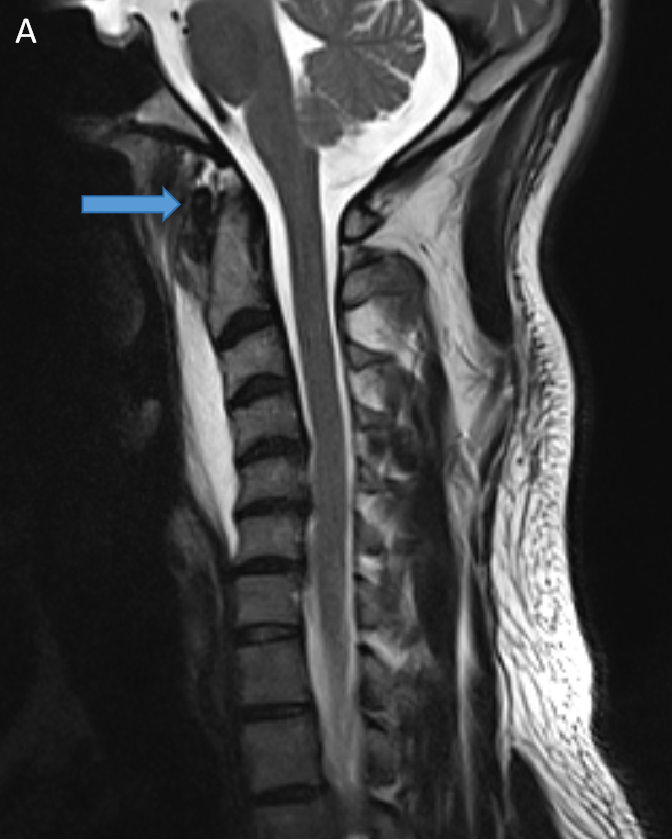
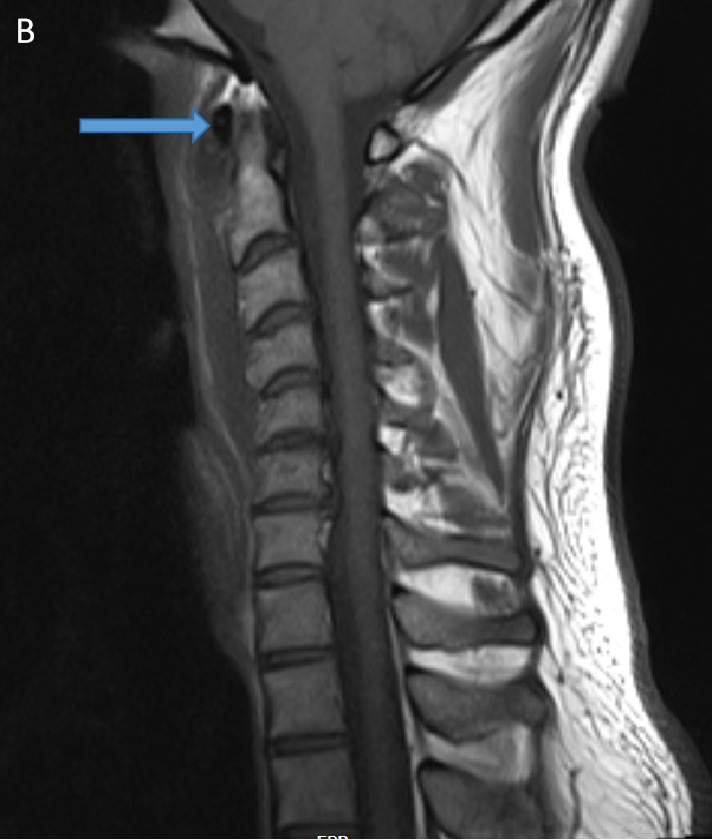
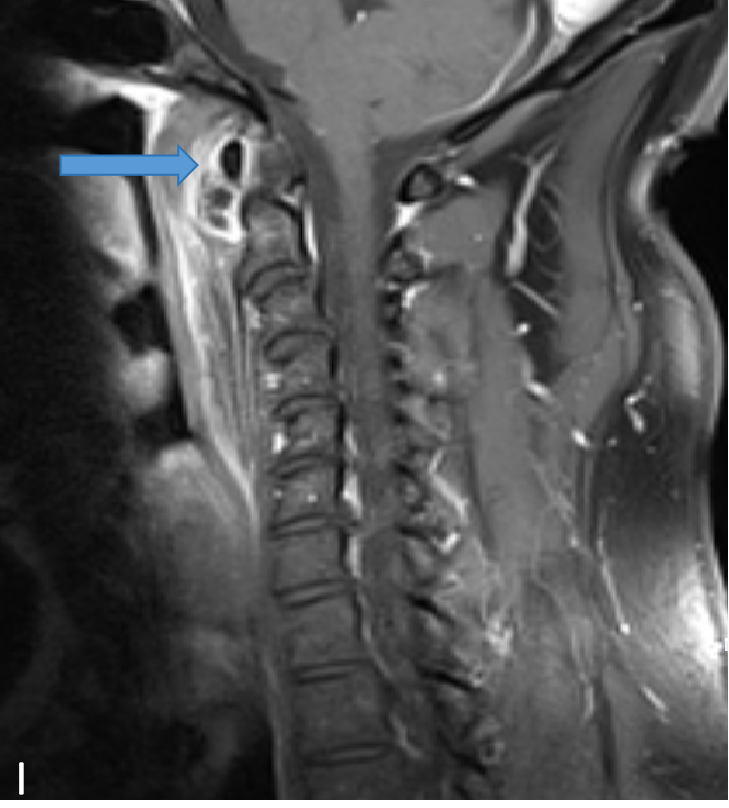
- T2W (A) and T1W (B) sagittal images show a preveretbral T2 hyperintense and T1 hypointense collection fromC2-C6 levels with arrows depicting calcifications.
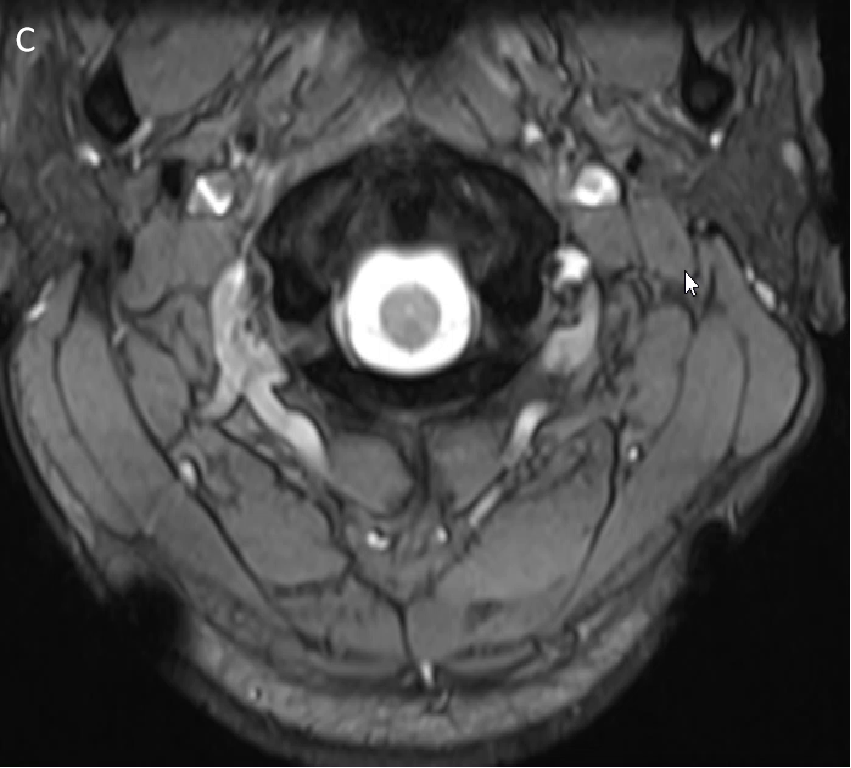
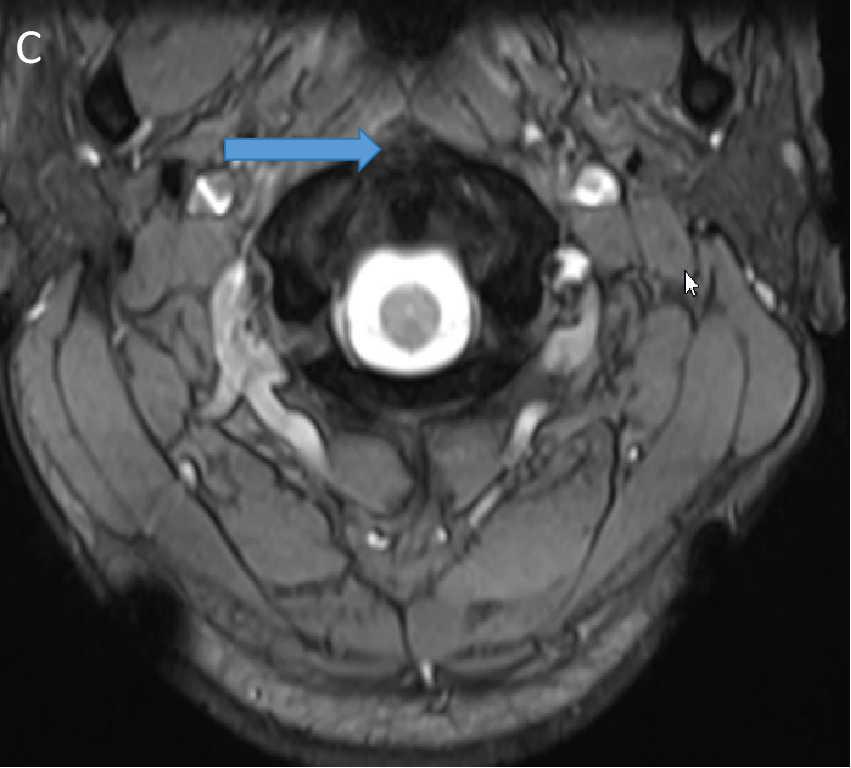
- T2W (C) axial images arrows depicting calcifications.
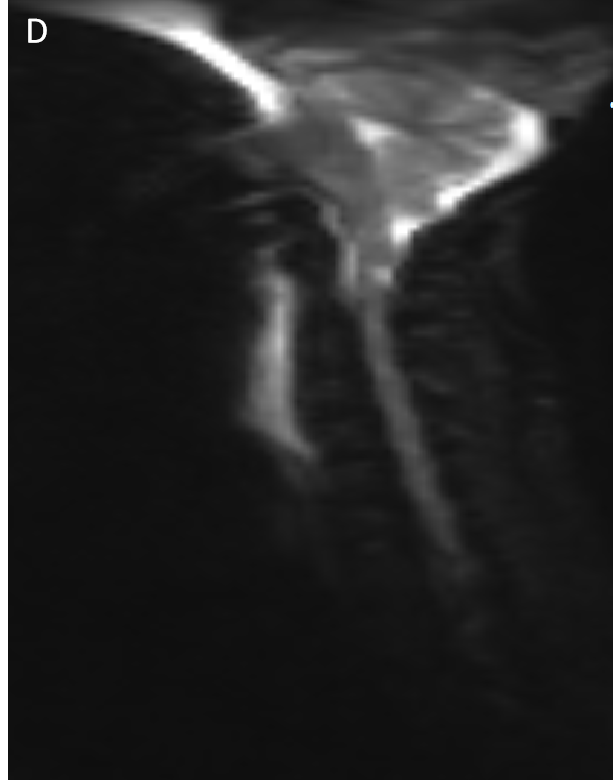
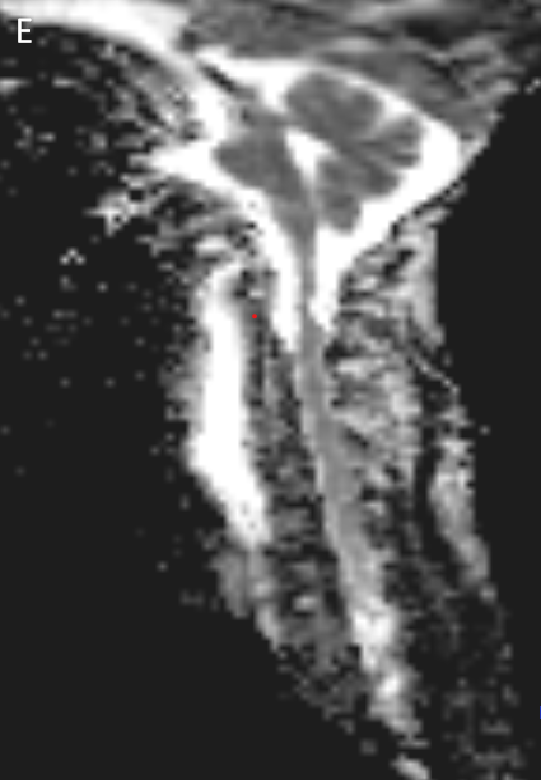
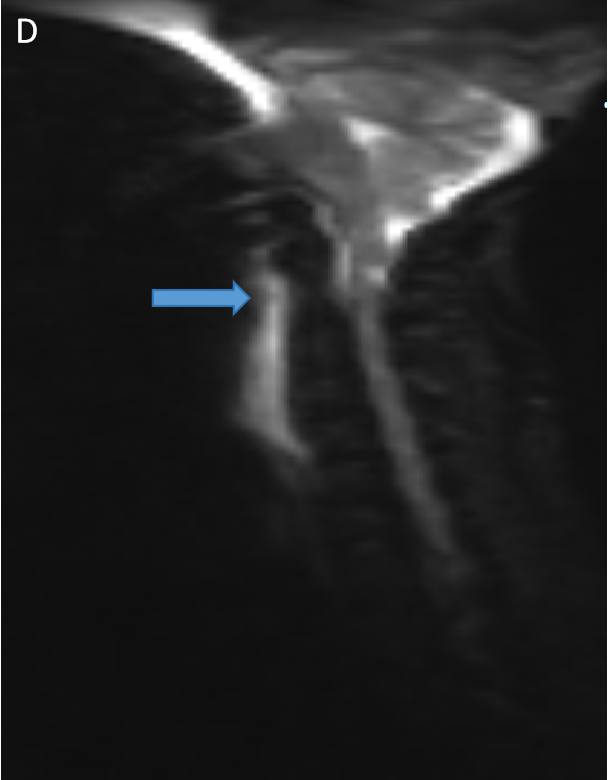
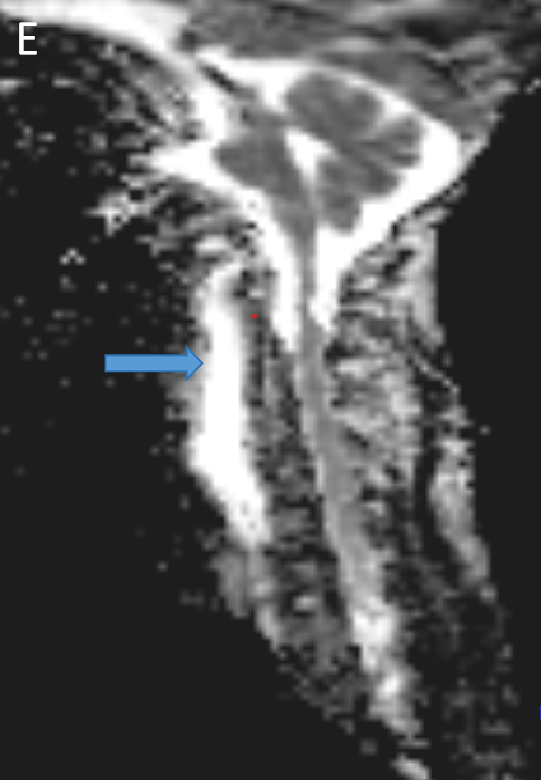
- DWI (D) and ADC (E) sagittal images with arrows depicting hyperintense signal on both images.
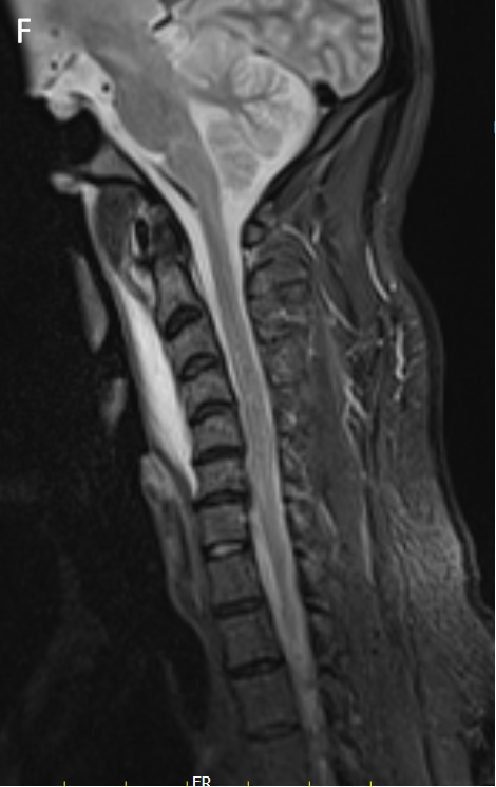
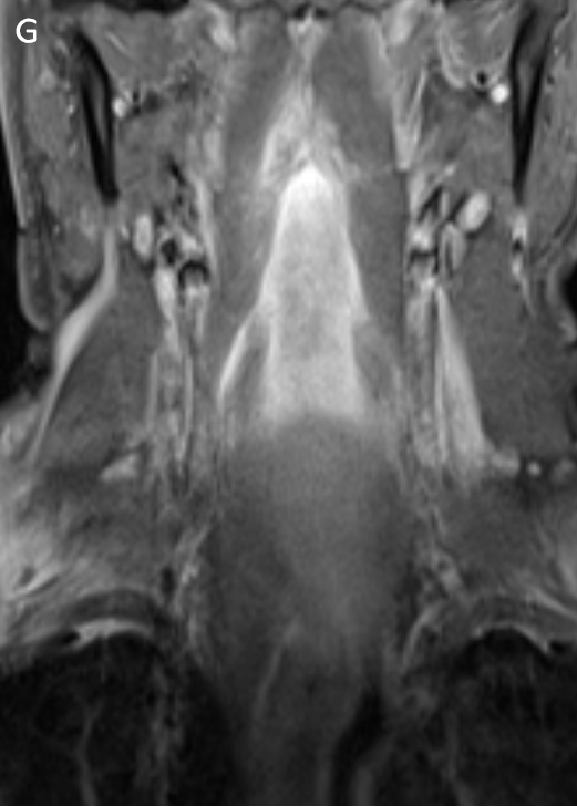
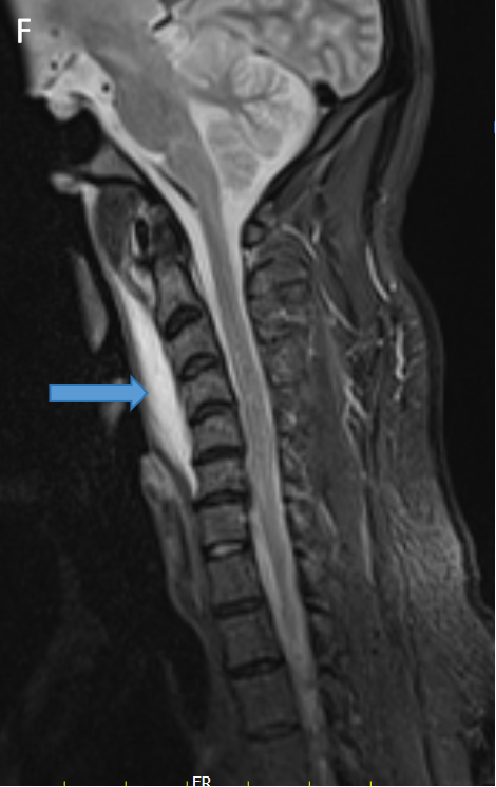
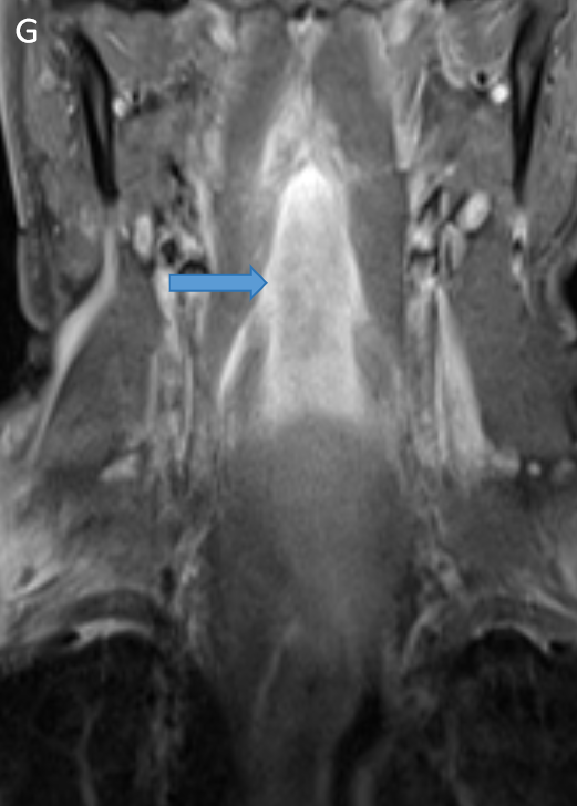
- STIR sagittal (F) and coronal (G) images show preveretbral hyperintense collection fromC2-C6 levels .
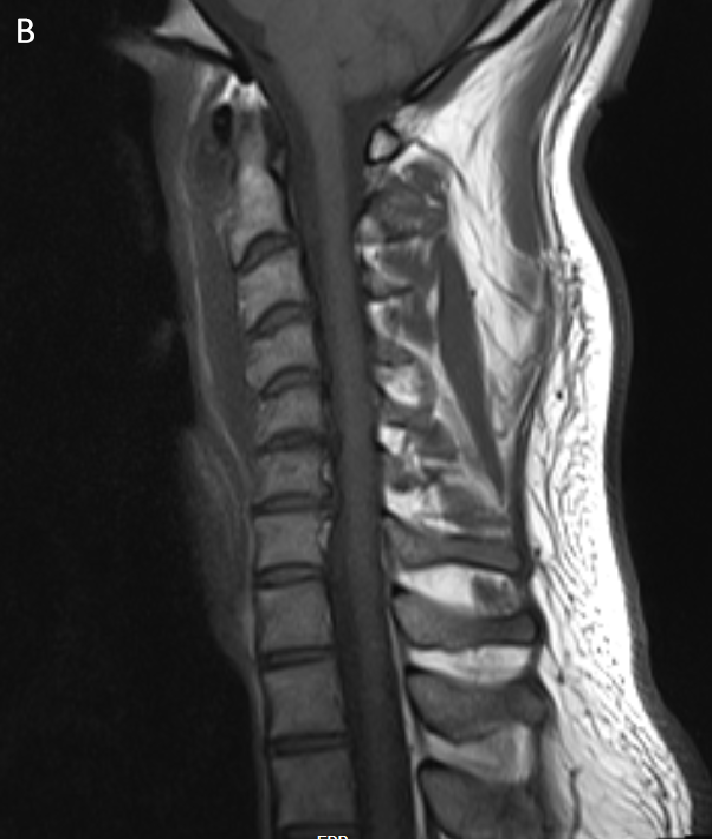
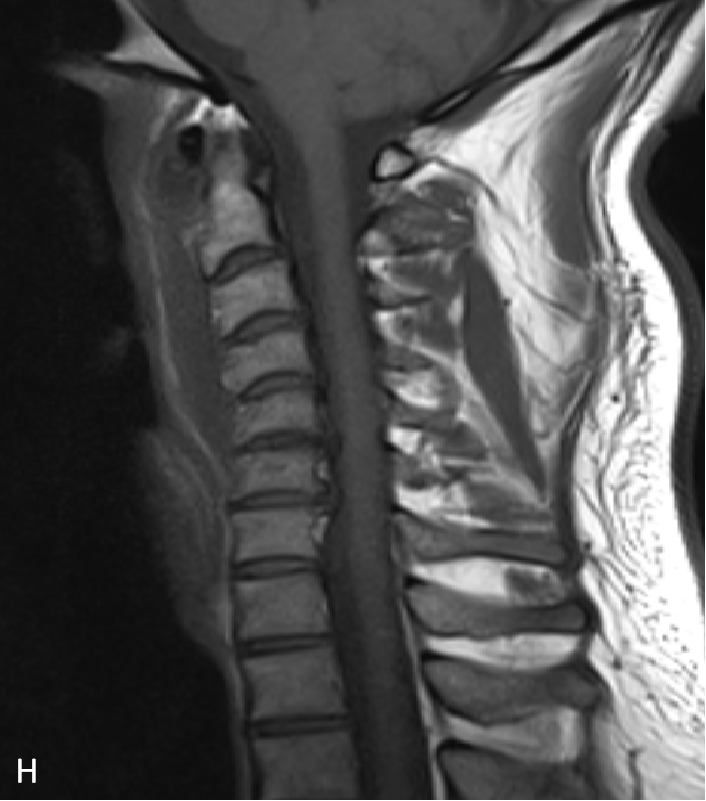
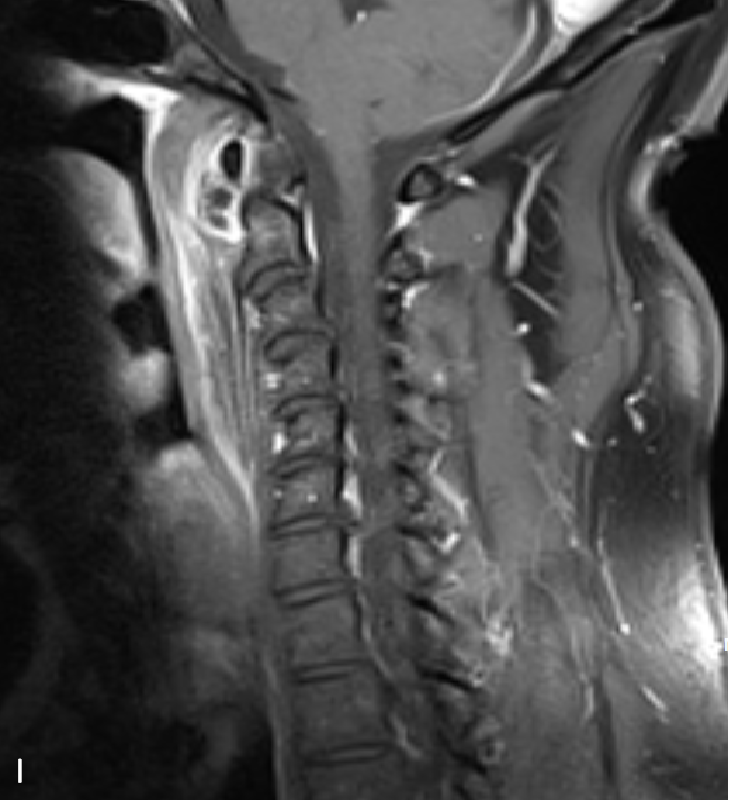
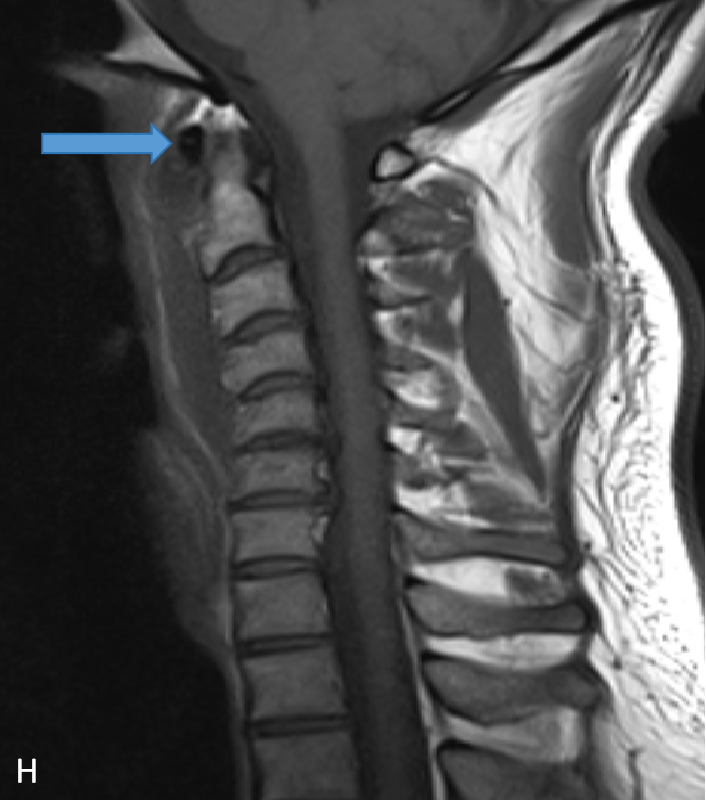
- T1W (H) and T1W Post contrast (I) sagittal images show preveretbral hypointense collection with with arrows depicting calcification and enhancing inflammatory changes on respective images.
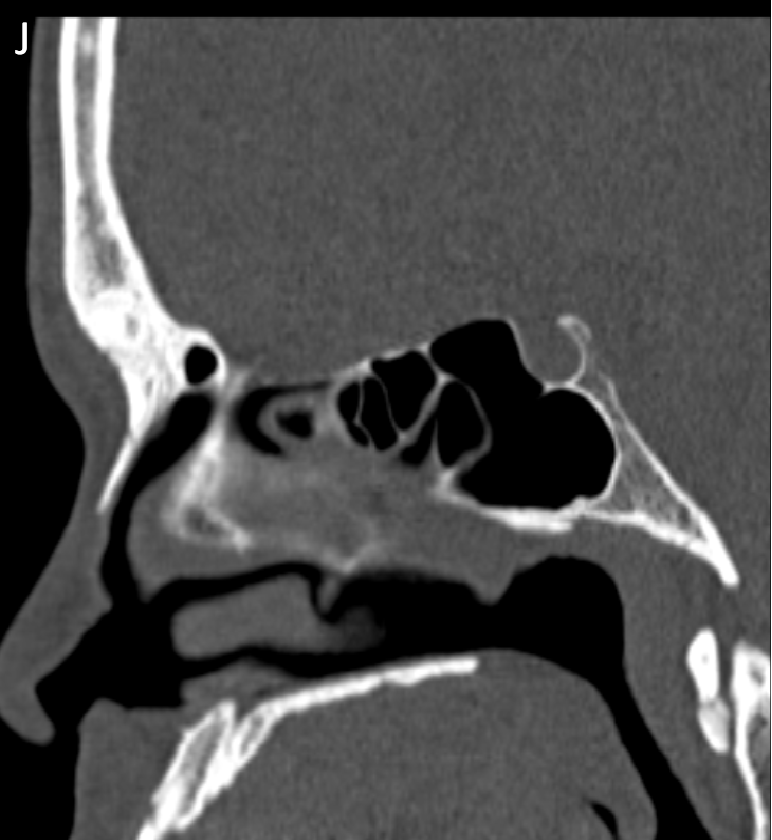
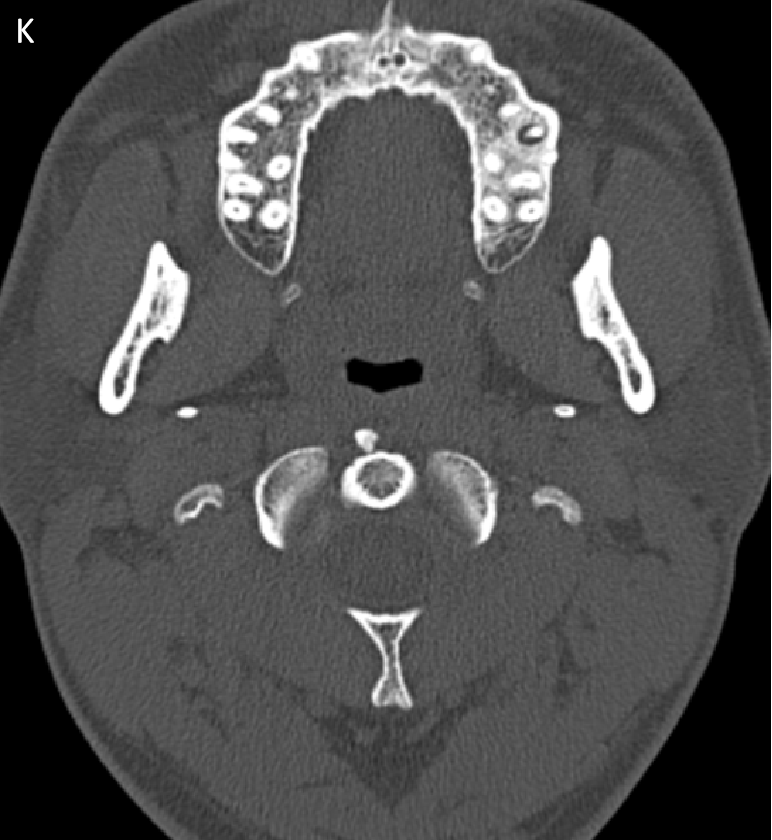
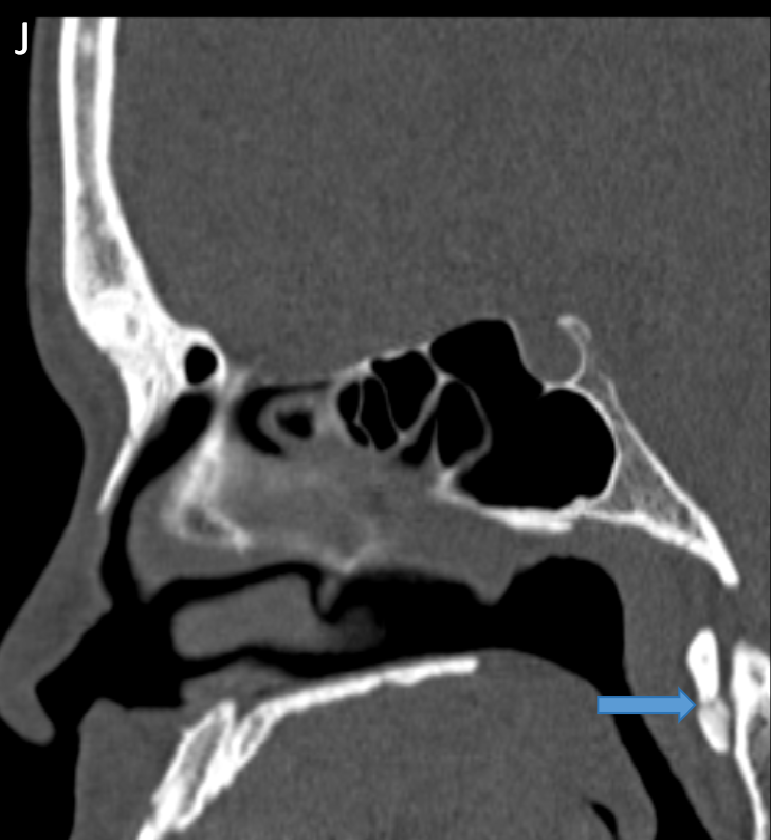
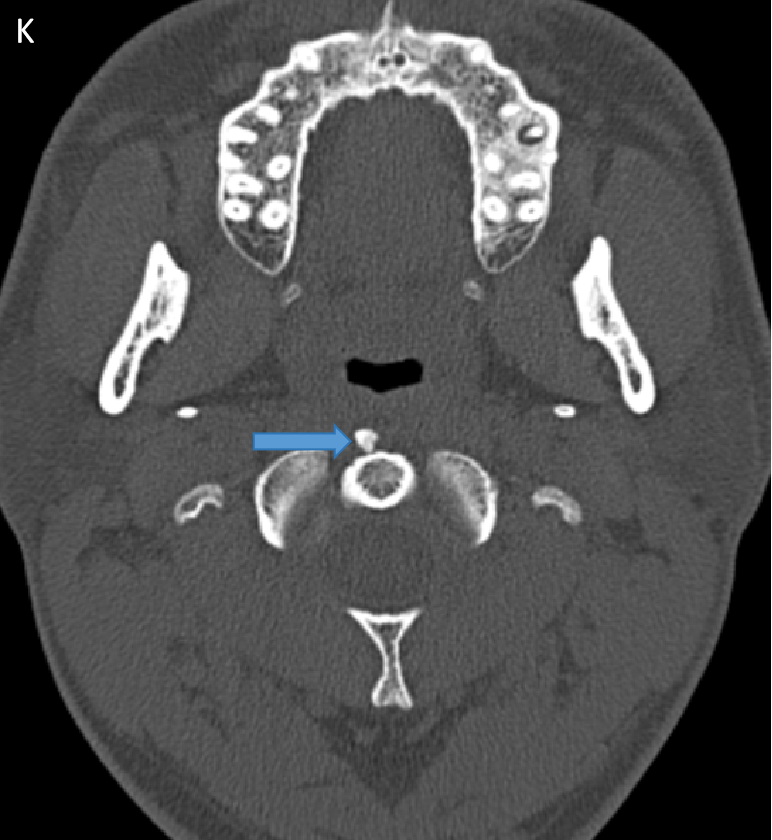
- CT Sagittal (J) and Axial (K) images. These were retrospectively seen in a previous PNS scan confirmed the calcifications with arrows depicting calcifications.
Diagnosis- Acute prevertebral / Longus Colli calcific tendinitis
- Effusion in the retropharyngeal space dissecting into the Longus Colli muscles bilaterally.
- No diffusion restriction.
- Two small relatively well defined hypointensities are noted in caudal to the anterior arch of atlas without post-contrast enhancement.
- On limited CT correlation images amorphous calcifications are demonstarted.
DISCUSSION
- Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscles is an inflammatory/ granulomatous response to the deposition of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals in the tendons of the longus colli muscle. It is sometimes more generically known as calcific prevertebral tendinitis or, less accurately, as retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis.
Differential Diagnosis:
RETROPHARYNGEAL ABCESS
- Retropharyngeal abscesses are rare but potentially life-threatening infections that primarily affect children of age 5 and younger and, occasionally, adults.
- Retropharyngeal abscesses are pus-filled collections within the retropharyngeal space, located between the buccopharyngeal fascia anteriorly and the alar fascia posteriorly.
- It occurs secondary to viral upper respiratory infection,retropharyngeal infection may also arise from oropharyngeal trauma or dental disease.
- C/o generalized irritability, fever,drooling, neck swelling, limited range of motion and stridor.
REFERENCES
- https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/818561.
- Radiol Oncol 2023; 57(4): 430-435.
Dr. Ritika Chamadia
Consultant Radiologist,
Manipal Hospital, Kharadi, Pune.
Dr. Madhuri
Radiology Resident,
Manipal Hospital,Kharadi, Pune.