31 year old lady, known case of Sjogren’s syndrome presents with chief complaints of dry cough and shortness of breath for 6 months.
31-year-old lady, a known case of Sjogren’s syndrome presents with chief complaints of dry cough and shortness of breath for 6 months.
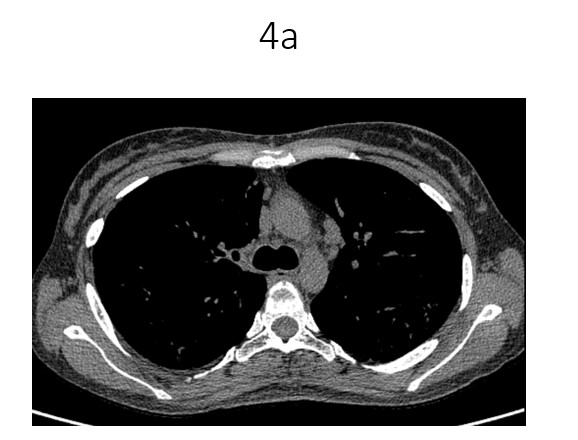
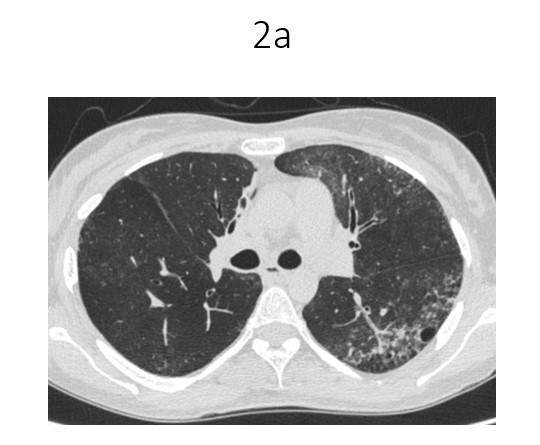
- Near symmetric confluent interlobular septal thickening and ground glass opacities in bilateral lower lobes, more in basal segments.
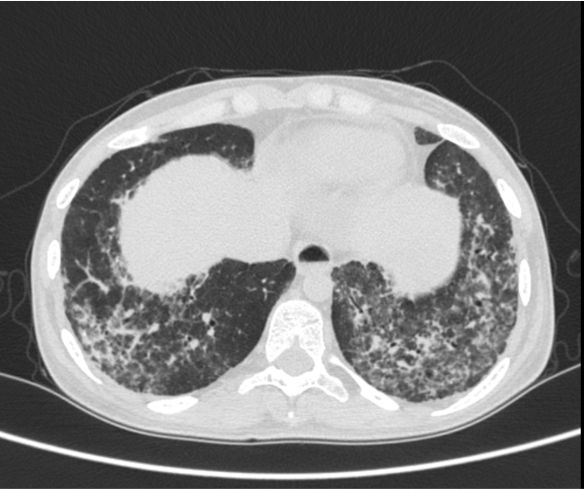
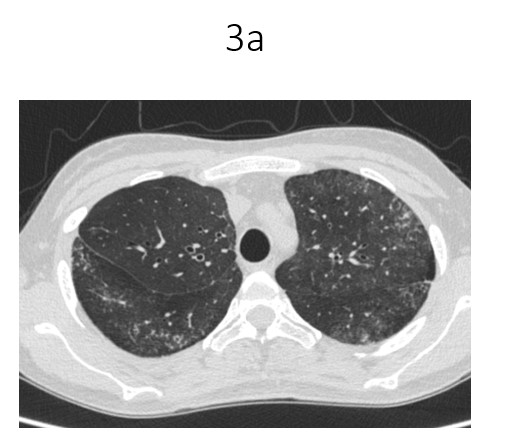
- Multiple small cysts interspersed with reticulations in superior segment of left lower lobe. Few small cysts also noted in bilateral posterior basal segments.
- Multiple fine reticulations with ground glass opacities and fine random nodules seen in left upper lobe and superior segment of right lower lobe.
- Mosaic attenuation in bilateral lungs.
- Few prominent aortopulmonary window nodes,largest measuring 11mm. Subcentimetre left para-aortic ,paratracheal and subcarinal nodes also noted
DIAGNOSIS:
In a known case of Sjogren’s syndrome, the HRCT chest findings are most likely in keeping with interstitial lung disease – Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis
DISCUSSION:
- Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disease that is characterized by lymphocyte infiltration of exocrine glands, resulting in dryness of the mouth and eyes. In addition, other organs can also be involved including the joints, lungs, gastrointestinal tract and blood vessels.
- Interstitial pneumonia is frequently observed in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome (1).
- Carrinon and Liebow first described lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (2).
- This type of pneumonia is characterized by diffuse infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells. It has been associated with idiopathic or acquired human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Epstein Barr virus infection and others.
Epidemiology
- Most patients are adults with a mean age of 52-56 years.
- There is a significant female predilection
- Clinical presentation:
- Gradual onset of dyspnea and cough
- Less frequently fever, night sweats, weight loss and arthralgia
Radiographic features
- Plain radiograph:
- Lower zone predominant bilateral reticular opacities, chronic bilateral airspace opacification
CT
- Mid to lower lobe pneumonia
- Thickening of bronchovascular bundles
- Interstitial thickening along lymph channels.
- Ground glass changes.
- Scattered thin walled cysts, usually deep within lung parenchyma, typically abut vessels , size range 1-30 mm.
- Mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
Differential diagnosis
- Pneumocystis pneumonia
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis
References:
- Ji –Young Kim , Sung–Hoon Park et al, Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia in Primary Sjogren’s syndrome : A case report , Korean J.Intern Med .2011 Mar ; 26(1): 108-111
- Liebow A , Carrington C ,Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia . Am J Pathol.1966;48:36
Dr. Deepali Saxena, DNB, Fellowship Cardiothoracic Imaging (USA)
Lead Cardiothoracic Imaging
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group.
Dr. Shashwat Priyadarshi,
DNB, Fellow
Manipal Hospitals Radiology Group.